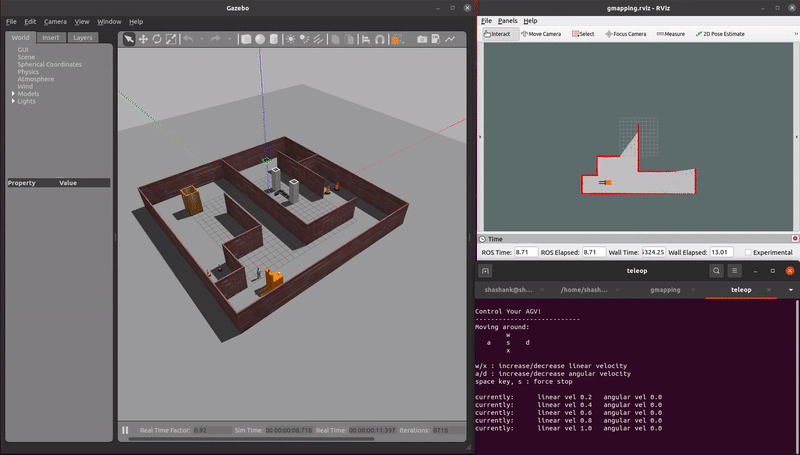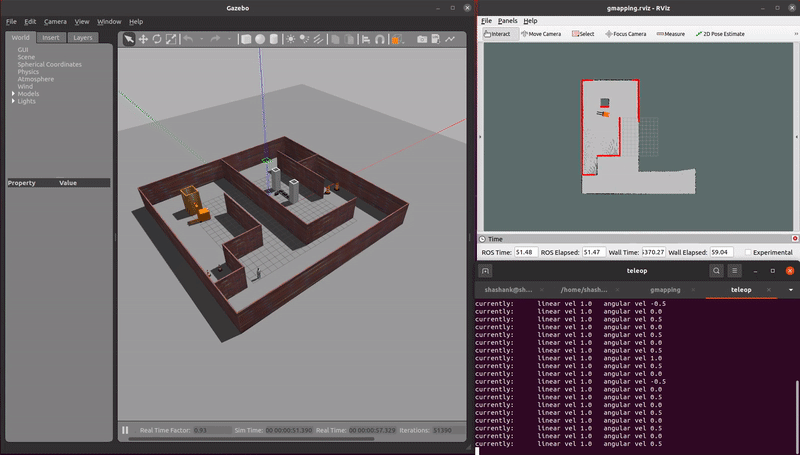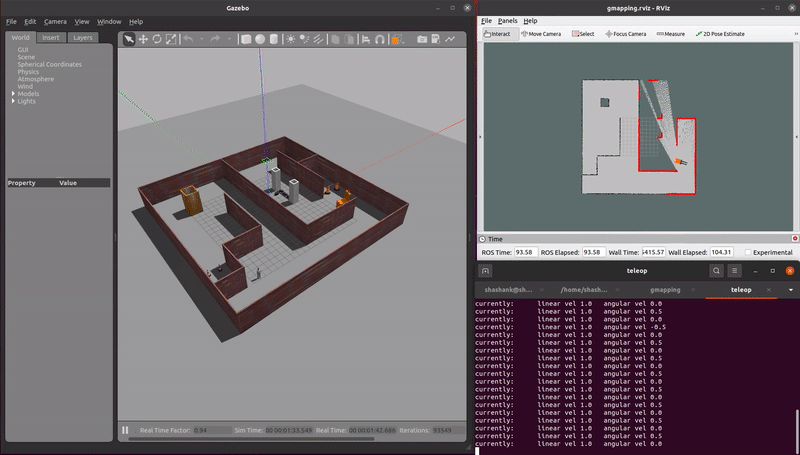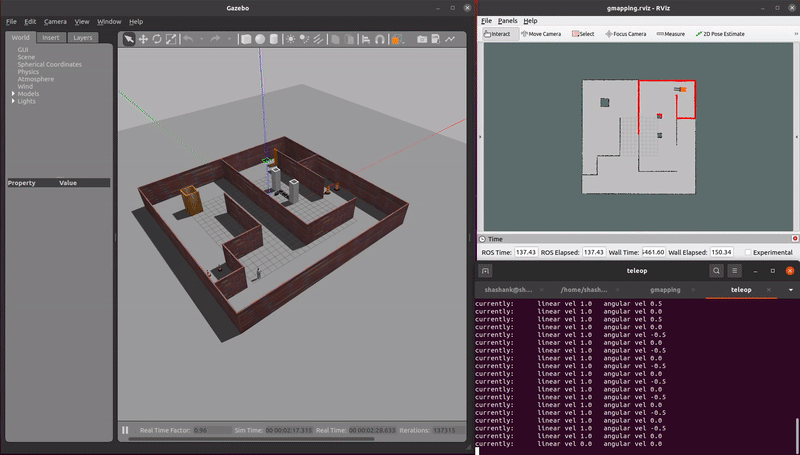
This repo is a ROS pacakge which simulates AGVs and AMRs in warehouse enviromnents. Multiple localization, mapping, and navigation algorithms are tested using these virtual simulations.
