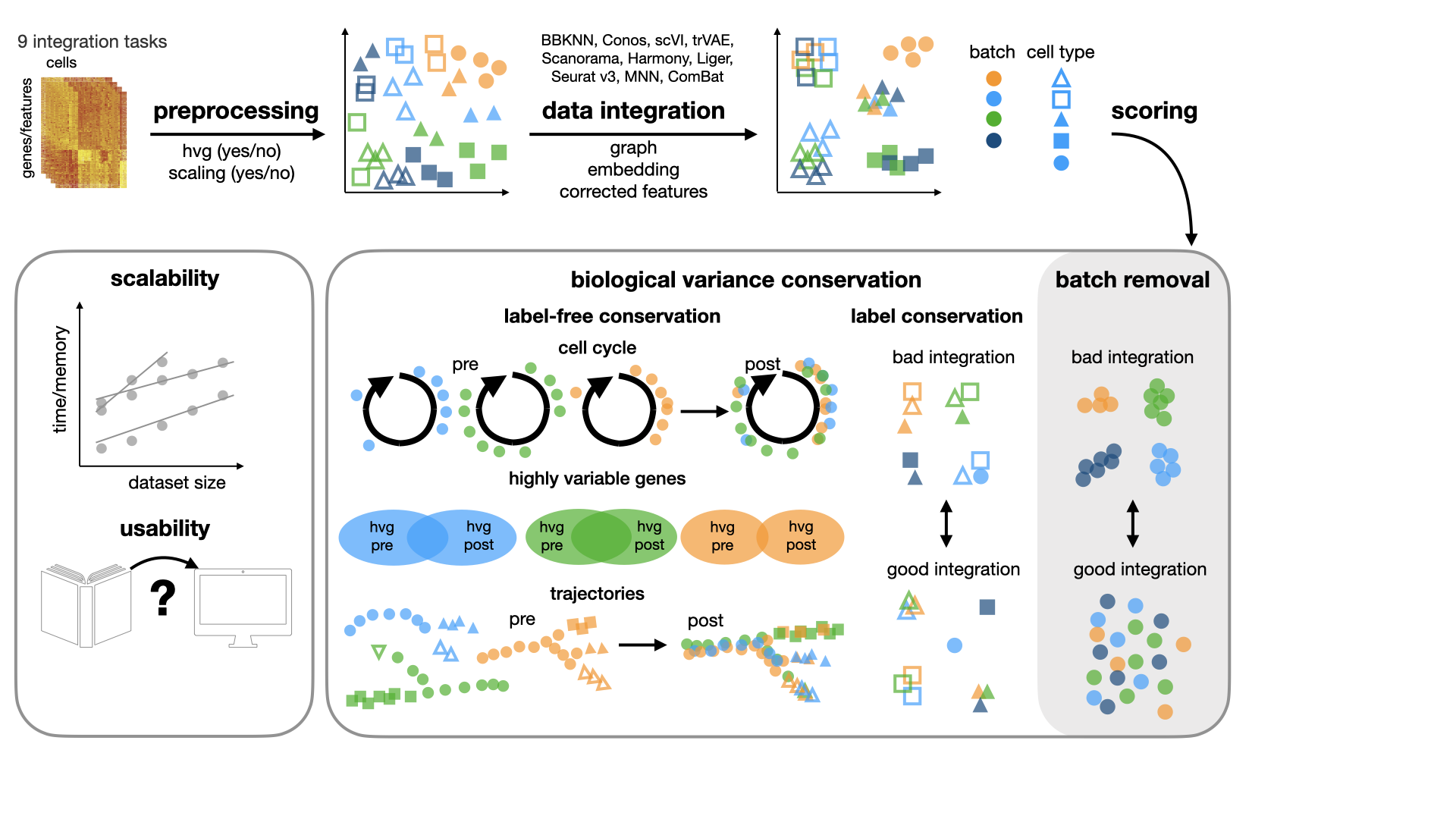
This repository contains code and analysis for the benchmarking study for data integration tools. In this study, we benchmark 10 methods (see here) with 4 combinations of preprocessing steps leading to 40 methods combinations on 60 batches of gene expression and chromatin accessibility data.
We created the python package scIB to streamline the integration process and to integrate it into
a scanpy workflow. Additionally, we created an environment to allow easy integration of R integration methods
into the scanpy workflow.
Furthermore, the package allows for evaluation of integration quality of different datasets if cell type annotations are present using our novel metrics.
The scIB python package is in the folder scIB. It can be installed using pip install -e . run in the root directory.
R helper functions for R integration methods can be found in the R directory.
The scripts folder contains scripts for preparing the data, running the methods, postprocessing and calculation of the metrics.
The notebooks folder contains jupyter notebooks for testing and demonstrating functions of the scIB package as well as notebooks
for preprocessing of the data.
To reproduce the results from this study, three different conda environments are needed. There are different environments for the python integration methods, the R integration methods and the conversion of R data types to anndata objects.
For the installation of conda, follow these instructions or use your system's package manager. The environments have only been tested on linux operating systems although it should be possible to run the pipeline using Mac OS.
To create the conda environments use the .yml files in the envs directory.
To install the envs, use
conda env create -f FILENAME.ymlTo set the correct paths so that R the correct R libraries can be found, copy env_vars_activate.sh to etc/conda/activate.d/
and env_vars_deactivate.sh to etc/conda/deactivate.d/ to every environment.
In the scIB-R-integration environment, R packages need to be installed manually.
Activate the environment and install the packages scran, Seurat and Conos in R. Conos needs to be installed using R devtools.
See here.
This package allows to run a multitude of single cell data integration methods in both R and python.
We use Snakemake to run the pipeline.
The parameters of the run are configured using the config.yaml file.
See the DATA_SCENARIOS section to change the data used for integration.
The script expects one .h5ad file containing all batches per data scenario.
To load the config file run snakemake --configfile config.yaml.
Define the number of CPU threads you want to use with snakemake --cores N_CORES. To produce an overview of tasks that will be run, use snakemake -n.
To run the pipeline, simply run snakemake.
The package contains several modules for the different steps of the integration and benchmarking pipeline.
Functions for the integration methods are in scIB.integrate. The methods are called using scIB.integration.runMETHOD(adata, BATCH).
scIB.preprocessing contains methods for preprocessing of the data such as normalisation, scaling or highly variable gene selection per batch.
The metrics are located at scIB.metrics. To run multiple metrics in one run, use the scIB.metrics.metrics() function.
For a detailed description of the metrics implemented in this package, please see the manuscript.
Batch removal metrics include:
- Principal component regression (
pcr_comparison()) - Batch ASW (
silhouette()) - K-nearest neighbour batch effect (
kBET()) - Graph connectivity (
graph_connectivity()) - Graph iLISI (
lisi_graph())
Biological conservation metrics include:
- Normalised mutual information (
nmi()) - Adjusted Rand Index (
ari()) - Cell type ASW (
silhouette_batch()) - Isolated label score F1 (
isolated_labels()) - Isolated label score ASW (
isolated_labels()) - Cell cycle conservation (
cell_cycle()) - Highly variable gene conservation (
hvg_overlap()) - Trajectory conservation (
trajectory_conservation()) - Graph cLISI (
lisi_graph())
Tools to be compared include: