Inference of Clonal Copy Number Variation in Single Cells
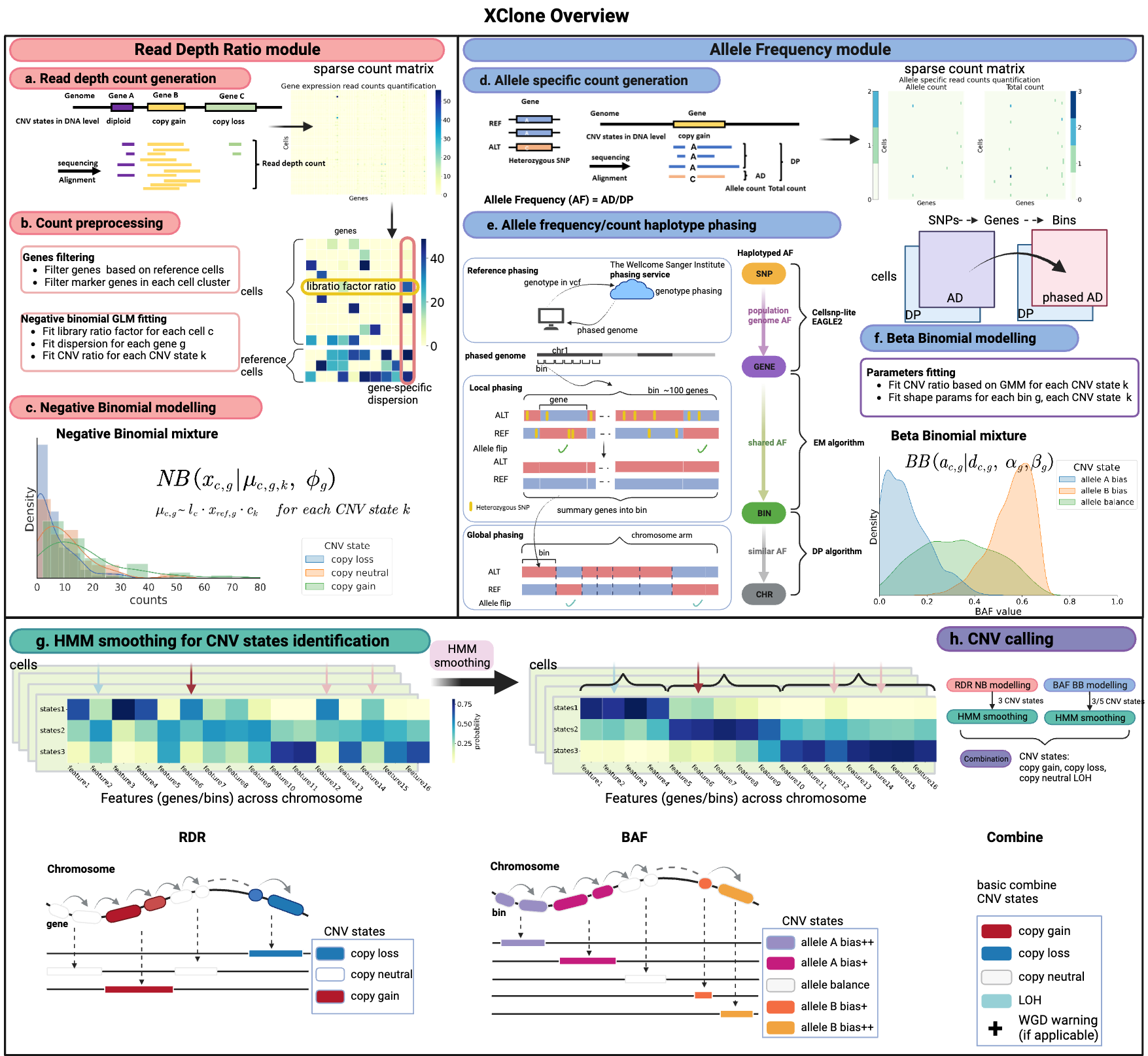
XClone is an algorithm to infer allele- and haplotype-specific copy numbers in individual cells from low-coverage and sparse single-cell RNA sequencing data (e.g., those generated by 10x Genomics, Smart-seq, etc.). The full description of the algorithm and its application on published cancer datasets are described in
[full-text](link here)
The demo of XClone and results on the 3 processed cancer datasets are available at [xclone-data](https://github.com/Rongtingting/xclone-data)
Please frequently read Development and keep software up to date since XClone is being updated and improved frequently at this stage.
XClone requires Python 3.7 or later. We recommend to use Anaconda environment for version control and to avoid potential conflicts:
conda create -n xclone python=3.7 conda activate xclone
XClone package can be conveniently installed via PyPI:
pip install xclone
or directly from GitHub repository (for development version):
pip install git+https://github.com/single-cell-genetics/XClone
xcltk is a toolkit for XClone preprocessing. xcltk is avaliable through pypi. To install, type the following command line, and add -U for upgrading:
pip install -U xcltk
Alternatively, you can install from this GitHub repository for latest (often development) version by following command line:
pip install -U git+https://github.com/hxj5/xcltk