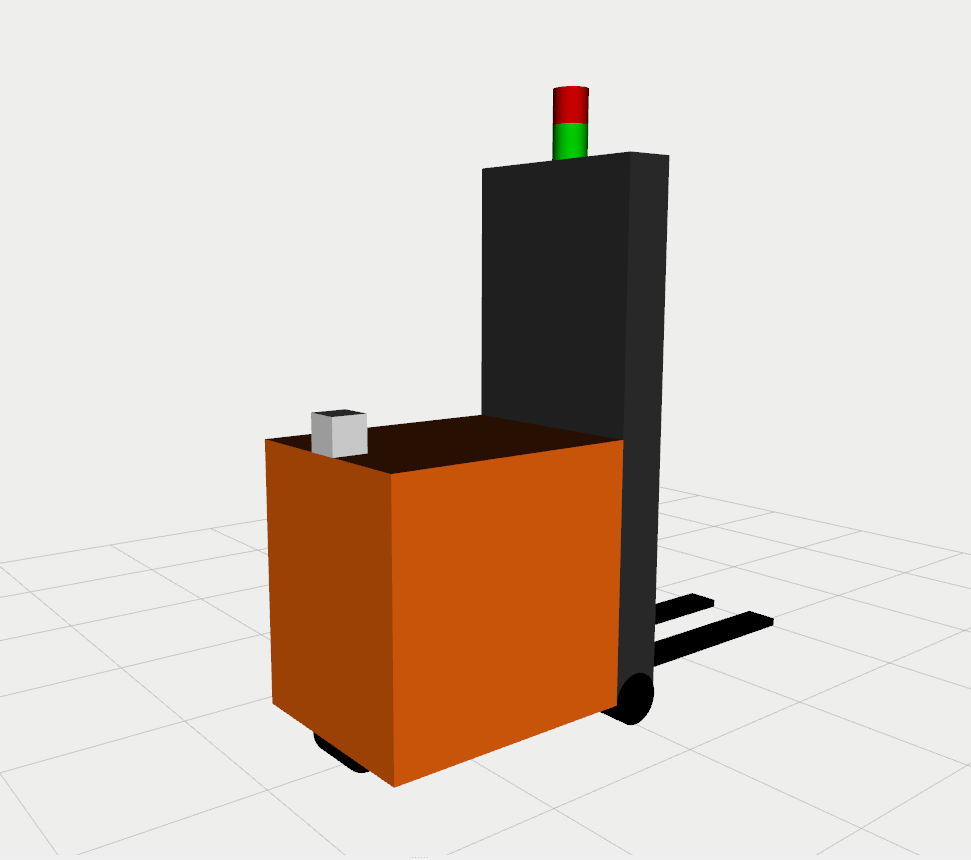
This repo includes urdf files for AGV and AMR, equipped with lidars and cameras as shown below
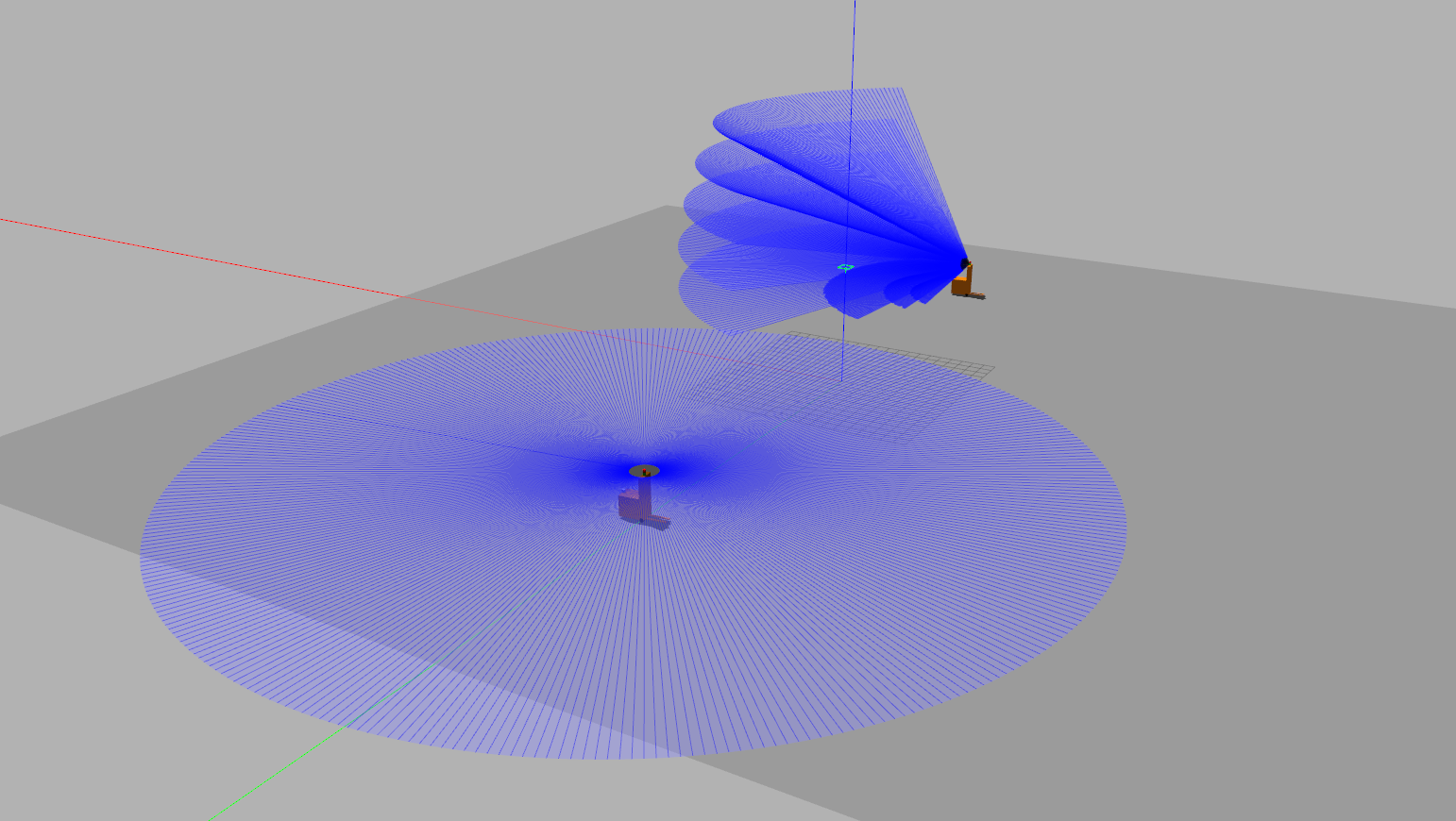
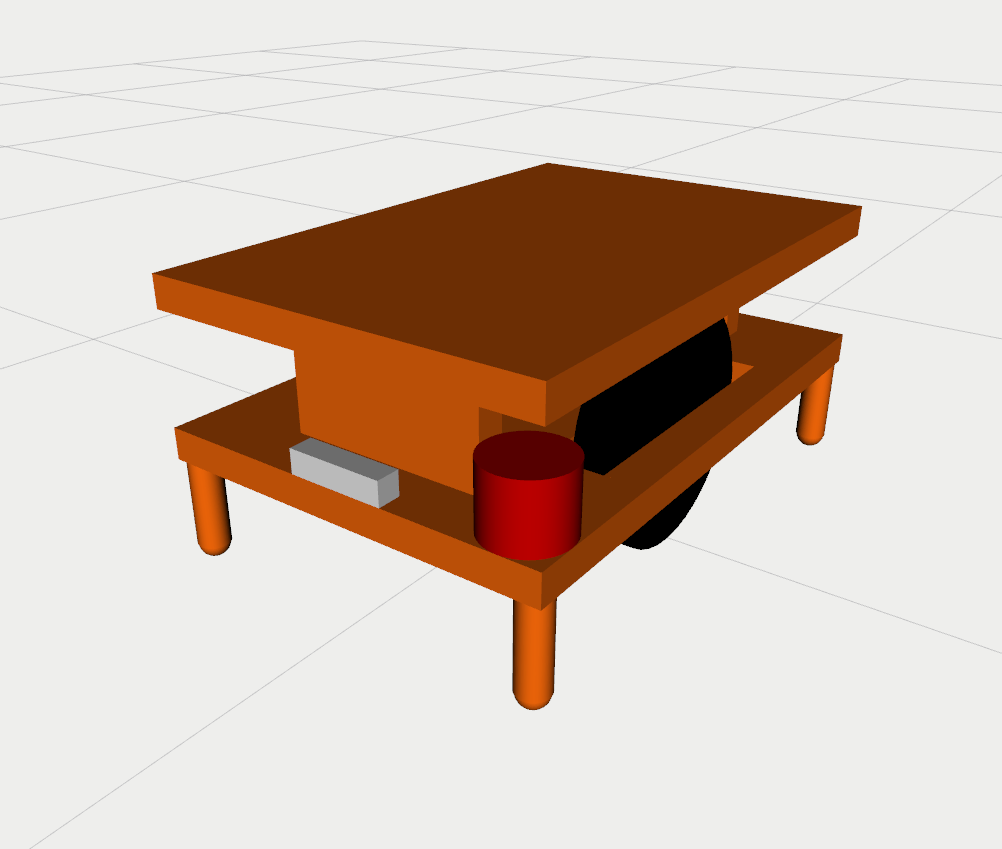
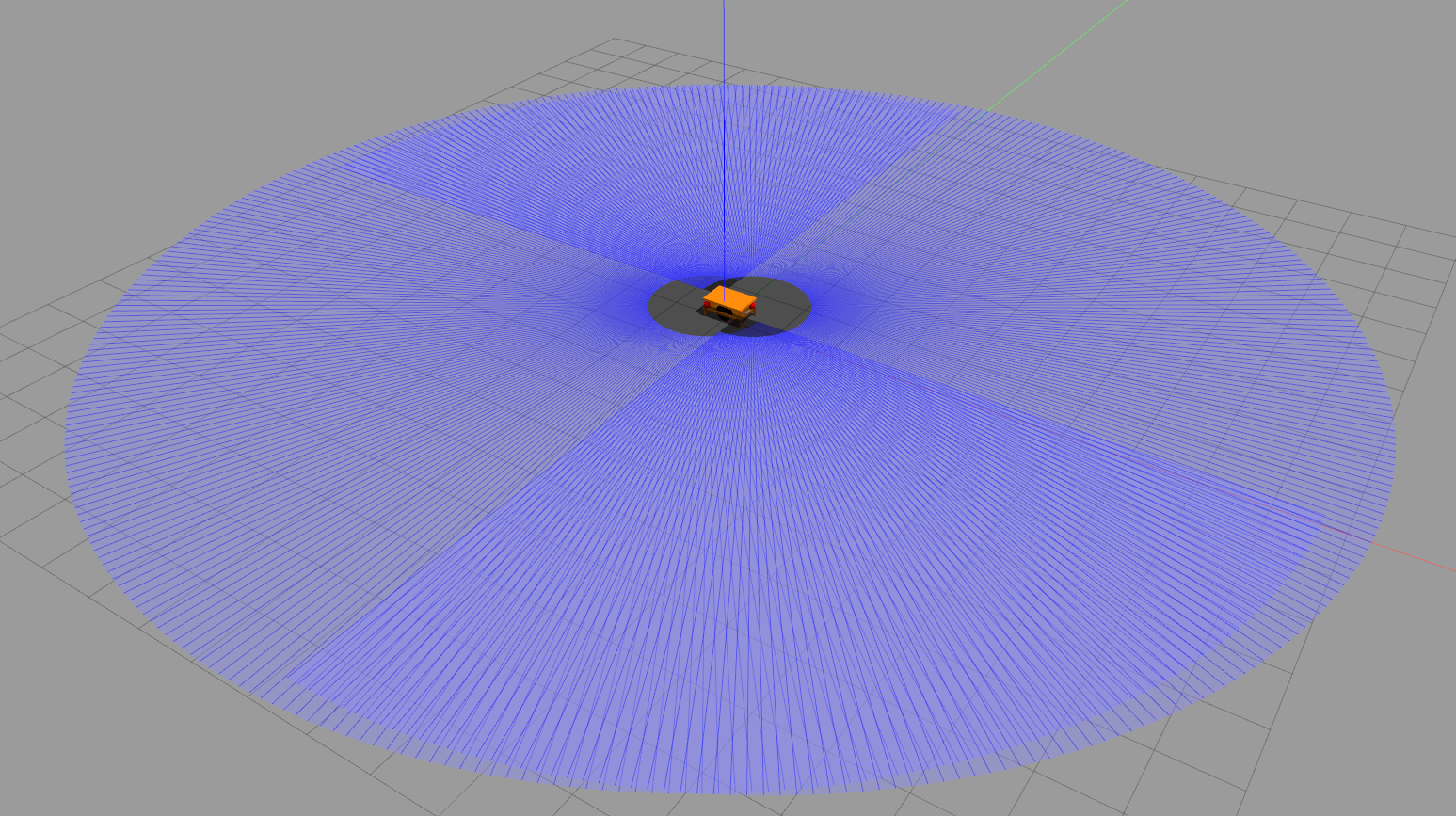
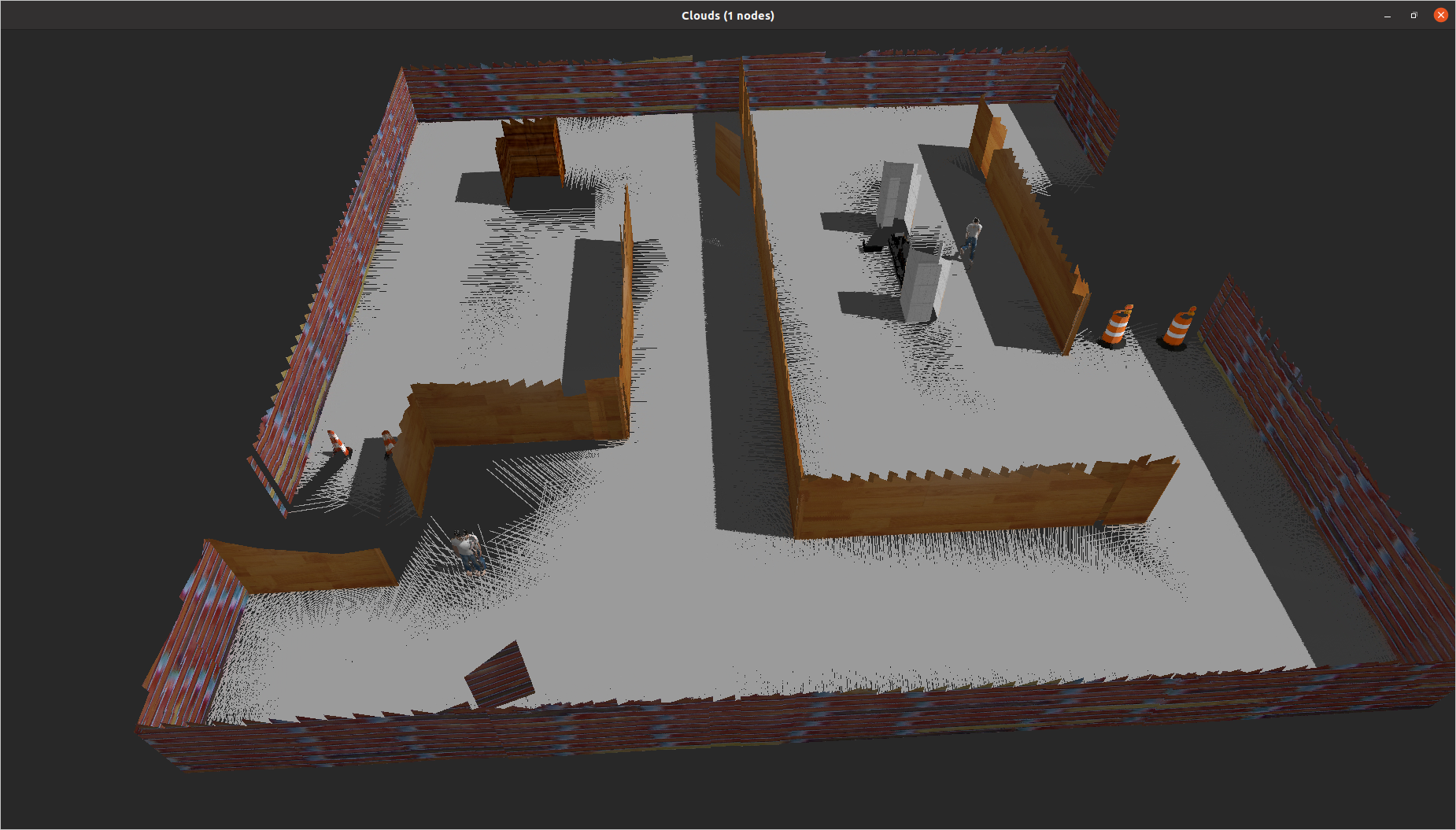
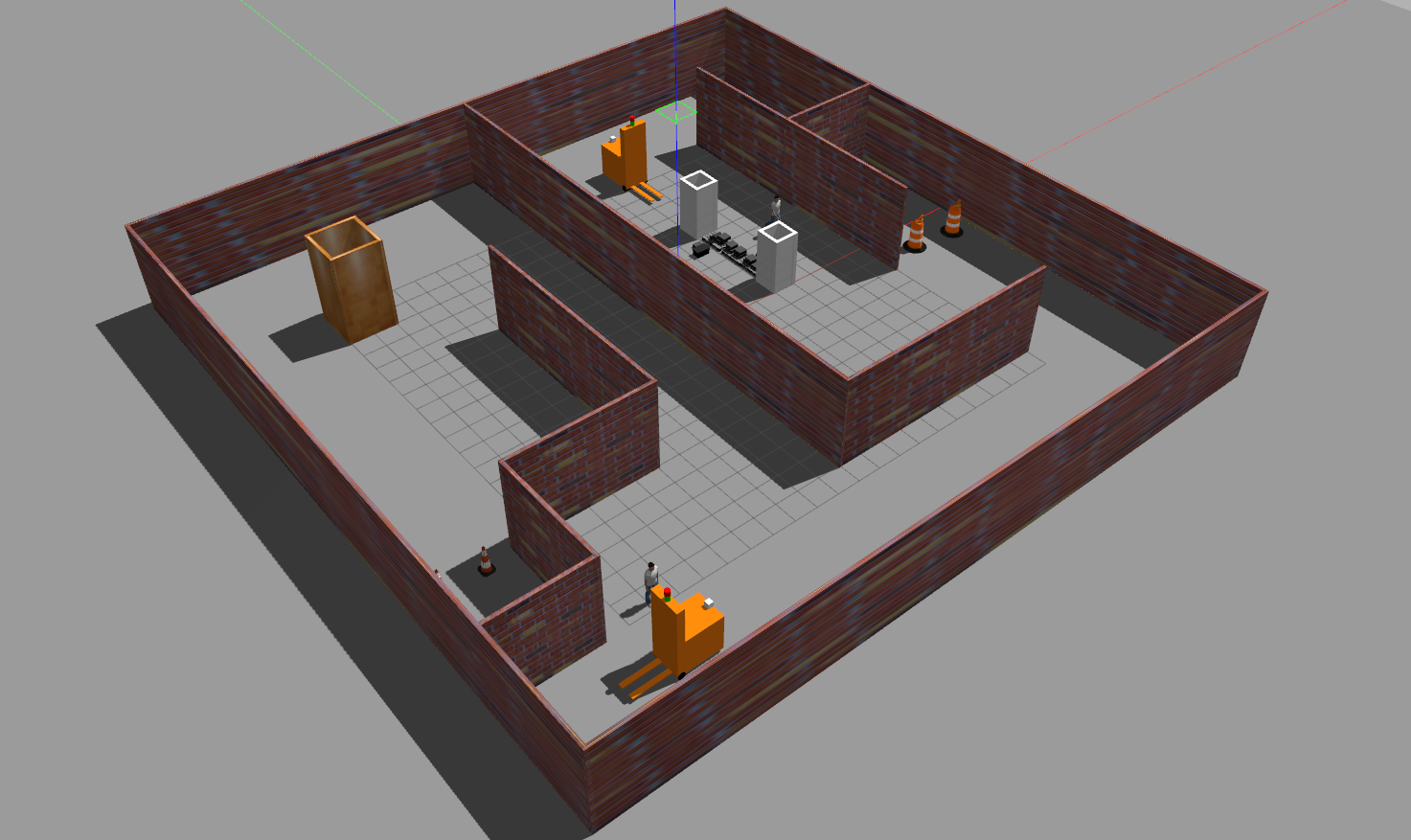
