A project for data analysis of Spotify usage, completely built with Docker.
The project integrates:
- Python, to make requests to the Spotify API through Spotipy
- MySQL, to store the data collected.
- Metabase, to visualize the data and create dashboards.
- Adminer, a tool for database debugging.
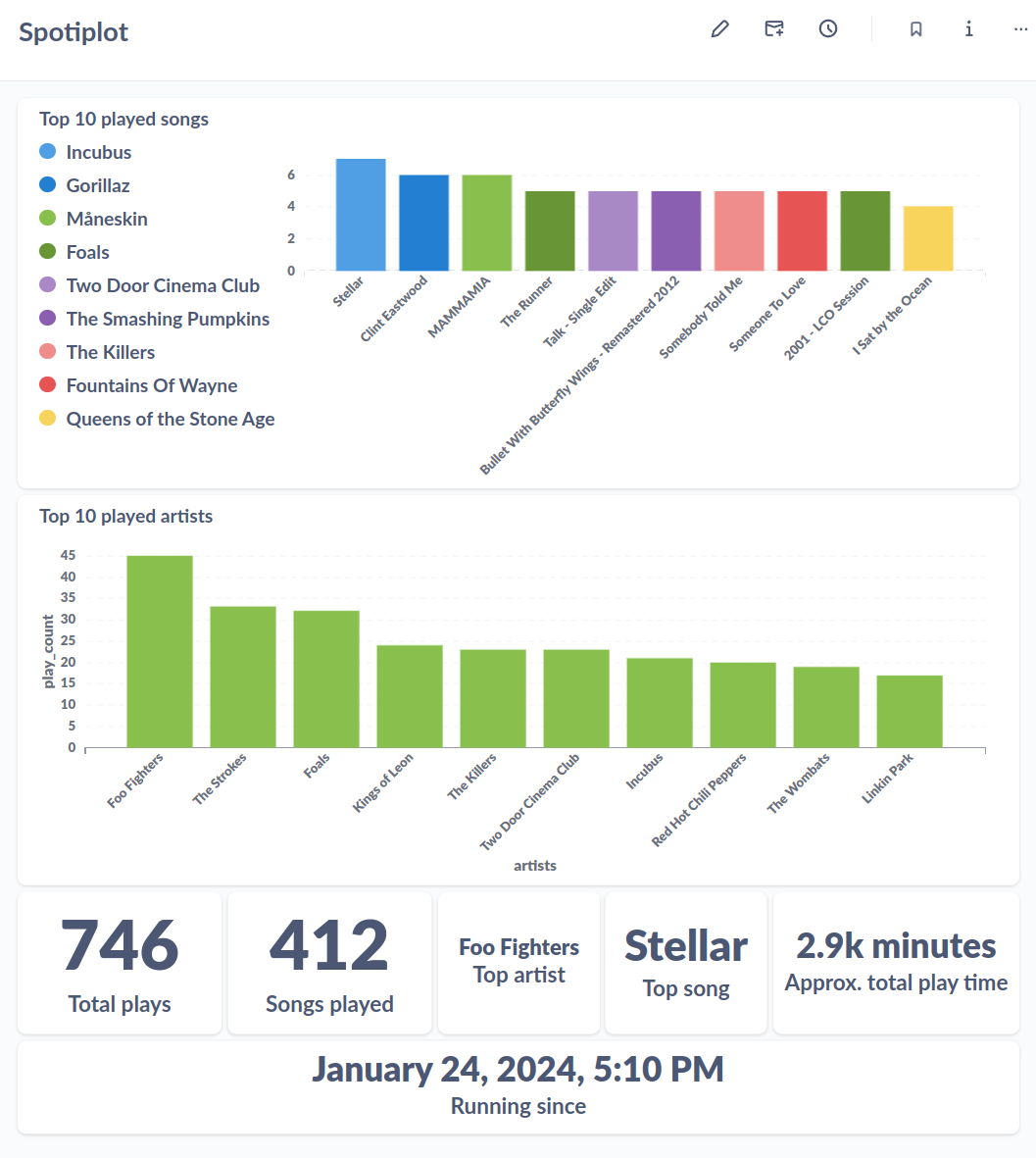
Here is an example of a possible dashboard:
A machine running Docker and Docker compose, which can run constantly. This can be either an online instance or a local machine (e.g., Raspberry Pi)
Note: Metabase requires the architecture amd64. It is possible to run the back-end services (Spotify monitor, MySQL database) in a armv8 unit (e.g., Raspberry Pi 3), and then run Metabase in a separate amd64 machine.
