Most self-supervised 6D object pose estimation methods can only work with additional depth information or rely on the accurate annotation of 2D segmentation masks, limiting their application range. In this paper, we propose a 6D ob- ject pose estimation method that can be trained with pure RGB images without any auxiliary information.
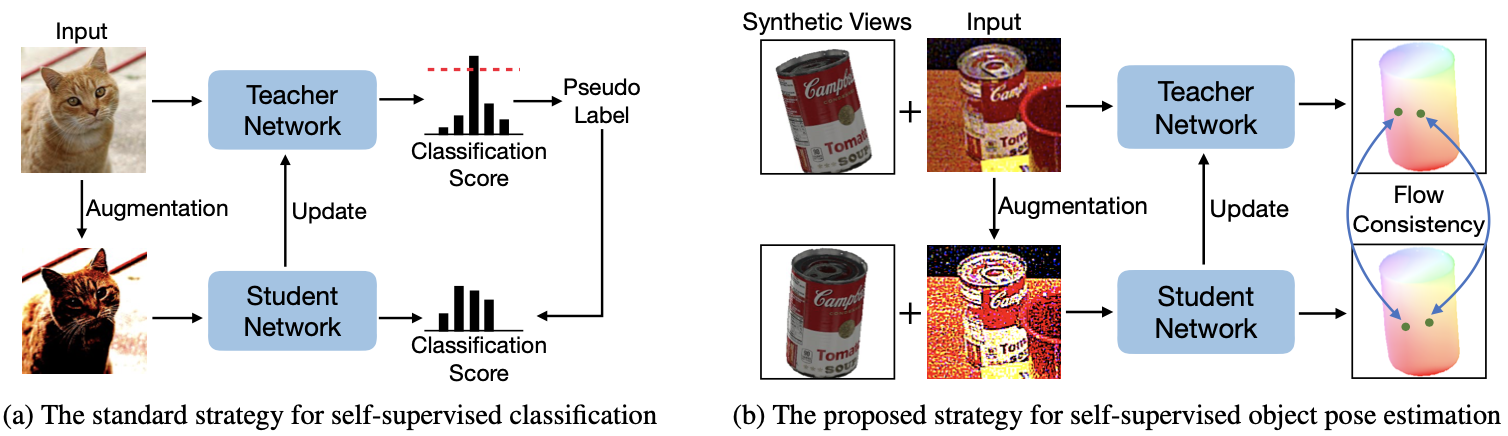
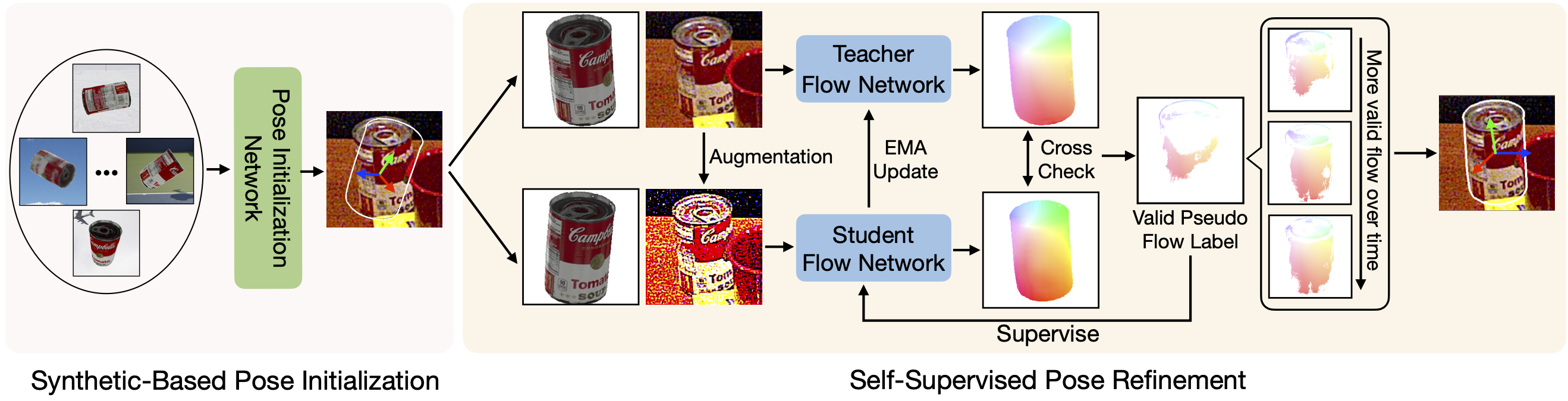
Figure 1. Self-supervised strategies in different fields. (a) Teacher-student learning scheme is a classical framework for self-supervised classification. The key is how to determine the quality of pseudo labels from the noisy prediction of the teacher network. For image classification, one can obtain the prediction quality by the output distribution after the softmax operation easily, which is usually implemented by checking if the probability of any class is above a threshold. (b) However, there is no such easy way to determine the quality of an object pose prediction without the ground truth. We propose to formulate pseudo object pose labels as pixel-level optical flow supervision signals, and then use the flow consistency between multiple views based on their underlying geometry constraint. Figure 2. Method overview. We first obtain the initial pose based on a pose estimation network trained only on synthetic images, and then train our refinement framework on real images without any annotations. Our proposed framework is based on a teacher-student learning scheme. Given a rough pose initialization, we render multiple synthetic images around this initial pose, and create multiple image pairs between the synthetic and real images. We dynamically produce pixel-level flow supervision signals for the student network during the training, by leveraging the geometry-guided flow consistency between those image pairs from different views. After getting 3D-to-2D correspondences based on the predicted flow, we use a PnP solver to get the final pose.- Install necessary packages by
pip install -r requirements.txt - Install Pytorch3D by building this code repo from source.
