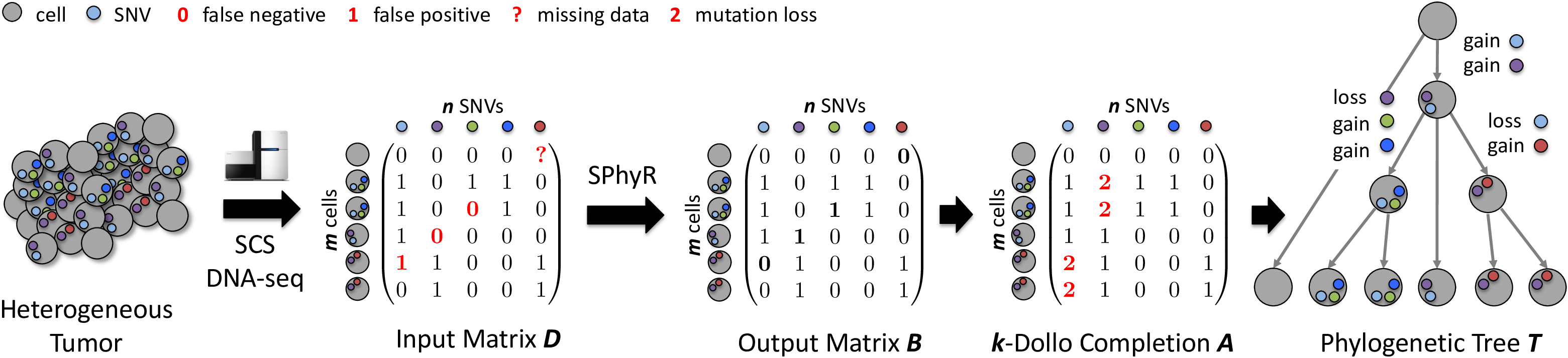
SPhyR is an algorithm for reconstructing phylogenetic trees from single-cell sequencing data. SPhyR employs the k-Dollo phylogeny model, where each SNV can only be gained once but lost k times.
SPhyR is written in C++11 and thus requires a modern C++ compiler (GCC >= 4.8.1, or Clang). In addition, SPhyR has the following dependencies.
Graphviz is required to visualize the resulting DOT files, but is not required for compilation.
In case doxygen is available, extended source code documentation will be generated.
To compile SPhyR, execute the following commands from the root of the repository:
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
In case CMake fails to detect LEMON, run the following command with adjusted paths:
$ cmake -DLIBLEMON_ROOT=~/lemon
The compilation results in the following files in the build directory:
| EXECUTABLE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
analyze |
Computes various performance statistics of a solution. |
kDP |
Solves the k-Dollo Phylogeny problem given a binary matrix B and integer k. |
kDPFC |
Solves the k-Dollo Phylogeny Flip and Clsuter problem given a binary matrix with missing data, an integer k, a false positve rate alpha, a false negative rate beta, a number s of taxon clusters and number t of character clusters. |
perturb |
Introduces false positives and false negatives in a given binary matrix. |
simulate |
Simulates a k-Dollo phylogenetic tree given a perfect phylogeny tree |
visualize |
Visualizes a phylogenetic treein Graphviz DOT format. |
SPhyR's input file is text based. The first line lists the number of taxa (cells), followed by the number of characters (SNVs) on the second line. Then, each subsequent line defines the value of each character for each taxon. More specifically, the allowed values are 0, 1 and -1, where 0 denotes the absence of the mutation, 1 denotes the presence of the mutation and -1 indicates missing data.
In the k-Dollo Phylogeny problem, we are given a binary matrix B and integer k, and wish to determine whether there exists a k-Dollo phylogeny for B, and if so construct one.
Usage:
./kDP [--help|-h|-help] [-M int] [-T int] [-k int] [-t int] [-v] input
output
Where:
input
Input file
output
Output file
--help|-h|-help
Print a short help message
-M int
Memory limit in MB (default: -1, unlimited)
-T int
Time limit in seconds (default: -1, unlimited)
-k int
Maximum number of losses per character (default: 1)
-t int
Number of threads (default: 1)
-v
Verbose output
An example execution:
$ ./kDP -k 1 ../data/k_dollo/m25_n25_s7_k1_loss0.4.B > outputA.txt
Step 1 -- elapsed time 0.00345898 s
Step 1 -- number of constraints: 138
Step 1 -- number of active variables: 54
Step 1 -- introduced 3 constraints
Step 2 -- elapsed time 0.00559616 s
Step 2 -- number of constraints: 141
Step 2 -- number of active variables: 58
Step 2 -- introduced 0 constraints
CPLEX: [2000 , 2000]
Elapsed time: 0.013164
The file outputA.txt contains the k-Dollo completion.
In the k-Dollo Phylogeny Flip and Cluster, we are given matrix D, error rates alpha, beta, integers k, s, t, and wish to find a binary matrix A and tree T such that: (1)~B has at most s unique rows and at most t unique columns; (2) \Pr(D \mid B, alpha, beta)$ is maximum; and (3) T is a k-Dollo phylogeny for B.
Usage:
./kDPFC [--help|-h|-help] [-M int] [-N int] [-T int] [-a num] [-b num]
[-k int] [-lC int] [-lT int] [-s int] [-t int] [-v] input output
Where:
input
Input file
output
Output file
--help|-h|-help
Print a short help message
-M int
Memory limit in MB (default: -1, unlimited)
-N int
Number of restarts (default: 10)
-T int
Time limit in seconds (default: -1, unlimited).
-a num
False positive rate (default: 1e-3)
-b num
False negative rate (default: 0.3)
-k int
Maximum number of losses per SNV (default: 1)
-lC int
Number of character clusters (default: 15)
-lT int
Number of taxon clusters (default: 10)
-s int
Random number generator seed (default: 0)
-t int
Number of threads (default: 1)
-v
Verbose output
An example execution:
$ ./kDPFC ../data/CRC/CRC1.input -a 0.0152 -b 0.0789 > CRC1.A
Number of fixed characters = 0
Number of fixed taxa = 0
Base log likelihood = 0
Step 1 -- elapsed time 0.020782 s
Step 1 -- number of constraints: 150
Step 1 -- number of active variables: 217
...
The visualize executable generates a tree in DOT format.
Usage:
./visualize [--help|-h|-help] [-T] [-c str] [-t str] input
Where:
input
Input file
--help|-h|-help
Print a short help message
-T
Use tree instead of matrix
-c str
Character labels
-t str
Taxon labels
An example execution:
$ ./visualize CRC1.A -c ../data/CRC/CRC1_SNV.labels -t ../data/CRC/CRC1_cell.labels > CRC1.dot
$ dot -Tpng CRC1.dot -o CRC1.png