Before running this code, create a file named.env , and update MYSQL_PASSWORD and MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD passwords as you prefer. A default file named default.env is included in the project, and can be used as a reference:
MYSQL_PASSWORD: sample_password
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: sample_root_passwordTo use Spotiplot, it is necessary to create an application on your Spotify Developer Dashboard. You can create your own app name, description and website. Set the Redirect URI to 'http://0.0.0.0:8083', as it is the value expected by the Docker container. If this is set to a different value, modify the docker compose and the authenticator script accordingly.
It will also be necessary to create a file to store the Spotify credentials: app/spotiplot.env. The file should be populated with the information available on your personal developer dashboard. A default file named default_spotiplot.env is included in the project (inside the app folder), and can be used as a reference:
credentials:
client_id: '<client_id>'
client_secret: '<client_secret>'
redirect_uri: 'http://0.0.0.0:8083'The docker image for the spotiplot monitor contains two scripts:
- One for authenticating with Spotify, generating the access tokens and storing them as cache inside the container.
- One for monitoring the songs that are played.
The image should be built and executed before the docker compose. This will allow the authentication procedure, which requires user input, to retrieve the necessary tokens.
cd <path_to_spotiplot>
docker build -t spotiplot_monitor app/.
docker run -it -p 8083:8083 -v $(pwd)/app/cache:/app/cache spotiplot_monitorWhen the image is executed, it will provide an URL that should be copied into a browser. Authenticate with Spotify on this browser session, and then copy the resulting URL back into the docker container. This will store the necessary tokens.
Once the tokens are saved, it is possible to start the system through the command:
docker compose upMetabase is a powerful and user-friendly tool to generate graphs based on data stored in a database. On top of that, it is easily integrated into this project's docker architecture.
Through Metabase, it is possible to create several SQL queries, and combine their results in a dashboard. This dashboard will then automatically update when the data inside the database is updated.
On its free tier, Metabase does not support Serialization, so it is not possible to share dashboards. Users are then invited to create and customize their own dashboard as they prefer.
It is possible to run Metabase along with the monitor and the database in a server, and it is also possible to run it locally in your machine while connecting to the monitor and database containers running in a different machine.
First, ensure that you have the monitor and database containers running:
cd spotiplot
docker compose upOnce this is done, start the Metabase container (from Metabase Dockerhub):
docker run -p 3000:3000 --name spotiplot_metabase metabase/metabaseThen, proceed to the local Metabase page and perform the following:
- Choose your preferred language
- Create your credentials (it is not necessary to insert personal data). Note down the e-mail/password combination for future logins.
- Configure your connection to the database:
- Select MySQL as your database
- Create your own display name (e.g. Spotiplot)
- Enter the IP address of the machine running the other containers (if locally enter 0.0.0.0)
- Enter the MySQL port (default: 3306)
- Enter
spotiplotas the database name - Enter
spotiplotas the username - Enter the mysql credential as defined in your .env file
- Finish your setup about data collection and the Metabase newsletter as you want (all this is performed by Metabase, Spotiplot does not store any of your data).
- Select "Take me to Metabase"
Once in Metabase's main panel, it is possible to perform SQL queries and plot their results, and also create dashboard to aggregate multiple queries. All of this is done through the blue + New button on the top-right corner.
Metabase provides a rich getting started page with instructions on how to work with your data.
In short, first create a dashboard, and then create multiple SQL queries based on the data that you want to analyse. When saving the query, select your dashboard to have it linked automatically. Finally, proceed to the dashboard to customize it's layout as preferred.
Some of the queries used for this dashboard can be found in the metabase folder
After the initial setup, it is interesting to commit your working container to resume its operation from there instead of starting from scratch. To do so, it is necessary to create a new image based on the current state of your container:
First, get the id of your running container:
docker container lsThen, commit your changes to a new image:
docker commit <container_id> metabase_spotiplotNow, docker will have an image saved with the name metabase_spotiplot. Check with the following command:
docker image lsTo start a container based on the committed Metabase image, simply run:
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 spotiplot_metabaseEnsure that your container will have access to the database to have everything working smoothly.
It is possible to integrate the metabase container into the docker compose, depending on the use case. For example, if running on an online server, this would allow your metabase instance to be accessible from anywhere through its public IP.
To achieve this, simply add the Metabase service by copying the lines below to the list of services inside docker-compose.yaml:
metabase:
image: spotiplot_metabase
ports:
- 3000:3000
networks:
- spotiplot-networkAdminer is included into the docker compose image to enable visualization of the content stored into the database (for debug purposes).
To log into Adminer:
- Make sure the docker compose environment is up.
- Go to the adminer login page
- Set server name to the MySQL service name
mysql - Set username to spotiplot
- Enter the password defined into the
MYSQL_PASSWORDvariable