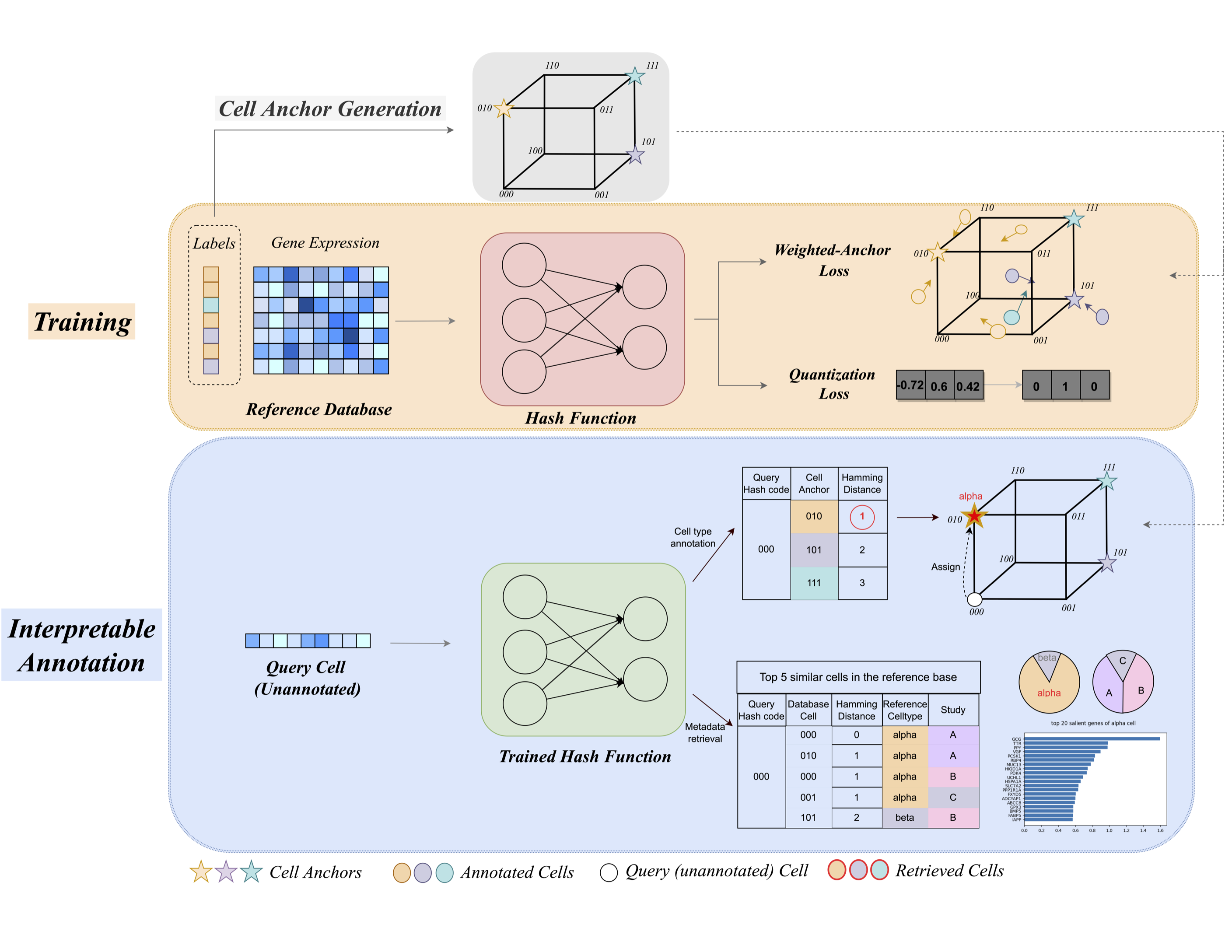
With the increasing availability of large-scale single-cell omics datasets, supervised learning-based cell type annotation tools have positioned their unique advantage in improving annotation accuracy without prior biological information. However, due to the inherent high-dimensionality of single-cell omics data, existing methods lack the capacity or efficiency to handle atlas-level annotation tasks. To address these challenges, we hereby propose scHash, an accurate, efficient, and interpretable deep hashing-based method that can build multi-million reference database and annotate tens of thousands of cells. scHash is robust to batch effects between the query set and the reference database, which is commonly seen in real query tasks. We demonstrate scHash’s accurate and efficient cell type annotation performance as well as its interpretable functionalities on single cell omics datasets across multiple heterogeneous batches and on atlas-level dataset with 1.4M cells. The full paper will be up soon.
scHash consists of three sequential steps:
(1) Cell anchor generation.
scHash generates
(2) Hash function training.
scHash trains a deep hash function that maps raw gene expression to
(3) Interpretable cell type annotation.
scHash can efficiently annotate large-scale scRNA-seq dataset and offer interpretability for its annotation through the metadata of most similar reference cells and saliency map.
- Linux/Unix
- Python 3.8
$ pip install scHashWe offer the following tutorials for demonstration: