Abstract
In planar grasp detection, the goal is to learn a function from an image of a scene onto a set of feasible grasp poses in SE(2). In this paper, we recognize that the optimal grasp function is SE(2)-equivariant and can be modeled using an equivariant convolutional neural network. As a result, we are able to significantly improve the sample efficiency of grasp learning, obtaining a good approximation of the grasp function after only 600 grasp attempts. This is few enough that we can learn to grasp completely on a physical robot in about 1.5 hours.
PaperCitation
@misc{zhu2022sample,
title={Sample Efficient Grasp Learning Using Equivariant Models},
author={Xupeng Zhu and Dian Wang and Ondrej Biza and Guanang Su and Robin Walters and Robert Platt},
year={2022},
eprint={2202.09468},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO}
}
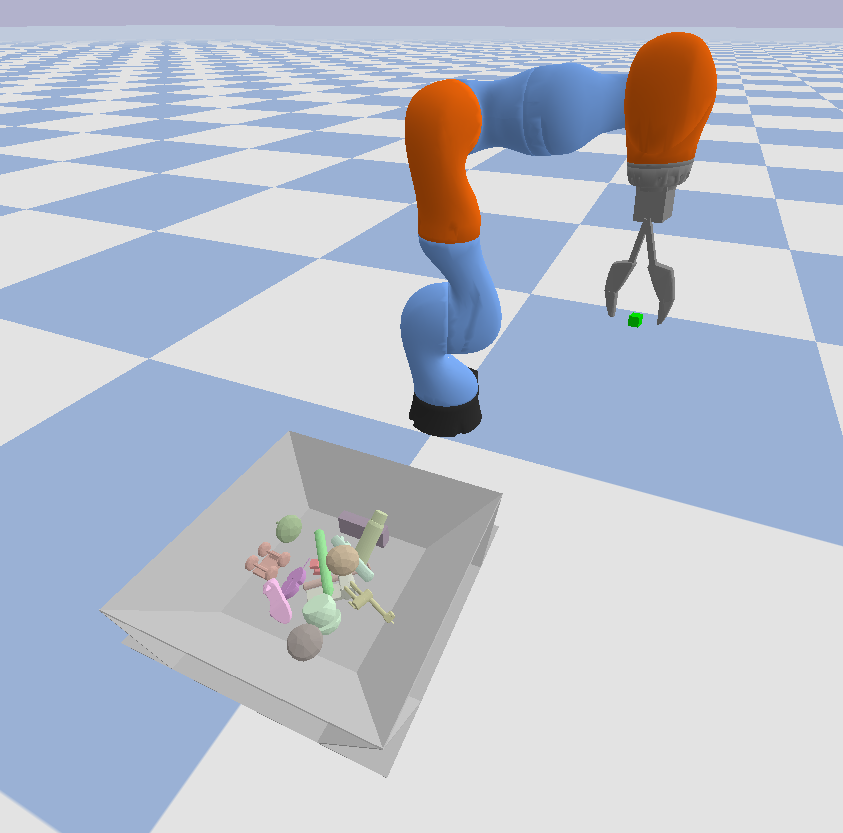
| The simulation environment is random_household_picking_clutter_full_obs_30. This environment is implemented in /helping_hands_rl_envs/envs/pybullet_envs. |
| The physical robot environment is DualBinFrontRear. To train on this environment, a physical robot set up is required. |
- Install anaconda
- Create and activate a conda virtual environment with python3.7.
sudo apt update conda create -n eqvar_grasp python=3.7 conda activate eqvar_grasp - Download the git repository and checkout "with_supervised_learning" branch.
git clone https://github.com/ZXP-S-works/SE2-equivariant-grasp-learning.git cd SE2-equivariant-grasp-learning - Install PyTorch (Recommended: pytorch==1.8.1, torchvision==0.9.1)
- Install CuPy
- Install other requirement packages
pip install -r requirements.txt - Clone and install the environment repo
git clone https://github.com/ColinKohler/helping_hands_rl_envs.git -b xupeng_realistic cd helping_hands_rl_envs pip install -r requirements.txt cd .. - Go to the scripts folder of this repo to run experiments
cd asrse3/scripts
Our method
python3 ./scripts/main.py To visualize the simulation and the policy learning, set --render=f.
