The objective of this project is to clone human driving behavior using a Deep Neural Network. In order to achieve this, we are going to use a simple Car Simulator. When we navigates the car via keyboard, the simulator records training images from left, center and right cameras. Then those recorded images and the corresponding sheering angles are used to train the 5 layers neural network. Trained model was tested on two tracks, namely track1 and track2. The two following animations show the performance of the final model in both training and validation tracks.
| Track1 | Track2 |
|---|---|
 |
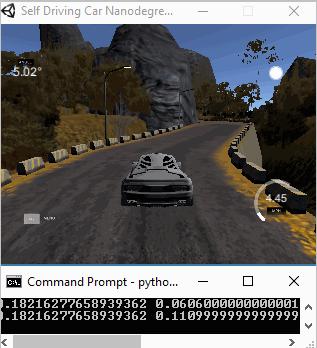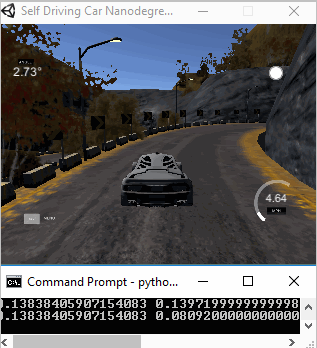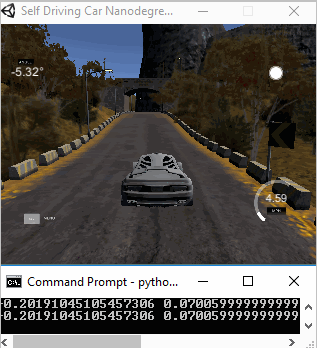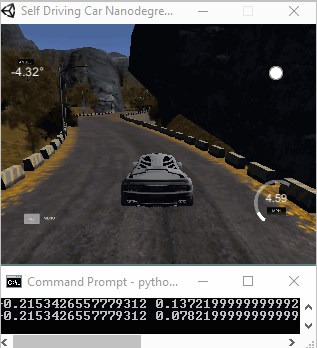 |
model.py - The script used to create and train the model. drive.py - The script to drive the car. model.h5 - The trained model.
I used the dataset provided by Udacity. The dataset contains 8037 images for each camera (left, centre, right). The total number is 8037*3. I did not record images myself. The image format JPG and the image dimension is 160x320x3. The following images are from Udacity Dataset.
| center | Left | right | steering | throttle | brake | speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
0.0617599 | 0.9855326 | 0 | 2.124567 |
 |
 |
 |
-0.0787459 | 0.9855326 | 0 | 30.18633 |
 |
 |
 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 22.14829 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
As the size of training set may not broad enough, data augmentation is used to increase sample size by adjusting brightness, changing direction and using other cameras.
Irrelevant information (i.e sky, tree and so on) is removed by croping the image. The noise is reduced by normalizing images.
The network model is similar to the model from NVIDIA's End to End Learning for Self-Driving Cars paper. The main difference between my model and the NVIDIA mode is that dropout layers are used after each Convolutional Layer to avoid overfitting issue. The network architecture is as below:
____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to ==================================================================================================== convolution2d_1 (Convolution2D) (None, 32, 32, 24) 1824 convolution2d_input_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_1 (ELU) (None, 32, 32, 24) 0 convolution2d_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ convolution2d_2 (Convolution2D) (None, 16, 16, 36) 21636 elu_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_2 (ELU) (None, 16, 16, 36) 0 convolution2d_2[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 36) 0 elu_2[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ convolution2d_3 (Convolution2D) (None, 8, 8, 48) 43248 dropout_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_3 (ELU) (None, 8, 8, 48) 0 convolution2d_3[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 8, 8, 48) 0 elu_3[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ convolution2d_4 (Convolution2D) (None, 8, 8, 64) 27712 dropout_2[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_4 (ELU) (None, 8, 8, 64) 0 convolution2d_4[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ convolution2d_5 (Convolution2D) (None, 8, 8, 64) 36928 elu_4[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_5 (ELU) (None, 8, 8, 64) 0 convolution2d_5[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 4096) 0 elu_5[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_1 (Dense) (None, 1164) 4768908 flatten_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_6 (ELU) (None, 1164) 0 dense_1[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dropout_3 (Dropout) (None, 1164) 0 elu_6[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_2 (Dense) (None, 100) 116500 dropout_3[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_7 (ELU) (None, 100) 0 dense_2[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_3 (Dense) (None, 50) 5050 elu_7[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_8 (ELU) (None, 50) 0 dense_3[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_4 (Dense) (None, 10) 510 elu_8[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ elu_9 (ELU) (None, 10) 0 dense_4[0][0] ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_5 (Dense) (None, 1) 11 elu_9[0][0] ==================================================================================================== Total params: 5,022,327 Trainable params: 5,022,327 Non-trainable params: 0 ____________________________________________________________________________________________________
The Udacity dataset are divided into 80% for training and 20% for validation. Each training epoch consumes 20000 images, which are generated on the fly using the data augmentation described above. In addition to that, 3000 images also generated on the fly for validation. We used Adam optimizer with default 0.001 learning rate. 3 training epochs are able to produce the weights that work well on both training and validation tracks.
If the computer is not able to perform the forward pass quickly enough, then there will be a time lag between receiving input and generating a steering angle output. In this case, the car may drive off the track directly. PD control is added to make the car move at a constant speed.