menelaus
In this repo, a single quadcopter maintains a group of friendly ground vehicles in camera view. The ground vehicles are considered friendly because they are periodically broadcasting their positions. Simulation takes place in the morse simulator, and communication between robots is handled through a publisher/subscriber scheme implemented with redis.
Need to stabilize the camera and smooth out the waypoint following!
Description
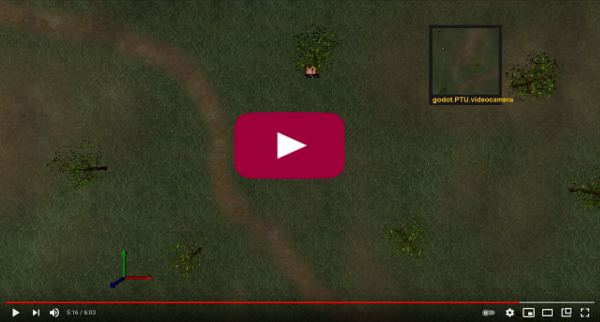
Given a group of ground vehicles, the goal is to keep as much of the group as possible in camera view by following them with a quadcopter. The quadcopter is able to tail-chase the group's centroid, while adjusting the camera angle toward the centroid. The quadcopter can also adjust its elevation to change the size of the camera footprint as the ground vehicles get closer or further from each other. However, the quadcopter hovers in place whenever possible. This is because it is more efficient to hover than chase and it is easier to capture stable video.
The quadcopter relies entirely on position messages recieved from the ground vehicles. This is more reliable than computer vision, assuming a steady stream of accurate positions. The quadcopter's onboard computation is freed up for other tasks. The disadvantage is the reliance on communication, so it must be part of a cooperate system.
I developed the bulk of this system for a 2016 AI Robotics class taught by Dr. Robin Murphy. For the class, I conducted experiments on the effect of the position broadcast rate on the ability to maintain the targets in view. Too few messages obviously lead to gaps where the quadcopter loses the targets and has to catch up, but too many needlessly floods the network.
Quick start
The following instructions are for Ubuntu Linux, but should be very similar for other Linux distributions. The most recently tested is Ubuntu 18.04. Not the prettiest instructions. Would prefer to use a virtual environment and avoid modifying shell environment variables
In the following, <DIR> is whatever directory you were in when you performed the git clone step.
Install dependencies
sudo apt-get install morse-simulator python3-morse-simulator
sudo apt-get install redis-server
pip3 install redis
Install
git clone https://github.com/ekrell/menelaus.git
Add the following line to your .bashrc, or else run this every time you open a terminal.
export PYTHONPATH="${PYTHONPATH}:<DIR>/menelaus/lib"
Directory structure
menelaus
├── inData Files with start points and waypoints for the ground robot trajectories
├── lib Python modules
├── README.md This document
├── robots Scripts that define quadcopter and rover. Vehicle behaviors and communication instantiated here.
├── scenes Scripts with morse simulator scenes. Vehicles and environment instantiated here.
└── scripts Scripts defining behaviors for an already instantiated robot, such as "follow_targets" and "monitor_position"
Architecture
The morse simulator is instantiated with a scene script that defines what 3D environment to load and with what robots/sensors/etc.
Executing this script launches the morse simulator and vehicles, but they are just sitting there waiting for instructions.
Scene scripts are located in menelaus/scenes.
Each robot type (quadcopter and rover) has a corresponding robot script in menelaus/robots/.
These scripts setup the publisher/subscriber communication for the robots defined in the morse scene,
as well as some default functionality. Each robot in morse has a unique name that is used when
executing the script to instantiate the specified robot. That is, python3 robots/rover.py -n susan will
setup the communication for a rover that has a unique name of susan in a currently running morse scene.
Robots may be assigned tasks with behaviors in menelaus/scripts. Read on for a demonstration of follow_targets.py.
Demonstration: follow targets
This demonstration uses a quadcopter named Godot to follow target rovers Susan and Anton.
Do each of the following in a separate terminal after navigating to <DIR>/menelaus.
Launch Morse scene
morse run scenes/field_exercise_1.py
Start a rover named susan
python3 robots/rover.py -n susan -w inData/round10/susan.waypoints
Start a rover named anton
python3 robots/rover.py -n anton -w inData/round10/anton.waypoints
Start a quadcopter named godot
python3 robots/copter.py -n godot
Initiate follow behavior
python3 scripts/follow_targets.py -q godot -t susan,anton