- Install bop_toolkit(Optional).
- Download BOP YCB-V Dataset, and place them under
datadirectory. - Download the image lists and other data related to YCB-V, which will be used in this code, from here.
- Download the detected bounding boxes by RADet, from here.
- Train the pose initialization network, which is WDR-Pose equipped with RADet pre-processing, on synthetic images.
python train.py --config configs/estimator/extended_wdr.py --mode estimator- Train the optical flow network on synthetic images.
python train.py --config configs/flow_refine/raft_flow_mask.py --mode refiner- Infer the initial poses of un-annotated real training images.
python test.py --config configs/estimator/extended_wdr.py --mode estimator --checkpoint work_dirs/wdr_ycbv_pbr/latest.pth --format-only --save-dir data/initial_poses/extended_wdr/ycbv_pbr_train- Train the optical flow network on un-annotated real images, which will load the pretrained weights and use the above initial poses for training.
python train.py --config configs/flow_refine/pfc_raft_flow_mask.py --mode refinerNotes: To reproduce the results in our paper, the first three steps can be skipped by accessing the pretrained model weights from here and initial pose of unlabeled real images from here.
- Infer the initial poses on testing images, and save them.
python test.py --config configs/estimator/extended_wdr.py --checkpoint work_dirs/wdr_ycbv_pbr/latest.pth --format-only --save-dir data/initial_poses/extended_wdr/ycbv_pbr_test- Run the trained optical flow network to refine the above initial poses.
python test.py --config configs/flow_refine/pfc_raft_flow_mask.py --checkpoint work_dirs/pfc_real_selfsup/latest.pth --evalNotes: The trained model on YCB-V can be found here and initial pose for testing images can be found here.
- Save the results.
python test.py --config configs/flow_refine/pfc_raft_flow_mask.py --checkpoint work_dirs/pfc_real_selfsup/latest.pth --format-only --save-dir work_dirs/pfc_real_seflsup/results- Convert to BOP format.
python tools/convert_to_bop19.py work_dirs/pfc_real_seflsup/results data/ycbv/test_targets_bop19.json work_dirs/pfc_real_seflsup/results_bop19.json- Follow the bop_toolkit instruction for evaluation.
If you find this project is helpful, please cite:
@inproceedings{yang2023pseudoflow,
title={Pseudo Flow Consistency for Self-Supervised 6D Object Pose Estimation},
author={Yang Hai and Rui Song and Jiaojiao Li and David Ferstl and Yinlin Hu},
booktitle={ICCV},
year={2023}
}
@inproceedings{yang2023radet,
title={Rigidity-Aware Detection for 6D Object Pose Estimation},
author={Yang Hai and Rui Song and Jiaojiao Li and Mathieu Salzmann and Yinlin Hu},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2023}
}
@inproceedings{yang2023scflow,
title={Shape-Constraint Recurrent Flow for 6D Object Pose Estimation},
author={Yang Hai and Rui Song and Jiaojiao Li and Yinlin Hu},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2023}
}
@inproceedings{yinlin2022wdr,
title={Wide-Depth-Range 6D Object Pose Estimation in Space},
author={Yinlin Hu, Se ́bastien Speierer, Wenzel Jakob, Pascal Fua, Mathieu Salzmann},
booktitle={CVPR},
year={2022}
}