sGMYC runs a single-threshold GMYC analysis (Pons et al. 2006) using the splits package (Fujisawa & Barraclough 2013) with subsamples of sequences obtained from within the species delimited using all sequences. It also plots a heatmap of conspecificity probabilities among samples based on functions of the bGMYC package (Reid & Carstens 2012). When more than one tree are provided, sGMYC can implement the analysis with multiple cores using the parallel and doParallel packages.
You can install the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("arleyc/sGMYC")- Load an example dataset (hypotree) included with the sGMYC package:
library(sGMYC)
data("hypotree")
ape::print.phylo(hypotree)
#>
#> Phylogenetic tree with 58 tips and 57 internal nodes.
#>
#> Tip labels:
#> 11281H_Colinas, 11291H_Colinas, 12184H_12185Hraba, 12187_12186_12243Hraba, 164H_Silvania, 167H_19222_Silvania_Uberlandia, ...
#>
#> Rooted; includes branch lengths.- Run a single-threshold GMYC analysis with the splits package:
library(splits)
#> Loading required package: ape
#> Loading required package: MASS
#> Loading required package: paran
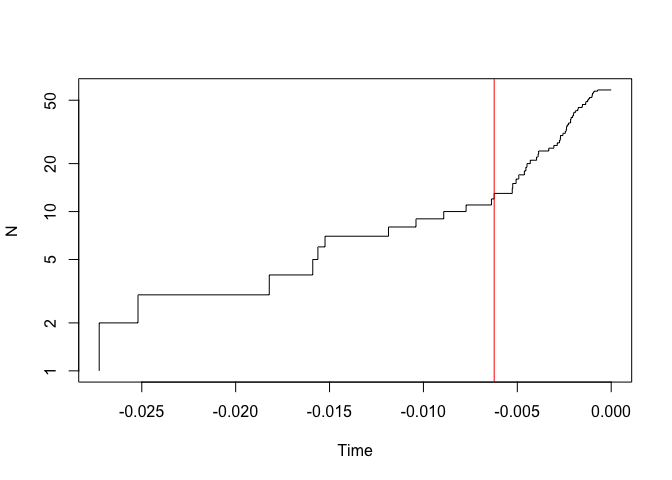
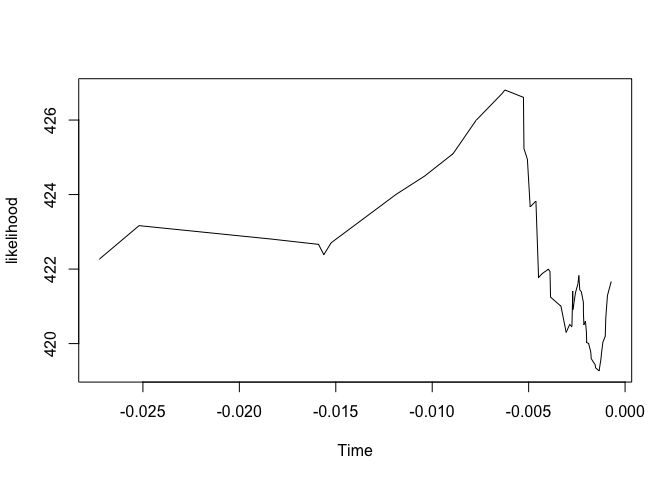
gmyc(hypotree, quiet=TRUE)->fullgmyc
summary(fullgmyc)
#> Result of GMYC species delimitation
#>
#> method: single
#> likelihood of null model: 422.263
#> maximum likelihood of GMYC model: 426.8078
#> likelihood ratio: 9.089746
#> result of LR test: 0.01062152*
#>
#> number of ML clusters: 10
#> confidence interval: 8-12
#>
#> number of ML entities: 12
#> confidence interval: 9-15
#>
#> threshold time: -0.006232079
plot(fullgmyc)- GMYC estimates 12 (9-15) species. Next, use bGMYC to implement a full Bayesian GMYC analysis:
library(bGMYC)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'bGMYC'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:sGMYC':
#>
#> spec.probmat
fullbgmyc<-bgmyc.singlephy(hypotree, mcmc=10000, burnin=1000, thinning=100)
#> You are running bGMYC on a single phylogenetic tree.
#> This tree contains 58 tips.
#> The Yule process rate change parameter has a uniform prior ranging from 0 to 2 .
#> The coalescent process rate change parameter has a uniform prior ranging from 0 to 2 .
#> The threshold parameter, which is equal to the number of species, has a uniform prior ranging from 2 to 51 . The upper bound of this prior should not be more than the number of tips in your trees.
#> The MCMC will start with the Yule parameter set to 1 .
#> The MCMC will start with the coalescent parameter set to 0.5 .
#> The MCMC will start with the threshold parameter set to 50 . If this number is greater than the number of tips in your tree, an error will result.
#> Given your settings for mcmc, burnin and thinning, your analysis will result in 90 samples being retained.
#> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
#> is.binary.tree() is deprecated; using is.binary() instead.