This package also includes Gazebo worlds representing factory environments are shown below

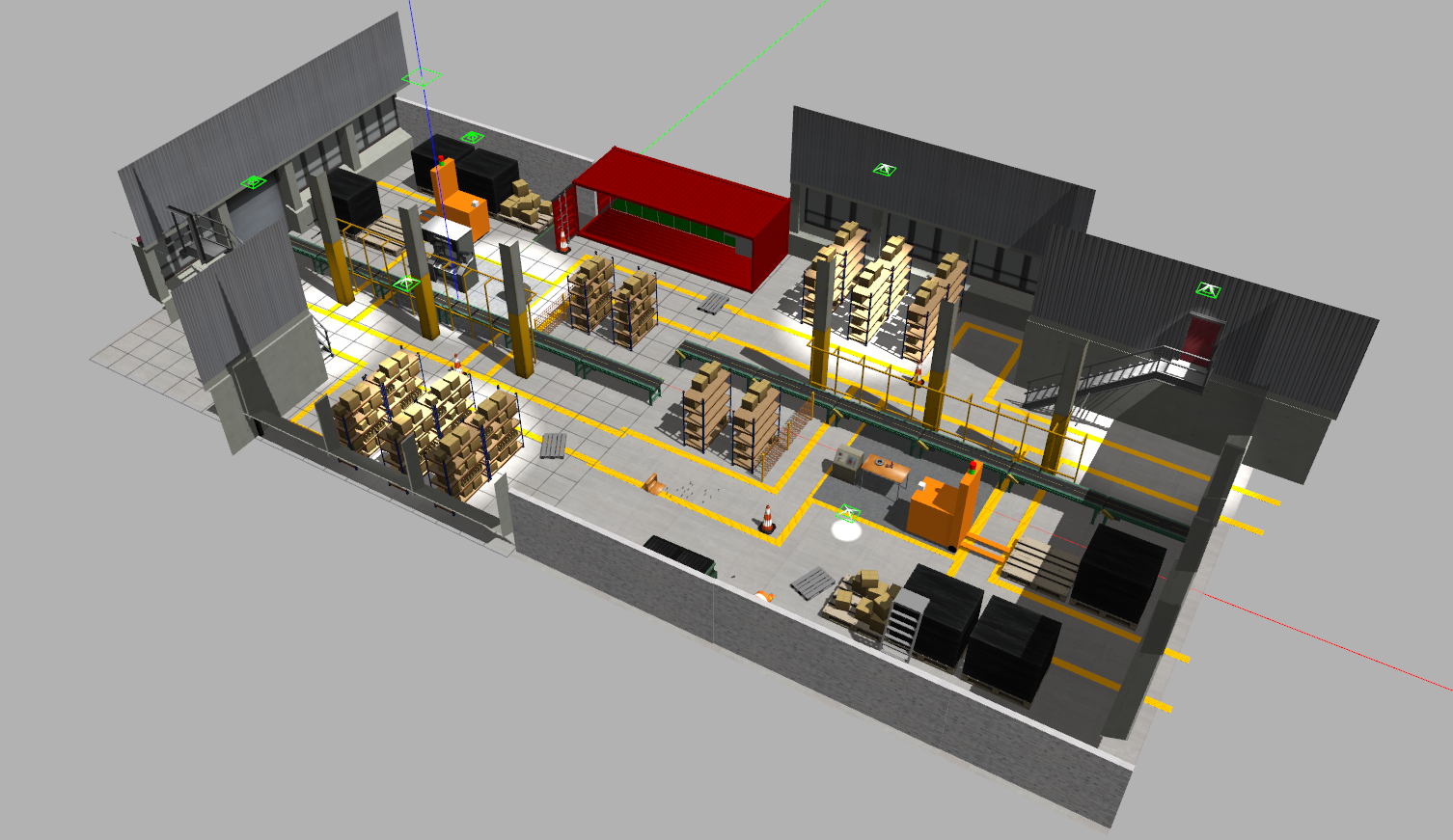
The repo included launch files for multiple demo:
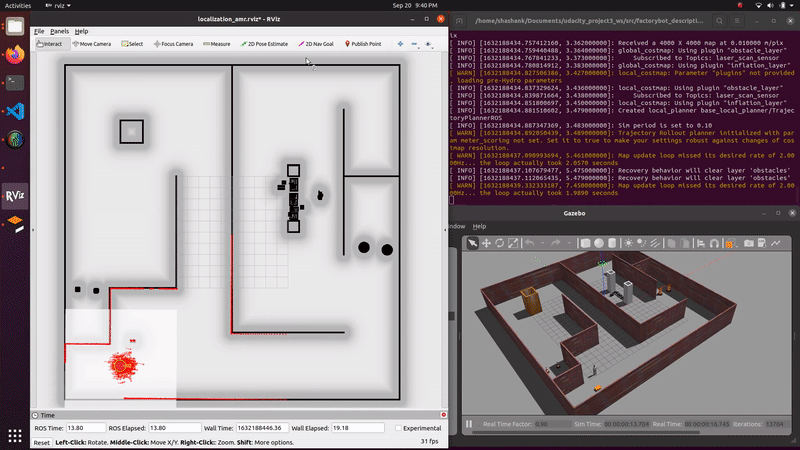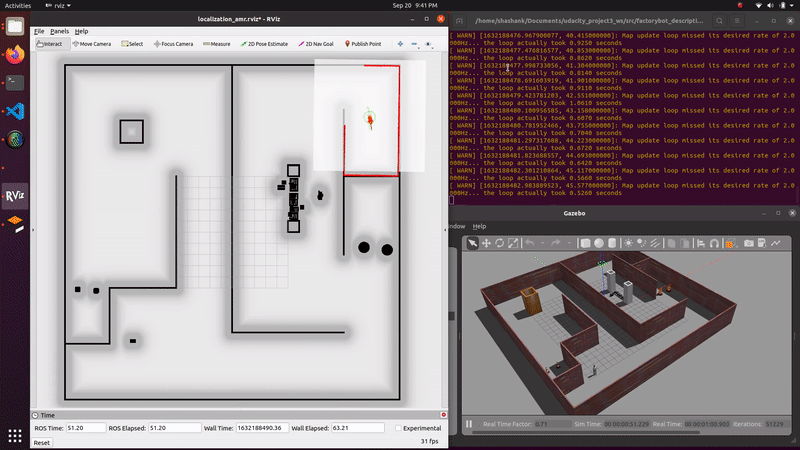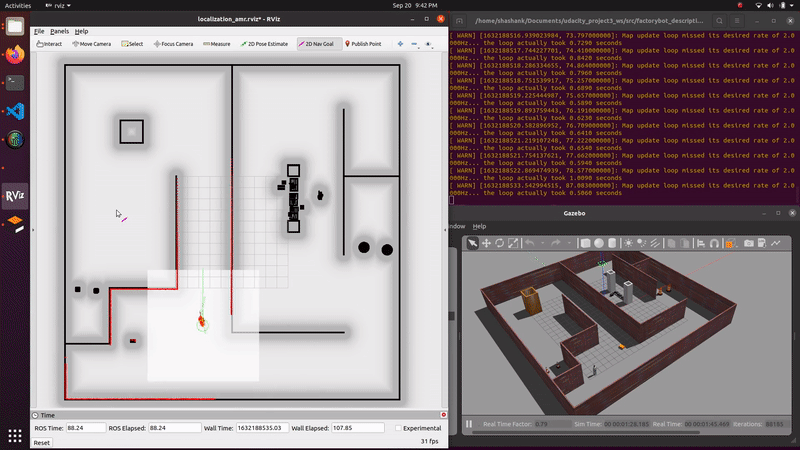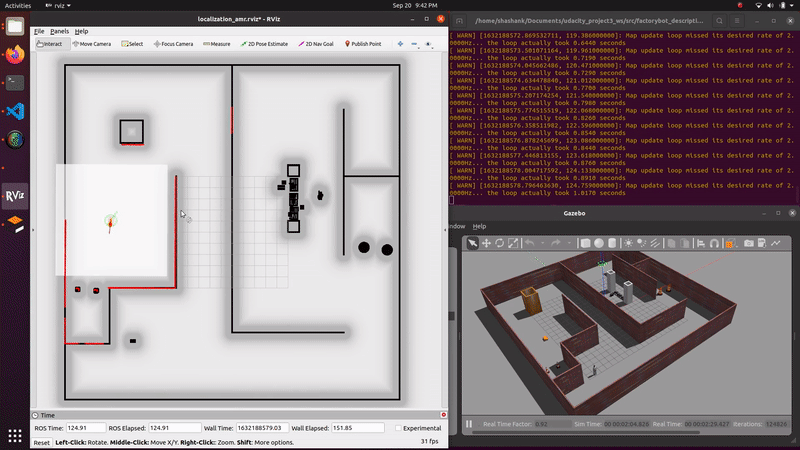
demo_mapping_gmapping.launch: Manually move an AGV through a virtual environment and create an occupancy grid map. Mapping is done using gmapping. Only a 2D lidar sensor is used.demo_localization_amcl_teleop.launch: Manually move an AMR through a previously mapped virtual environment while localizing. Localization is done using AMCL. Only a 2D lidar sensor is used.demo_localization_amcl_nav.launch: Autonomously move an AMR through a previously mapped virtual environment while localizing and path planning. Path planning is done using move_base and localization is done using AMCL. Only a 2D lidar is used.
