This repository contains the code (config, src and script files) to set up and run a Cob-Jenkins CI Server using the Cob-Pipeline-PlugIn.
Before starting with this guide, please setup one machine with the following properties:
- Operation system: Ubuntu 12.04
- user: jenkins (admin)
assumptions:
- we're only using one machine which is master and slave at the same time
apt-cacheris running on master- there's a github user that has read access to all repositories which should be build and write access to a jenkins_config repository (e.g. http://github.com/ipa320/jenkins_config)
For further informations read the detailed Jenkins Guide.
Install basic packages
sudo apt-get install git-core pbuilder devscripts pigz python-jenkins python-mock python-nose python-paramiko vim openssh-server
Install basic ROS packages
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu precise main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
wget http://packages.ros.org/ros.key -O - | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install ros-hydro-ros
Add the jenkins debian repository and install jenkins
wget -q -O - http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key | sudo apt-key add -
sudo su -c 'echo "deb http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/debian binary/" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install jenkins
Install apt-cacher
sudo apt-get install apt-cacher-ng
We've tested the setup on Jenkins version v1.544. You can find the war file here.
cd /usr/share/jenkins/
sudo rm -rf jenkins.war
sudo wget http://mirrors.jenkins-ci.org/war/1.544/jenkins.war
restart jenkins
sudo /etc/init.d/jenkins restart
After a successful installation you can access the jenkins server in your browser at http://localhost:8080.
Download the .hpi file from https://github.com/ipa320/cob-pipeline-plugin/tree/master/releases (latest) and place it in /var/lib/jenkins/plugins.
cd /var/lib/jenkins/plugins
sudo wget https://github.com/ipa320/cob-pipeline-plugin/raw/master/releases/v0.9.6/cob-pipeline.hpi
All scripts and configurations will be stored in /home/jenkins/jenkins-config.
mkdir ~/jenkins-config
All tarballs will be stored in ~/chroot_tarballs
mkdir -p ~/chroot_tarballs
mkdir -p ~/chroot_tarballs/in_use
Setup ssh configuration (create ssh-key if it doesn't exist already and add github.com and localhost to known hosts)
ssh-keygen
touch ~/.ssh/known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H github.com >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H localhost >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
You have to add this key to your GitHub user http://github.com/settings/ssh.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Setup git configuration on master
git config --global user.name "<USER_NAME>"
git config --global user.email "<EMAIL>"
Clone the jenkins_setup and jenkins_config repositories
git clone git@github.com:ipa320/jenkins_config.git ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_config
git clone git@github.com:ipa320/jenkins_setup.git ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup
Add the jenkins_setup module to the $PYTHONPATH (adapt the ROS_RELEASE).
sudo su -c 'echo "export PYTHONPATH=~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/src" > /etc/profile.d/python_path.sh'
sudo su -c 'echo "source /opt/ros/hydro/setup.sh" >> /etc/profile.d/python_path.sh'
Create softlinks in userContent directory pointing to jenkins_setup, jenkins_config, chroot_tarballs and .ssh
ln -s ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup /var/lib/jenkins/userContent/jenkins_setup
ln -s ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_config /var/lib/jenkins/userContent/jenkins_config
ln -s ~/chroot_tarballs /var/lib/jenkins/userContent/chroot_tarballs
ln -s ~/.ssh /var/lib/jenkins/userContent/.ssh
Enable passwordless sudo rights for the jenkins user by adding the following line at the end of /etc/sudoers (open with sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers).
jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Enable password-less ssh login from master to slave and slave to master (even if your're using locahost).
ssh-copy-id localhost
ssh localhost
ssh <JENKINS_MASTER_NAME>
Afterwards reboot your machine
sudo reboot now
Go to http://localhost:8080/configureSecurity
- Check enable security
- Check Jenkins's own user database under Access Control/Security Realm. And check Allow users to sign up.
