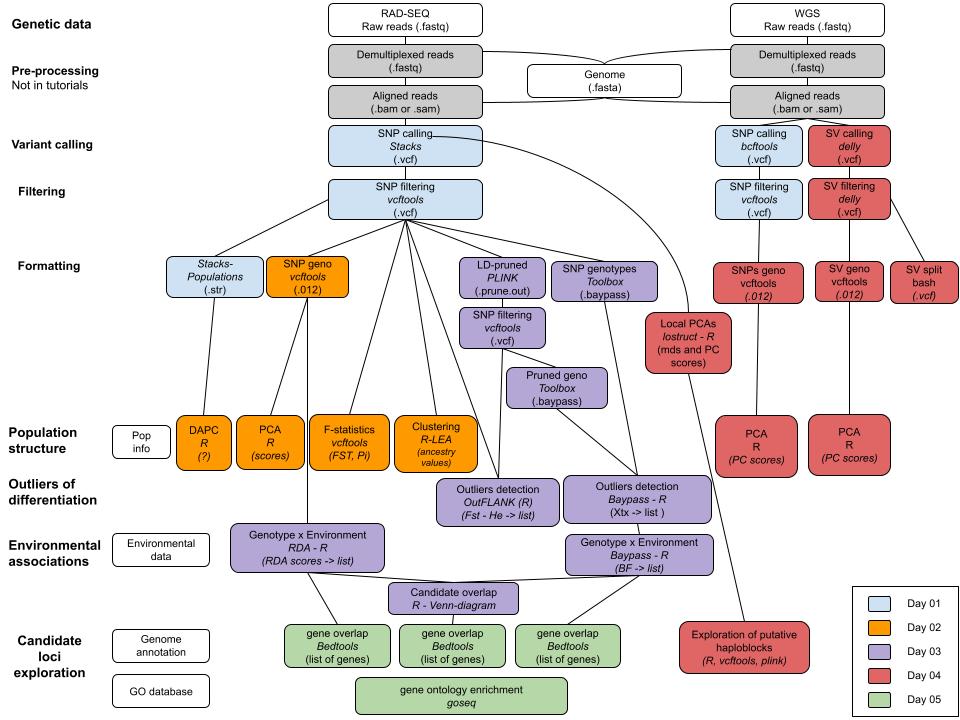
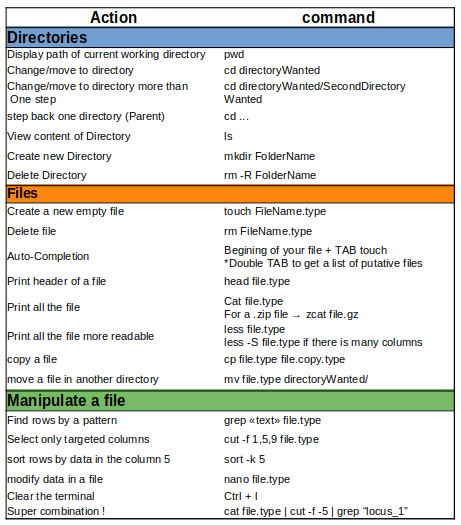
This repository includes scripts and data associated with the practical sessions of the 2023 Physalia Course on Adaptation Genomics prepared by Anna Tigano, Yann Dorant and Claire Mérot.
Except for day 1 in which you won't have the bam files, all the tutorial can be completed with the compressed files stored in the github page for each day (day 2 to day 5). Each daily tutorial can be run independantly of the other days.
Here is the tentative schedule for the week. Within each block we'll keep some flexibility to have plenty of time for questions and discussion.