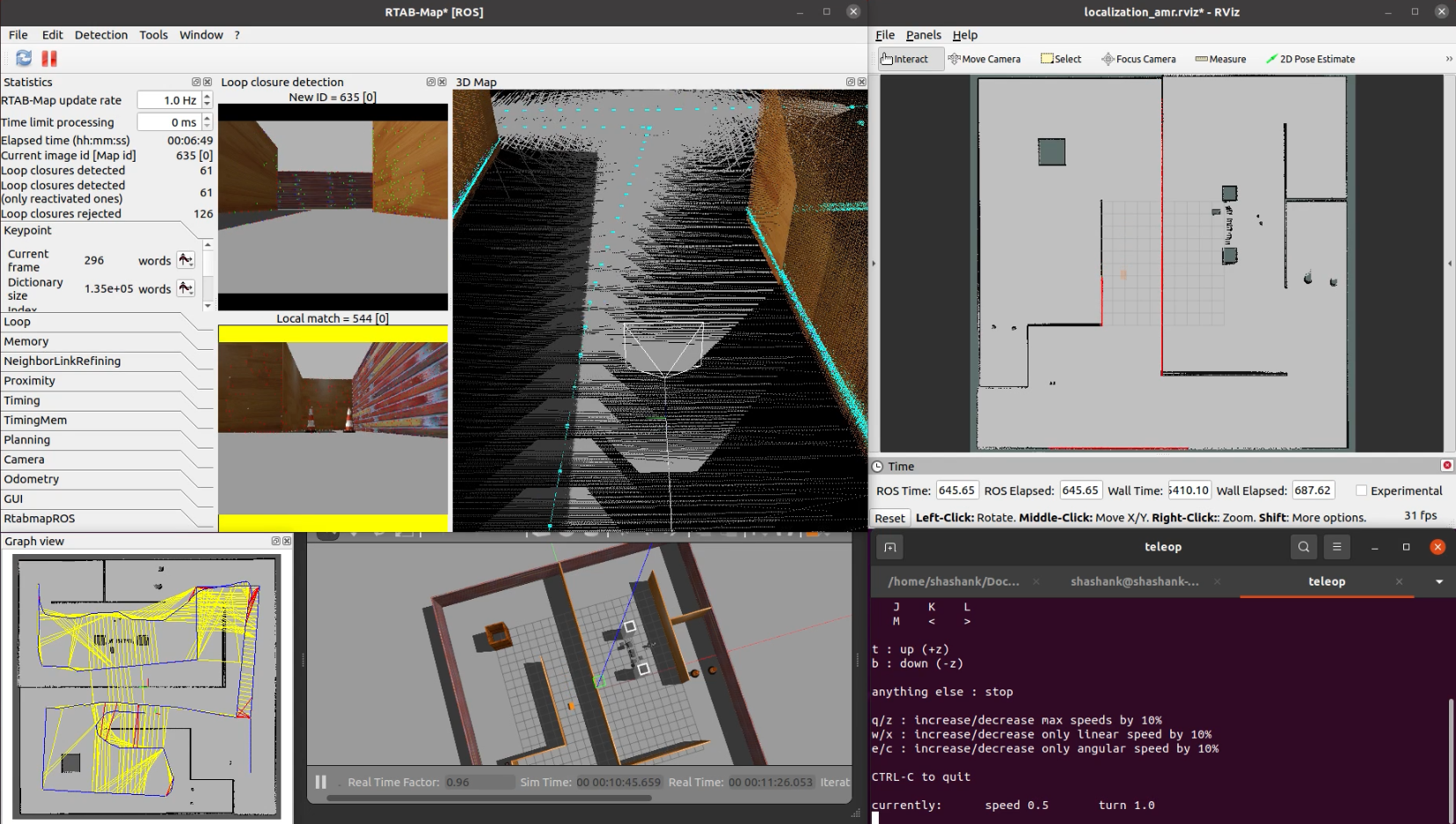
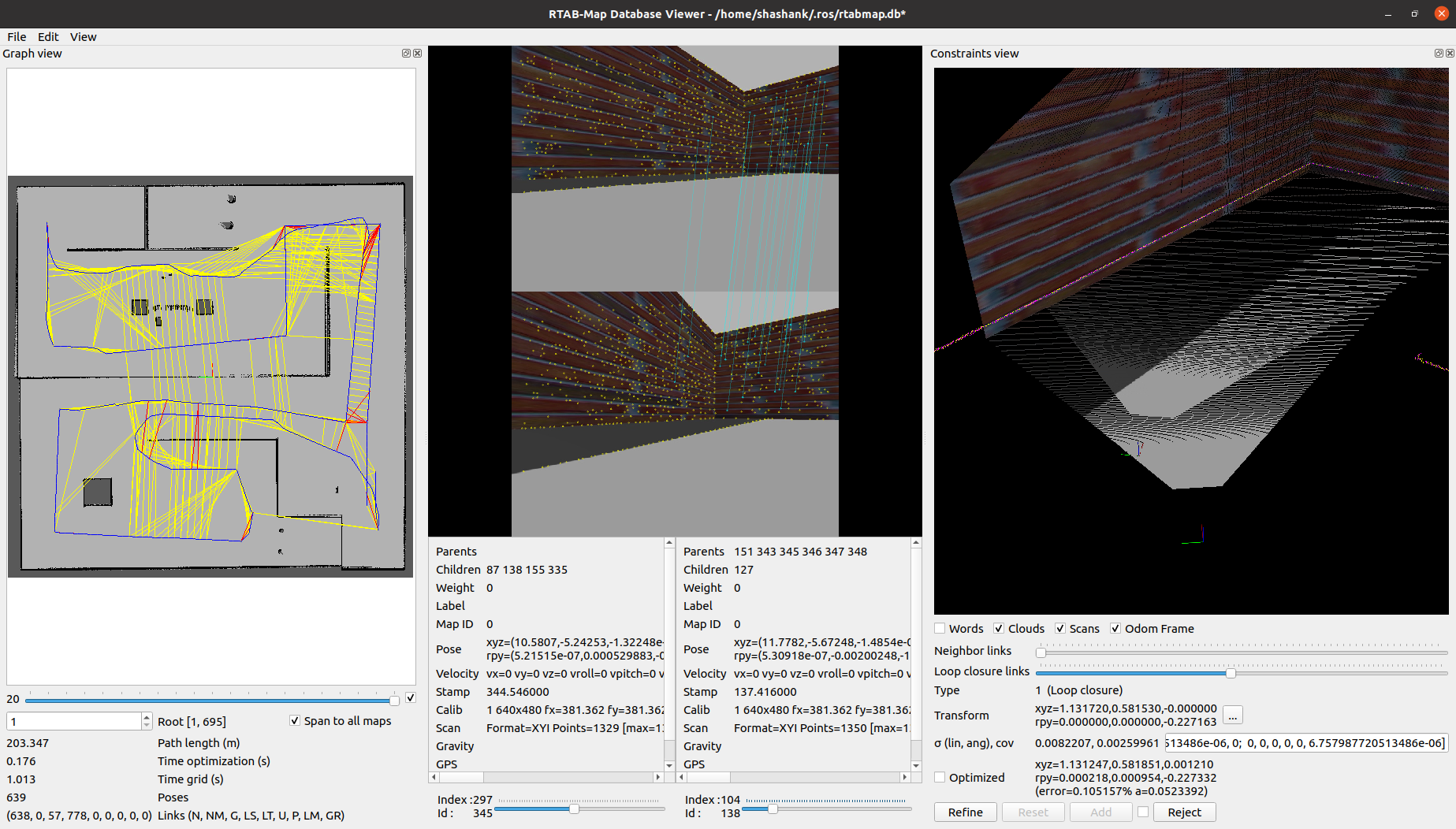
demo_mapping_rtabmap.launch: Manually move an AMR through a virtual environment and create a loop-closed 3D graph map using RTAB-Map. A 3D camera sensor with a 2D lidar sensor is used.demo_localization_rtabmap.launch: Manually move an AMR through a previously mapped virtual environment and localize