Default parameters:
--env=random_household_picking_clutter_full_obs_30
--num_processes=1
--eval_num_processes=10
--render=f # set it to True to see the actual simulation & training process
--learning_curve_avg_window=50
--training_offset=20
--target_update_freq=20
--q1_failure_td_target=non_action_max_q2
--q1_success_td_target=rewards
--alg=dqn_asr
--model=equ_resu_nodf_flip_softmax
--q2_train_q1=Boltzmann10
--q2_model=equ_shift_reg_7_lq_softmax_last_no_maxpool32
--q2_input=hm_minus_z
--q3_input=hm_minus_z
--patch_size=32
--batch_size=8
--max_episode=1500
--explore=500
--action_selection=Boltzmann
--hm_threshold=0.005
--step_eps=0
--init_eps=0.
--final_eps=0.
--log_pre=../results/household_repo/rand_household_picking_clutter/
--sample_onpolicydata=t
--onlyfailure=t
--num_rotations=8
--aug=0
--onpolicy_data_aug_n=8
--onpolicy_data_aug_flip=True
--onpolicy_data_aug_rotate=True
--num_eval_episodes=1000
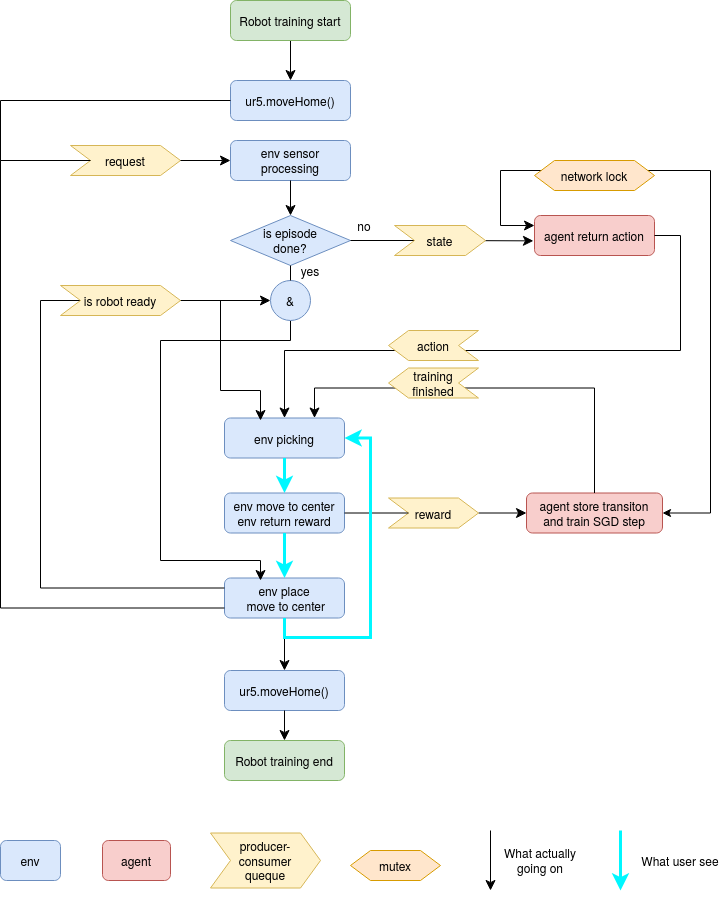
The parallel training is only implemented in physical robot environment. However, one can easily modify it to any environment.
??? python3 ./scripts/train_robot_parallel.py --env=DualBinFrontRear --hm_threshold=0.015 --step_eps=20 --init_eps=1. --final_eps=0.
| The right figure illustrates the parallel training. |