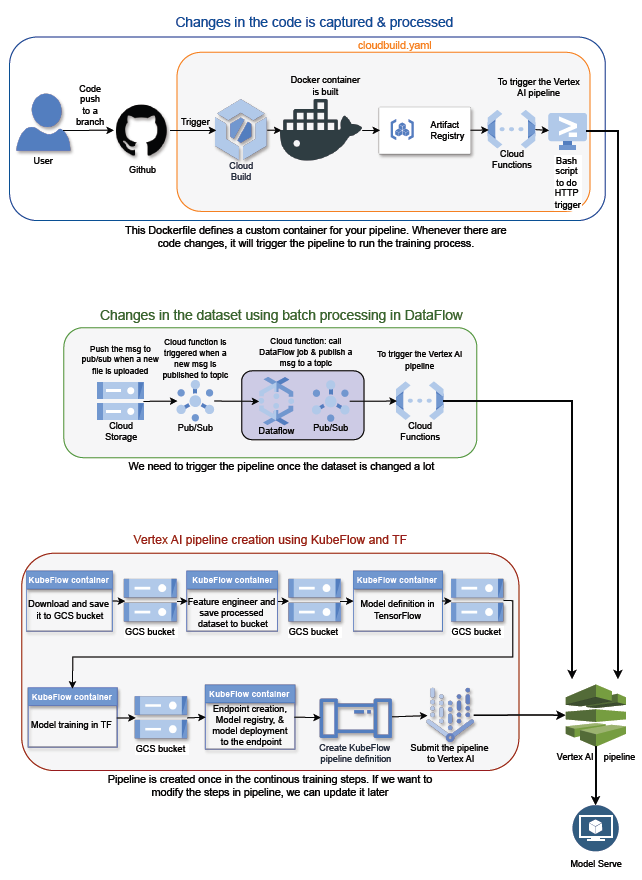
Continuous training means that the ML system automatically and continuously retrains machine learning models to adapt to changes in the data before it is redeployed. Possible triggers for rebuilding include data changes, model changes, or code changes[1].
In this repo, we demonstrate continous training from both code and data changes.
- We can build the container and push to artifact registry using the below code
# Building the docker container
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args:
- build
- '-t'
- '$_AR_HOSTNAME/$PROJECT_ID/$_AR_REPO/$_SERVICE_NAME:$COMMIT_SHA'
- .
# Pushing docker container image to artifact registry
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args:
- push
- '$_AR_HOSTNAME/$PROJECT_ID/$_AR_REPO/$_SERVICE_NAME:$COMMIT_SHA'
- These variable are coming from the Cloud Build trigger page which we set up to bind the cloud build and GitHub.
There are two ways to create cloud functions. The one is though cloud build which I will explain here and the second method is by creating it manually through Cloud Functions page (you can see the instruction at "Manual Cloud Functions setup" section)
- Create main.py and requirements.txt files as described in "Manual Cloud Functions setup" section
- Create a zip file and upload to the GCS bucket and add the location of it to the '--source' section in the cloudbuild.yaml file as shown in the next step.
- Add below code to cloudbuild.yaml file
# Creating Cloud Functions
- name: gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdktool/cloud-sdk
args:
- gcloud
- functions
- deploy
- 'cloudbuild_mnist_vertex_pipeline_cloudfunction' # function name in the main.py
- '--region'
- 'us-central1'
- '--source'
- 'gs://mlops-heavy-workflow-bucket/cloud_functions/cloudbuild_mnist_vertex_pipeline_cloudfunction.zip' # it has to be stored as zip file with main.py and requirements.txt
- '--trigger-http'
- '--gen2'
- '--allow-unauthenticated'
- '--runtime'
- 'python312'
- '--memory'
- '512M'
- This will create the cloud functions
- Once the cloud function is deployed, the http-trigger based cloud functions will have url which can be used to trigger the Cloud Functions by invoking it.
- Getting this url is a manual proccess in the first stage, but squbsequent updates can execute automatically by adding this static url to our bash script to invoke it
- We can add the following code to cloudbuild.yaml to automate the triggering of Cloud Functions once we have the url from the deployed Cloud function.
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud
entrypoint: "bash"
args:
- "-c"
- |
RESPONSE=$(curl -i https://us-central1-mlops-heavy-workflow-project.cloudfunctions.net/cloudbuild_mnist_vertex_pipeline_cloudfunction | grep HTTP | cut -d' ' -f2)
if [ "200" != "$$RESPONSE" ]; then exit 1; fi
- The above is just a bash script step in the cloudbuild.yaml to curl the URl that is equivalent as invoking the URL.
- In this example, Vertex AI pipeline will be run (code in the main.py does this).
- Compile the pipeline and store it to the bucket
- Enable CF and go to the functions page and click the create function.
- Fill the necessary infos, more importantly, select the trigger type. In this, we chose the HTTP trigger. For the http trigger, we get URL which will call the cloud functions whenever we invoke the URL.
- Choose "Allow unauthenticated invocations" as authentication and click next
- Select the runtime as Python ans source code as inline.
- Paste the below code to main.py
import functions_framework
import base64
import json
from google.cloud import aiplatform
PROJECT_ID = <your project>
REGION = <your region>
PIPELINE_NAME = <your pipeline name>
GCS_BUCKET_NAME = <your bucket>
PIPELINE_ROOT = <your pipeline root>
pipeline_spec_uri = <your compiled pipeline file location>
@functions_framework.http
def hello_http(request):
"""HTTP Cloud Function.
Args:
request (flask.Request): The request object.
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#incoming-request-data>
Returns:
The response text, or any set of values that can be turned into a
Response object using `make_response`
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#flask.make_response>.
"""
request_json = request.get_json(silent=True)
request_args = request.args
if request_json and 'name' in request_json:
name = request_json['name']
elif request_args and 'name' in request_args:
name = request_args['name']
else:
name = 'World'
trigger_pipeline_run()
return 'Pipeline run started'
def trigger_pipeline_run():
PIPELINE_PARAMS = {
"bucket_name":GCS_BUCKET_NAME,
"display_name":PIPELINE_NAME,
"project":PROJECT_ID,
"location":REGION
}
# Create a PipelineJob using the compiled pipeline from pipeline_spec_uri
aiplatform.init(
project=PROJECT_ID,
location=REGION,
)
job = aiplatform.PipelineJob(
display_name=PIPELINE_NAME,
template_path=pipeline_spec_uri,
pipeline_root=PIPELINE_ROOT,
enable_caching=False,
parameter_values=PIPELINE_PARAMS
)
# Submit the PipelineJob
job.submit()
- Add following library name to requirements.txt
google-cloud-aiplatform
pyyaml