using RTAB-Map. A 3D camera sensor with a 2D lidar sensor is used.
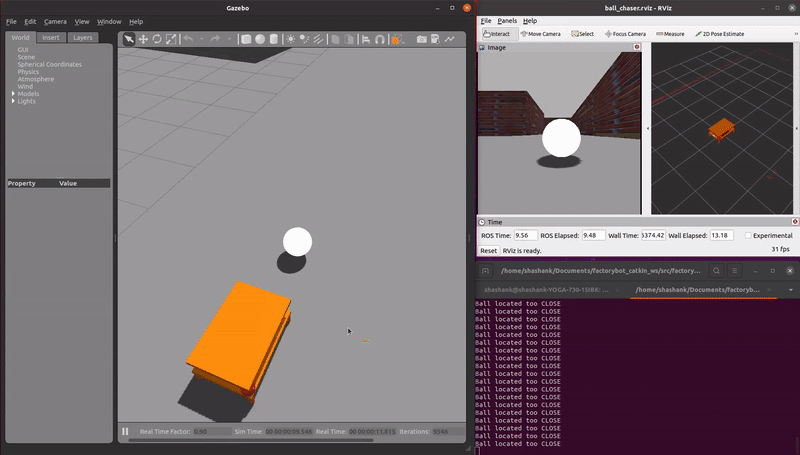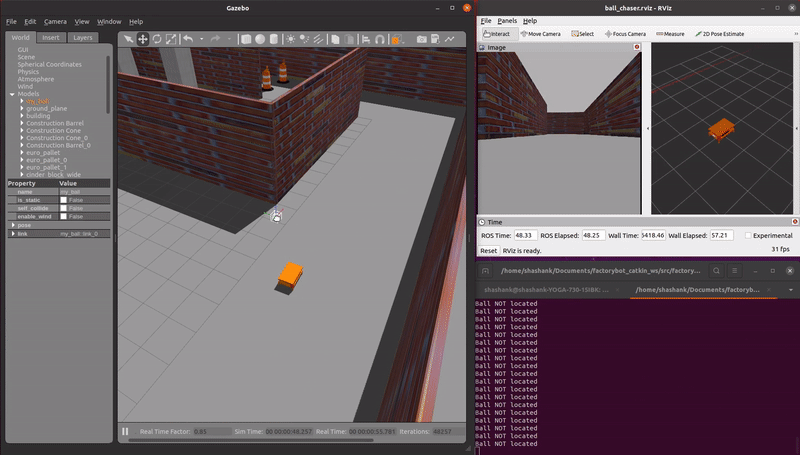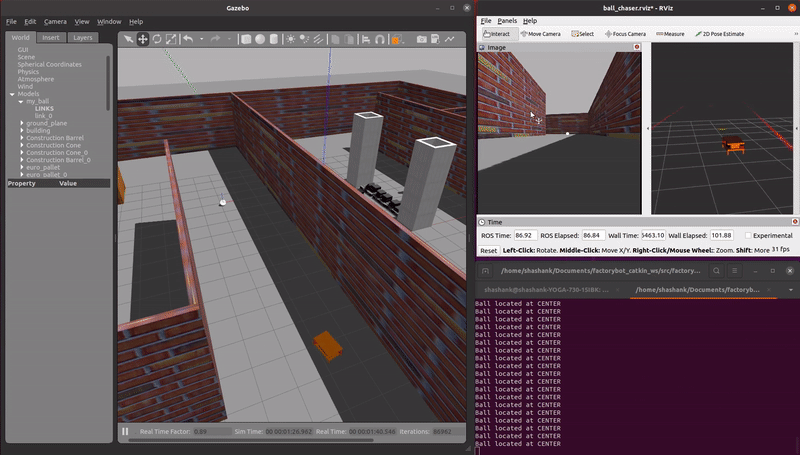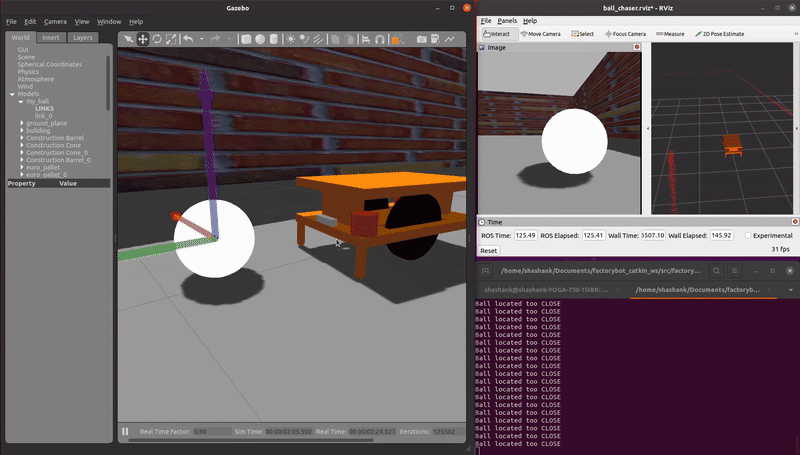
demo_ball_chasing.launch: An AMR autonomously follows a reflective ball target as the ball moves through the virtual environment. A RGB camera sensor is used.
