This repository hosts a project developed as part of my third year Bachelor's degree studies. The focus of the project is on the analysis and classification of EEG data. The main goals were to classify people (through something that can be approximated as being one's EEG signature), and tasks (which engage different parts of the brain and therefore should be classifiable).
We were able to classify people without too much difficulty, but we weren't able to classify different tasks as efficiently.
All of the code as well as the documentation is written in a Jupyter Notebook.
The project is divided into the following sections:
- This segment provides a detailed overview of the EEG dataset, including the extraction process and a thorough analysis of the dataset's characteristics.
- Comprising two major subsections: Classify people and Classify tasks, this portion delves into a variety of methods for EEG data classification.
- Classify People
- Data Visualization: Utilization of various data visualization techniques to gain deeper insights from the EEG data.
- First Step Towards Classification: An introductory approach to EEG data classification.
- Improving the QDA Classifier: Investigating different strategies to enhance the performance of the Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA) classifier.
- Coding the QDA Classifier: Step-by-step implementation of the QDA classifier.
- Multiple Electrodes: Examination of the significant role multiple electrodes play in EEG data analysis.
- Classify Tasks
- Using Raw Data for Classification: Comprehensive analysis and classification of raw EEG data.
- Feature Extraction: Various techniques for feature extraction from EEG data, including:
- Fourier Transform
- Power Spectral Density (PSD)
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Image Processing
- Implementation of a deep convolutional neural network for EEG data analysis
- Methods to reduce overfitting in the neural network model
- Additional research and experiments conducted using EEG data, including
- Compressed Sensing of EEG Data: The application of compressed sensing techniques to EEG data.
- Video: Visualization of "real time" functional connectivity (averaged across subjects) of two different tasks with the intent of being able to visually differentiate them.
You will find here bellow some snippets of the results:
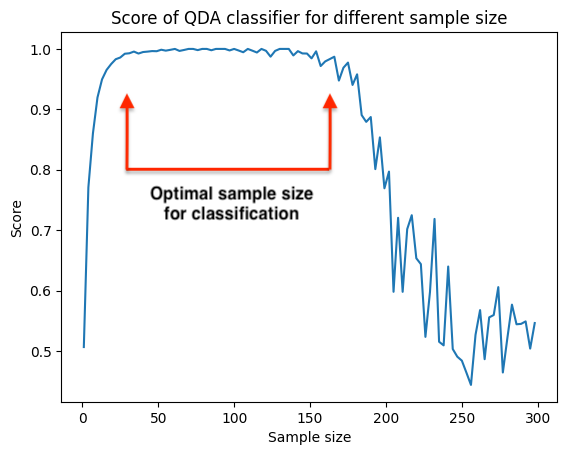
Finding the optimal sample size from EEG data to classify people:
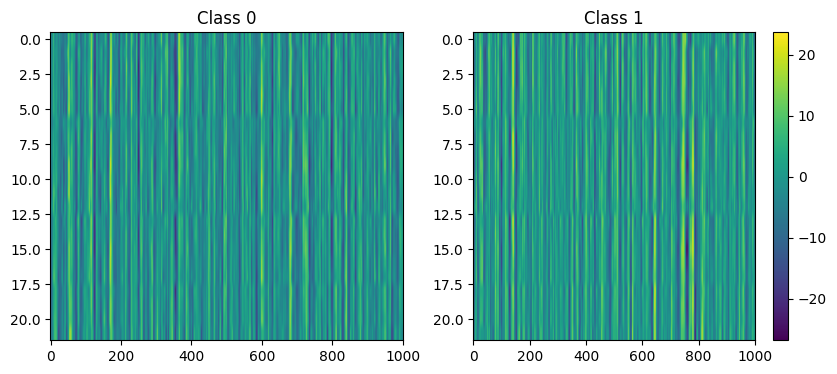
Creating an image out of EEG frequency patterns in order to apply image classification:
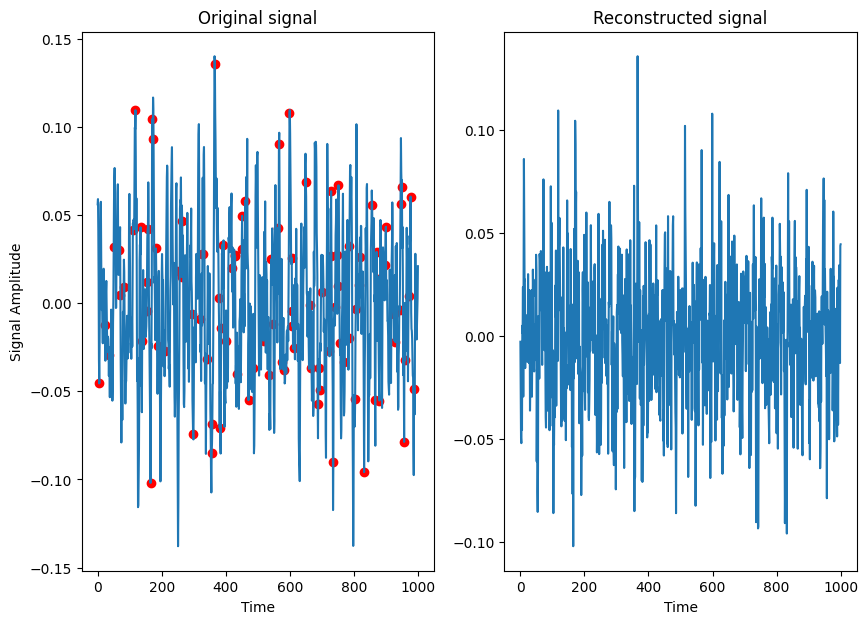
Compressed sensing reconstruction:
- My profound gratitude goes to James Camilleri, Badreddine Channoufi, and Adam Sekkat who have been an integral part of this project, contributing their valuable insights and expertise.
- I am thankful to Professor François Landes for his supervision throughout the completion of this project.
- Special thanks to Sylvain Chevallier for creating the Moabb module in Python, from which we extracted the EEG dataset for this project.