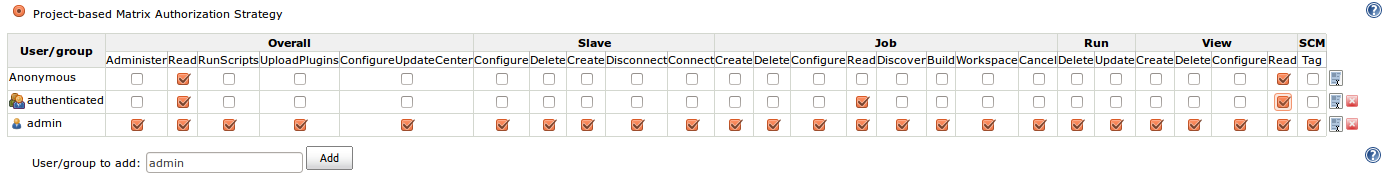
- Set Authorization to Project-based Matrix Authorization Strategy.
- Add an
admin-user and give him all rights. - Add an
anonymous-group and anauthenticated-group and give them rights according to the screentshot.
After click save the Server will throw you to a Login screen. Just register with the username admin.
- Github Authentication Plugin
Another way is to use the GitHub user database for user identification. The Github OAuth Plugin has to be installed. Configure the plugin as described here for an 'omnipotent' GitHub user.
Go to http://localhost:8080/configure
- Set # of executors to
1.
- Set Jenkins URL to your servers name.
- Set your System Admin e-mail address.
- Set SMTP server
You can keep the default values for all other entries.
Go to http://localhost:8080/computer
-
add new slave called
master-buildasDumb Slave -
set the
# of executorsto1 -
set
Remote FS rootto/home/jenkins -
set the
Labelstoupdate_tarballs prio_build regular_build prio_nongraphics_test regular_nongraphics_test -
set
Hosttolocalhost
Go to http://localhost:8080/pluginManager/available and install the following plugins:
- Git Plugin
- Parameterized Trigger Plugin
- Build Pipeline Plugin
- View Job Filters
- Build-timeout Plugin
- Warnings Plugin
- Cppcheck Plugin
- Multiple SCMs Plugin
- Copy To Slave Plugin
- Workspace Cleanup Plugin
- Build Blocker Plugin
Using RAM for chroot environment and parallel compression.
Add the following line to /etc/fstab
# pbuilder
tmpfs /var/cache/pbuilder/build tmpfs defaults,size=3200M 0 0
(This size should be arround 50% of the machines memory).
Mount tmpfs by entering
sudo mount -a
Create a file called ~/.pbuilderrc
touch ~/.pbuilderrc
Add the following content to ~/.pbuilderrc
# don't use aptcache
APTCACHE=""
# ccache
sudo mkdir -p /var/cache/pbuilder/ccache
sudo chmod a+w /var/cache/pbuilder/ccache
export CCACHE_DIR="/var/cache/pbuilder/ccache"
export PATH="/usr/lib/ccache:${PATH}"
EXTRAPACKAGES=ccache
BINDMOUNTS="${CCACHE_DIR}"
# pigz; multicore zipping
COMPRESSPROG=pigz
# tmpfs
APTCACHEHARDLINK=no
Afterwards reboot the Jenkins-Server
sudo reboot now
Go to the cob pipeline configuration section at http://localhost:8080/configure and fill the following fields (As soon as you fill out the fields, the values will be validated in the background.):
- Jenkins Admin Login/Password (This is the user you configured before in the Configure Security part with all the permissions. Enter its login name and password.)
- in case of using github oauth plugin: copy the API Token from http://localhost:8080/me/configure.
-
Configuration Folder (Enter the path of the cob-pipeline configuration folder.)
/home/jenkins/jenkins-config -
Tarball Location (enter the location where the tarballs are stored.)
jenkins@localhost:/home/jenkins/chroot_tarballs -
GitHub User Login/Password (This is the github user that has read-permission to all the repositories you want to be tested. It has also write-permission to your jenkins_config repository.)
