A bridge between AMPL and Python allowing users to define external functions in Python and use those functions inside AMPL models. This is based on existing work by PyOptimizer. Based on their work, the following modifications have been made;
- Make it work on windows.
- Because there is some problem with Clang on my computer, so I use gcc instead
- To achieve this, I need to modify the
Makefile
- To achieve this, I need to modify the
Because the official AMPL APIs to Python just allow us to transfer data with AMPL or to change the algebraic statements of the objectives and constraints. However, to the best of my knowledge, we are not allowed to use external Python functions inside AMPL models. Thus, this work is devoted to bridge this gap.
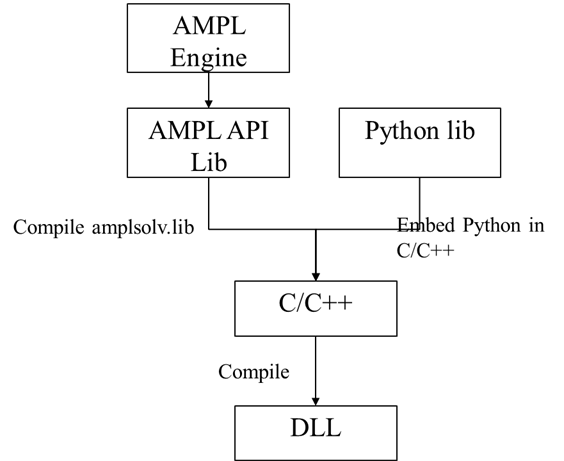
The whole flowchart are shown below.
1) Preparation
You need to have GCC or other compilers(e.g. Clang, MSVC) in your computer. For convenience, you could install Mingw, which is a collection of several compilers. You need to add it to you path to allow you run it from command line. One important note is if you are using 32-bit AMPL, you need to use 32-bit GCC or compile 32-bit DLL file. Also, you need to use 64 bit for 64-bit AMPL. Otherwise, you will get some errors because of compatibility issues
2) amplsolve.lib
First, we need to compile an AMPL Solver library-amplsolv.lib. This library is necessary for C/C++ to communicate with AMPl.
Step1. Change your directory to folder-ASL
Step2. Run command
make // You might need to run Mingw32-make or you can make an alias for this.
Step3. The previous steps should create amplsolv.lib
3)amplfunc.dll
Then, compile amplfunc.dll without embedding Python. The C file for this is funcadd.c.
Basically, the compilation of DLL files involves three steps: Pre-processing,compilation, and linking. Therefore, there are two issues that should gain significant attentions. That is, i) set correct include directories, where we could find all necessary .h files, and ii) correct lib directories, where we could find all required lib and dll files.
Usually the compilation tasks are defined in a Makefile file. There are many good Makefile tutorials available(e.g. 1), and necessary knowledge about Makefile could be easily gained by reading these tutorials. Therefore, both the include directories and lib directories are provided in Makefile, as below. These are the directories in my computer and should be modified accordingly.
After this, run maketo compile amplfunc.dll. If nothing goes wrong, we will get this dll file. Now we can load it in AMPL to see if it works. The test script is shown below.
load amplfunc.dll;
function ginv;
param p1;
let p1 := ginv(10);
display p1;
Again, if nothing goes wrong, AMPL will display >p1=0.1
3) amplfunc.dll with Python embedded
Now, we could embed Python to make Python functions accessible to AMPL.
Reference manual are available on Python's official website. There are mainly two ways to embed python in C: very high level embedding, and pure embedding. Through the official tutorials we could implement this by ourselves.
Now, we could add one more function in function.c which will call Python function in turn. Then, we have get our function.c version 2, which is also the function.c given in this repository.
Then, we could move forward to compile amplfunc.dll. In addition, we need to add Python to our include directories and lib directories.
After this, run make, and we will get a new amplfunc.dll. The following AMPL test script is used test if it works.
load amplfunc.dll;
function Py_log;
param p1;
let p1:=Py_log(1);
display p1;
If nothing goes wrong, we will get
p1=0;
1. Different from compiling an executable program, compiling an DLL file requires us to provide an argument--:-shared to gcc command.Otherwise, we will get the following error
C Programming undefined reference to `WinMain@16'
2. Because amplsolv.lib has redefined some C functions, like "printf". Therefore, we need to put Python.h before funcadd.h as below. Otherwise, we will get some errors.
#include "Python.h"
#include "asl/funcadd.h"3. No module named site on Windows Actually, I has not figured out the cause of this problem. However, I found a feasible solution that is putting the statement--Py_NoSiteFlag before initializing Python interpreter as below.
Py_NoSiteFlag = 1;
//Initialize python interpreter
Py_Initialize();4. There might be some deprecated Python functions or statements like PyUnicode_fromDouble, and this could be simply fixed by using PyString_fromDouble.