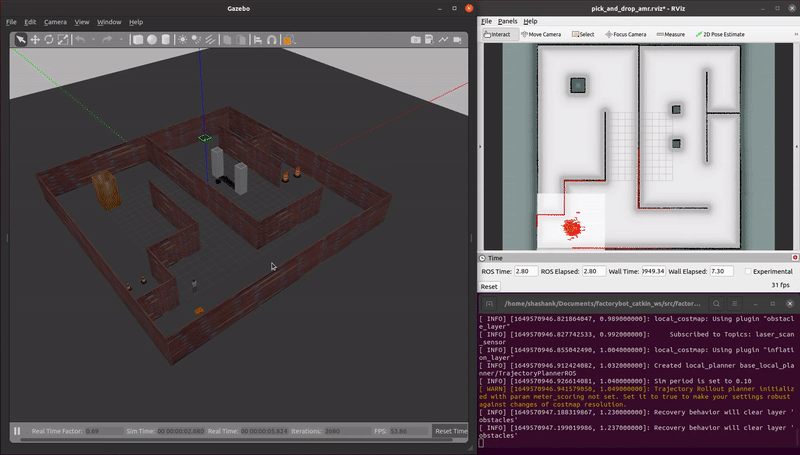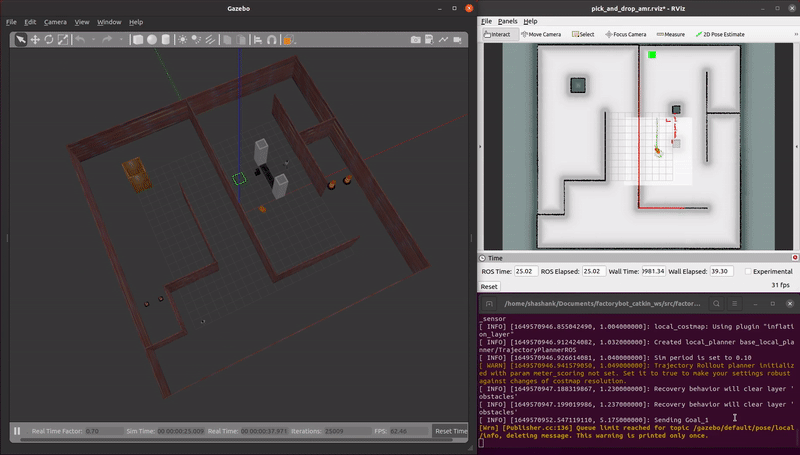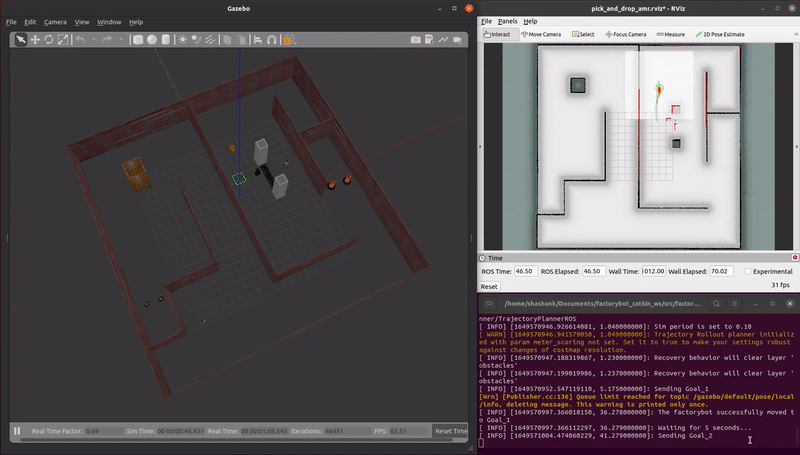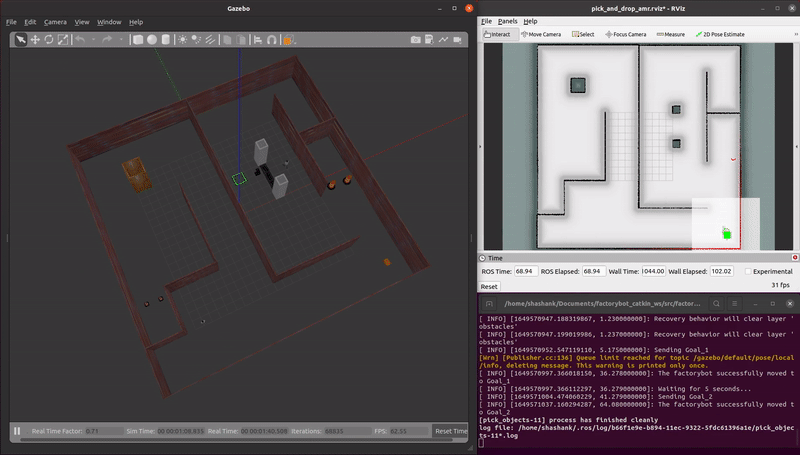
demo_pick_and_place.launch: An AMR autonomously completes a sequence movements to simulate a payload pick and place operation.
Videos for each demo are available here: https://github.com/ssharma1991/factorybot/tree/main/videos
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver 'hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80' --recv-key C1CF6E31E6BADE8868B172B4F42ED6FBAB17C654
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full
echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
sudo apt install ros-noetic-gmapping ros-noetic-velodyne-gazebo-plugins
mkdir -p factorybot_catkin_ws/src
cd factorybot_catkin_ws/src
git clone git@github.com:ssharma1991/factorybot.git
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch factorybot demo_mapping_gmapping.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_localization_amcl_teleop.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_localization_amcl_nav.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_mapping_rtabmap.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_localization_rtabmap.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_ball_chasing.launch
roslaunch factorybot demo_pick_and_place.launch
Gazebo uses many environment variables to locate files. These variables can be edited if the user wants to use additional files. Some examples are as follows
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=/home/user/catkin_ws/src/factorybot/factorybot_gazebo/model:$GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH
export GAZEBO_RESOURCE_PATH=/home/user/catkin_ws/src/factorybot/factorybot_gazebo/world:$GAZEBO_RESOURCE_PATH
export GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH=/home/user/catkin_ws/build:$GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH
Check if the paths were set correctly using env|grep -i gazebo
If previous instances of gzserver have not ended gracefully, the command might not work. Use killall -9 gzserver and try again.