-
Pipeline Repositories Owner/Fork (GitHub user that ownes the jenkins_setup and the jenkins_config repository.)
ipa320 -
ROS releases (ROS distributions that should be supported by your build/test pipeline)
groovy hydro -
Robots (Nodes which can be chosen for Hardware Build/Test jobs.)
keep empty if you have no hardware slaves
-
Target Platform Url (URL where the ROS
targets.yamlis stored, defining the Ubuntu target platforms for each ROS Version.)https://raw.github.com/ipa320/jenkins_setup/master/releases/targets.yaml
To set up the necessary chroot tarballs and keep them up-to-date an additional job is needed. Copy the prepared job config.xml into the job folder and make the jenkins user own it.
sudo mkdir /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_chroot_tarballs
sudo cp ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/templates/update_chroot_tarballs/UPDATE_CHROOT_TARBALLS_config.xml /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_chroot_tarballs/config.xml
sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_chroot_tarballs
Open /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_chroot_tarballs/config.xml and adjust it to your demands:
- set the
SERVERNAMEto your Jenkins server (e.g. localhost) - set the
APT_CACHER_ADDRESSto your apt-cacher (e.g. http://localhost:3142)
Afterwards Reload Configuration from Disk under http://localhost:8080/manage and run the job to create the tarballs.
To update all pipelines (e.g. after a general configuration change) an additional job is needed. Copy the prepared job config.xml into the job folder and make the jenkins user own it.
sudo mkdir /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_pipelines
sudo cp ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/templates/update_pipelines/UPDATE_PIPELINES_config.xml /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_pipelines/config.xml
sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_pipelines
Afterwards Reload Configuration from Disk under http://localhost:8080/manage and run the job to create the tarballs. you will have to start this job manually and give it the admin user and password (if using github OAuth, the use the token from http://localhost:8080/me/configure when logged in as the admin user.
To cleanup the workspaces of all slaves an additional job is needed. Copy the prepared job config.xml into the job folder and make the jenkins user own it.
sudo mkdir /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_cleanup_slaves
sudo cp ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/templates/update_pipelines/UPDATE_CLEANUP_SLAVES_config.xml /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_cleanup_slaves/config.xml
sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/update_cleanup_slaves
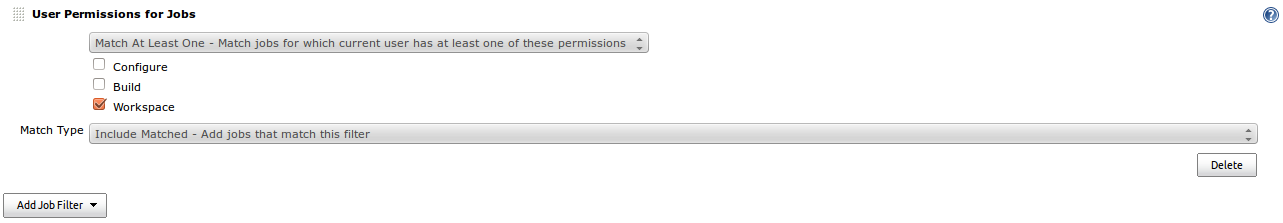
Login as admin and create a new view by pressing the '+'.
Name it current_user and select List View. Add Job Filter in the Job Filter section and select User Permissions for Jobs. Configure as shown in the picture and press OK.
Go to http://localhost:8080/configure and select 'current_user' as Default view.
Copy the jelly template for the email generation:
sudo mkdir /var/lib/jenkins/email-templates sudo cp ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/templates/email-templates/html-with-health-builds-tests.jelly /var/lib/jenkins/email-templates/ sudo chown -R jenkins:jenkins /var/lib/jenkins/email-templates
Prepare the jenkins node for graphical tests by installing VirtualGL and TurboVNC. You can run the following script to prepare the node
sudo ~/jenkins-config/jenkins_setup/scripts/graphicTest/prepareNode.bash
After running the above script, the computer must be restarted.
The graphics driver must be an version of the official nvidia driver. Successfully tested were the versions nvidia-current, nvidia-304 and nvidia-304-experimental. Other nvidia drivers are likely to work as well but are not tested yet.