#>
#> is.binary.tree() will be removed soon: see ?is.binary and update your code.
#> !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
#> 10 %
#> 20 %
#> 30 %
#> 40 %
#> 50 %
#> 60 %
#> 70 %
#> 80 %
#> 90 %
#> 100 %
#> acceptance rates
#> py pc th
#> 0.8215 0.7696 0.349
#Calculate matrix of conspecificity probabilities
fullbgmyc.probmat<-bGMYC::spec.probmat(fullbgmyc)
# Calculate a point estimate of the number of species
length(bgmyc.point(fullbgmyc.probmat,0.05))
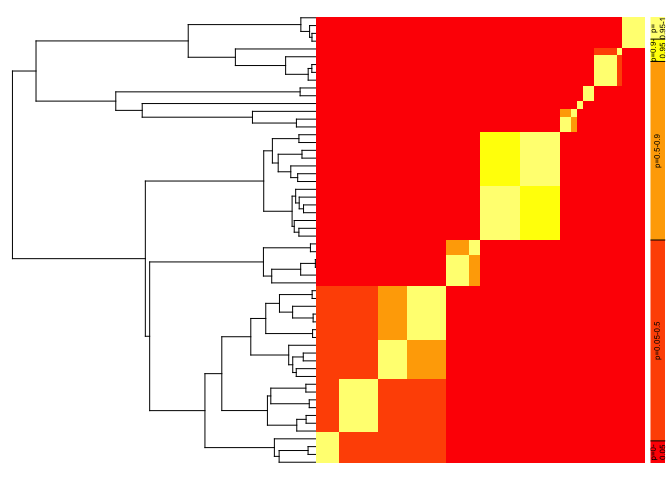
#> [1] 8- Based on cutoff value of PP=0.05, bGMYC estimates 8 species; use a heatmap plot to display the probabilities of conspecificity:
#Plot heatmap of conspecificity probabilities
plot.bgmycprobmat(fullbgmyc.probmat,hypotree)- In sGMYC, subsample two sequences from each of the species originally estimated with the full GMYC:
subgmyc<-sGMYC(hypotree,subsamp=2,nreps=100)
#> Subsampling of tree 1, Done!
#>
#> Number of species in full analysis vs. after subsampling
#> full_GMYC min_sGMYC max_sGMYC mean_sGMYC sd_sGMYC #reps #subsamp per sp
#> Tree 1 12 2 2 2 0 100 2
#>
#> Number of species vs. number of subsampling replicates
#> $`Tree 1`
#> #species #reps
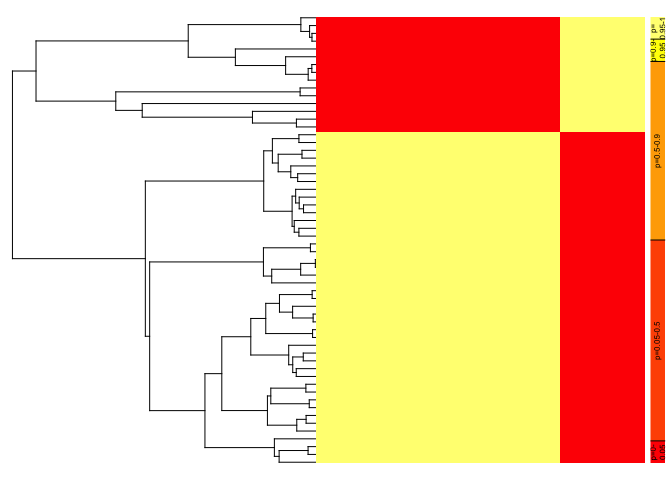
#> 1 2 100- sGMYC estimates 2 species across all 100 subsampling replicates. We can also plot a heatmap that summarizes the variation in species limits based on subsampling:
#Calculate matrix of conspecificity probabilities
subgmyc.probmat<-sGMYC::spec.probmat(subgmyc)
#Plot heatmap of conspecificity probabilities
plot.bgmycprobmat(subgmyc.probmat,hypotree)#Species delimitation with subsampling using multiple trees and computer cores
#Plotting heatmap of conspecificity probabilitiesFujisawa T & Barraclough TG. 2013. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Systematic Biology 62:707–724, doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syt033
Pons J, Barraclough TG, Gomez-Zurita J, Cardoso A, Duran DP, Hazell S, Kamoun S, Sumlin WD & Vogler AP. 2006. Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Systematic Biology 55:595-609, doi: 10.1080/10635150600852011.
Reid NM & Carstens BC. 2012. Phylogenetic estimation error can decrease the accuracy of species delimitation: a Bayesian implementation of the general mixed Yule-coalescent model. BMC Evolutionary Biology 12:196, doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-196.
de Magalhães RF, Santos MTT & Camargo A. 2024. Subsampling GMYC (sGMYC): a new algorithmic implementation of the generalized mixed Yule-coalescent model. I Brazilian Congress of Evolutionary Biology, Curitiba, Brazil.