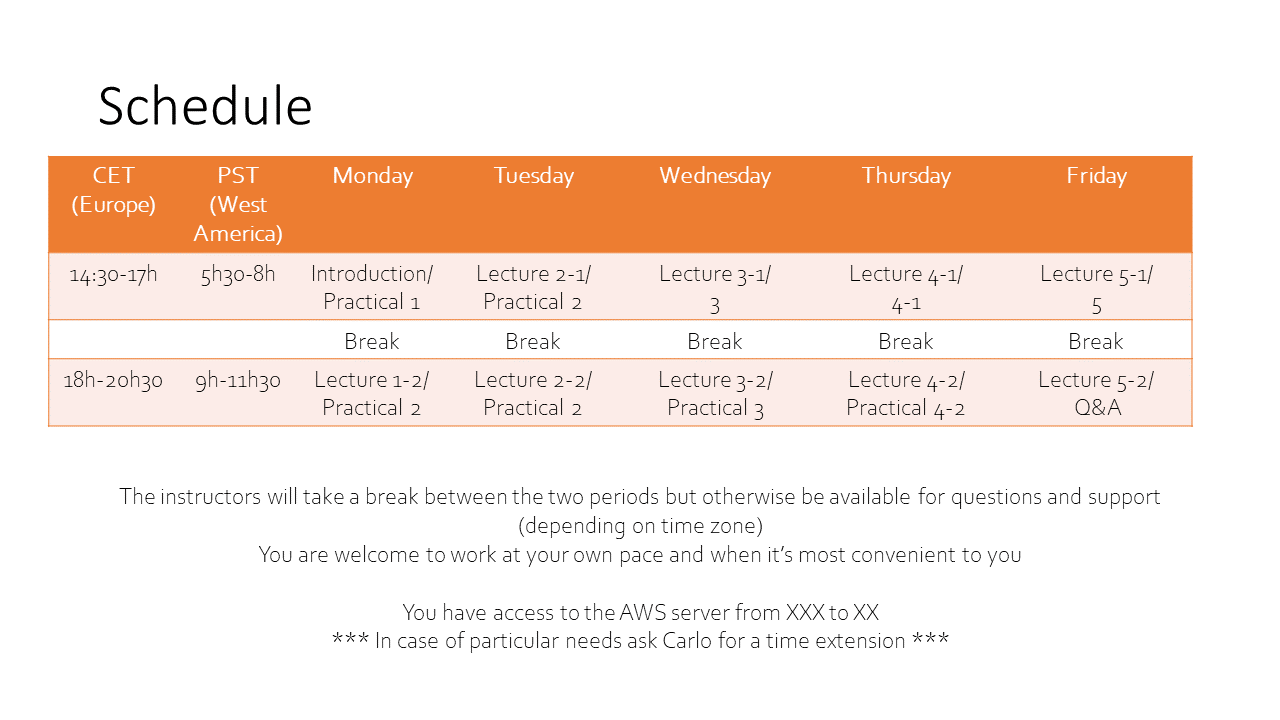
Please follow the instructions sent by Carlo
Additional info for AWS for Mac OS X and Linux users
Additional info for AWS for windows users using Putty/winSCP
Data: All our analyses will be based on the dataset presented in Cayuela et al. (2020), Molecular Ecology.
Genome assembly: For this course, we generated a dummy assembly of about 90 MB (instead of about 500 MB) and 5 chromosomes (instead of 24) to expedite analysis running time.
Raw data: Data were generated using a reduced-representation approach (GBS/RADseq) and sequenced with IonTorrent. Note that the analyses we'll learn during the course are scalable to whole genome resequencing data or other type of genomic data.
1-1: Getting familiar with Unix environment
1-2: From raw sequences to mapped reads
1-3: Calling variants with Stacks
2-1: Fst statistics with vcftools (optional: with Stacks, optional: Pairwise-Fst and isolation-by-Distance )
2-2: Principal component analysis (PCA)
2-3: Population clustering with FastStructure
2-4: Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC)
Data: We focus on 12 populations from Canada for which there is almost no geographic structure but great environmental variability
3-1: Genetic structure and LD-pruning
3-2: Outlier of differentiation with two methods (Outflank & Baypass)
3-3: Genotype-Environnement Associations with two methods (Baypass & redundancy analysis)
We focus on 12 population from Canada. We recommend that you pick one of the two tutorials (haploblocks by local PCA or CNVs from RAD-seq data)
4-1: Investigating haplotypes blocks ( ~inversions?)
This tutorial include working on local PCA, but also calculation of LD, Fst and observed fraction of heterozygotes which may be useful in other contexts
4-2: Filtering duplicated loci in RAD-seq data ( ~ Copy number variants)
This tutorial show how to filter RAD loci to exclude duplicated ones (keep a reliable dataset for SNP analysis), and then how to analyse the duplicated loci for environmental associations.
4-3: Detecting SV with Delly ??
5-1: SNPeff annotation of SNPs for coding & regulatory regions
5-2: Intersection between SNPs and genes with bedtools
5-3: Gene ontology enrichment
5-4: (Optional) Intersection between CNVs and repeats/TE