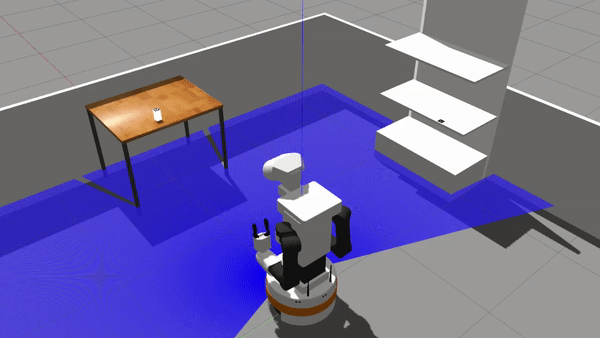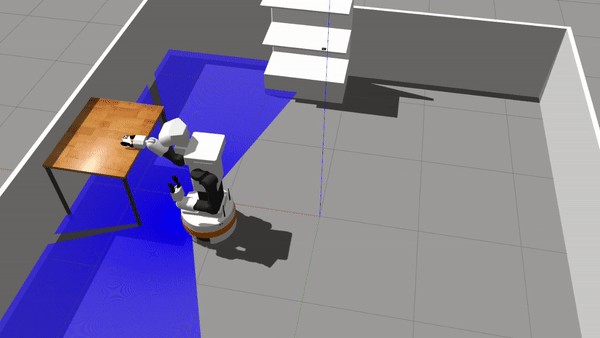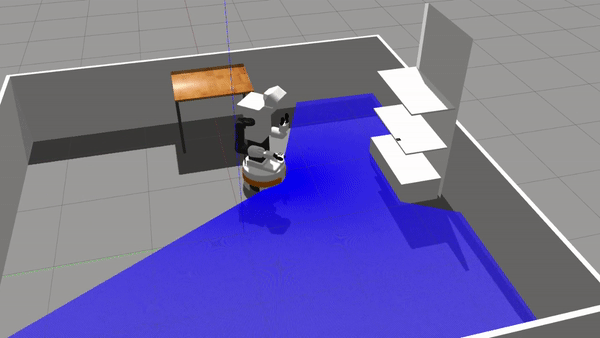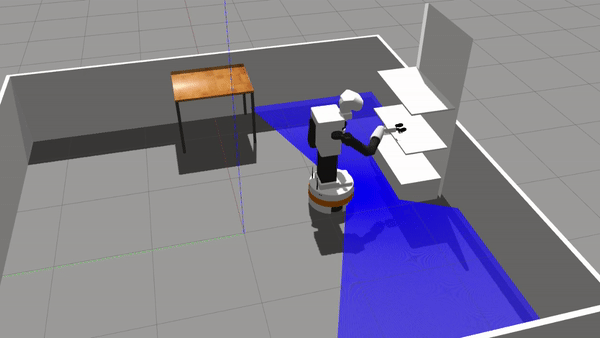
Repository for active inference and behavior trees for discrete decision making. This repository relies on a TIAGo simulation in a simplified retail store. Please read the associated paper for more theorethical considerations about the algorithms.
"Active Inference and Behavior Trees for Reactive Action Planning and Execution in Robotics"
Corrado Pezzato, Carlos Hernandez, Stefan Bonhof, Martijn Wisse, https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.09756
This repositiry contains a Matlab examples and a ROS package for active inference for task planning and execution.
Matlab:
- aip.m the active inference algorithm for decision making is illustrated in the case of heterogeneous states and actions.
- example.m example of use of active inference for discrete decision making in a robotic case where conflicts and preconditions checks are required. A robot is assumed to be able to navigate to a point (MoveBase), reach a location with its end effector (Move MPC), and pick and place things. Actions have preconditions and are assumed not instantaneous
ROS:
The other folders are related to the ROS package containing a Python implementation of active inference and behavior trees. You can run an example use case with TIAGo in a simplified retail store after installation of the package ad dependancies.
Simulation Environment
A singularity image can be downloaded from here.
Alternatively, you can build the singularity yourself:
-
create a sub directory called 'pkgs' (in the
singularity_environmentdirectory)mkdir pkgs
-
use
vcstool(orwstool) to clone/download the dependencies (as specified inretail_store_lightweight_sim.repos).vcs import < retail_store_lightweight_sim.repos pkgsAdding packages to
pkgwill allowrosdepto install all required build and run dependencies into the image, so students can then proceed to build those packages in their own workspaces (otherwise builds would fail due to missing dependencies).Note Packages in
pkgwill be installed on the image, their source will not be included in the image itself, so there may be some elements that are not installed. So far I've only noticed one required change. -
Modify the
CMakeList.txtfile from thepal_navigation_sminside thepkgsfolder.Change the
installinstruction (starts at line 10) by adding some scripts as follows.install( PROGRAMS scripts/map_setup.py scripts/pal_navigation_main_sm.py scripts/navigation.sh scripts/base_maps_symlink.sh scripts/cp_maps_to_home.sh scripts/cp_pose_to_home.sh DESTINATION ${CATKIN_PACKAGE_BIN_DESTINATION}) -
check the
VERSIONvariable inside thedocker_build.sh,build.shandSingularityfiles. This version should match the version of your singularity install (singularity -v) -
run
docker_build.sh./docker_build.sh
After some time and a successful build, a new docker image will be created. This requires Docker to be installed and configured.
-
run
build.sh./build.sh
After some time and a successful build, a new .simg should be generated by singularity in the cwd.
Behavior trees library
Install the BT library to use this package (tested in Ubuntu 18.04 with ROS Melodic). Before proceeding, it is recommended to to install the following dependencies:
sudo apt-get install libzmq3-dev libboost-dev
You can also easily install the Behavior Tree library with the command
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-behaviortree-cpp-v3
sudo apt-get update
Using the virtual environment
Access the simngularity image by using the regular Singularity shell action:
singularity shell /path/to/discrete_ai_tiago.simgUse the flag for nvidia drivers if applicable to your machine:
singularity shell --nv /path/to/discrete_ai_tiago.simgThen source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bash to access all the TIAGo dependencies installed on the image.
source /opt/ros/melodic/setup.bashHow to run a simple example with TIAGo
Create a new workspace and clone this repository in the src folder. Build the package using catkin build. Run the three commands below from within the singularity image after sourcing source/devel/setup.bash.
roslaunch retail_store_simulation tiago_simulation.launch
rosrun discrete_ai tiago_perception.py
rosrun discrete_ai active_inference_server.pyFrom a terminal outside the singularity image run the behavior tree:
rosrun discrete_ai demo_executeBTThe expected outcome is the following:
Note: The sills used in this simulation are based on standard moveBase and moveIt actions, thus robustness (especially of IK solutions) might make TIAGo fail the grasp. Aruco detection can also imprecise and will be improved over time.