This is the GitHub repository for the paper. The pre-print of the paper is on bioRxiv at DOI 10.1101/437277.
Single-cell transcriptomics and full-length virus sequencing of single influenza-infected A549 cells that have been enriched for IFN+ cells.
A549 cells were infected with A/WSN/1933 influenza virus at a relatively low MOI. These A549 cells contained a sortable marker under an IFN promoter. At 13-hours post-infection, the cells were sorted to enrich for IFN+ ones. These enriched IFN+ cells were mixed with some of the ones that did not sort as IFN+, and they were sequenced on the Chromium 10X platform.
A modest number of non-infected MDCK (canine) cells were also included to enable assessment of mRNA leakage and lsysis.
The virus used was a mix of wildtype and virus with synonymous "barcodes" near the 3' end to help enable identification of co-infection, similar to the approach in Russell et al (2018). But whereas in that experiment that viral genomes were barcoded only at the end that gives the 3' end of the mRNA, in this experiment they were barcoded at both ends.
The viral mRNA in the IFN-enriched sample was then amplified by semi-specific PCR and sequenced using PacBio long-read technologies to obtain full length sequences for the viral genomes.
The 10X transcriptomic data and the full-length viral gene sequences were analyzed to determine characteristics of infections that triggered IFN production.
Most of the analysis is performed by a set of Jupyter notebooks that contain detailed descriptions of the results.
The entire analysis can be run by executing the Snakemake file Snakefile with:
snakemake
To run this command on the Fred Hutch computing cluster across multiple nodes, execute the file run_snakemake_Hutch_cluster.sbatch with:
sbatch run_snakemake_Hutch_cluster.sbatch
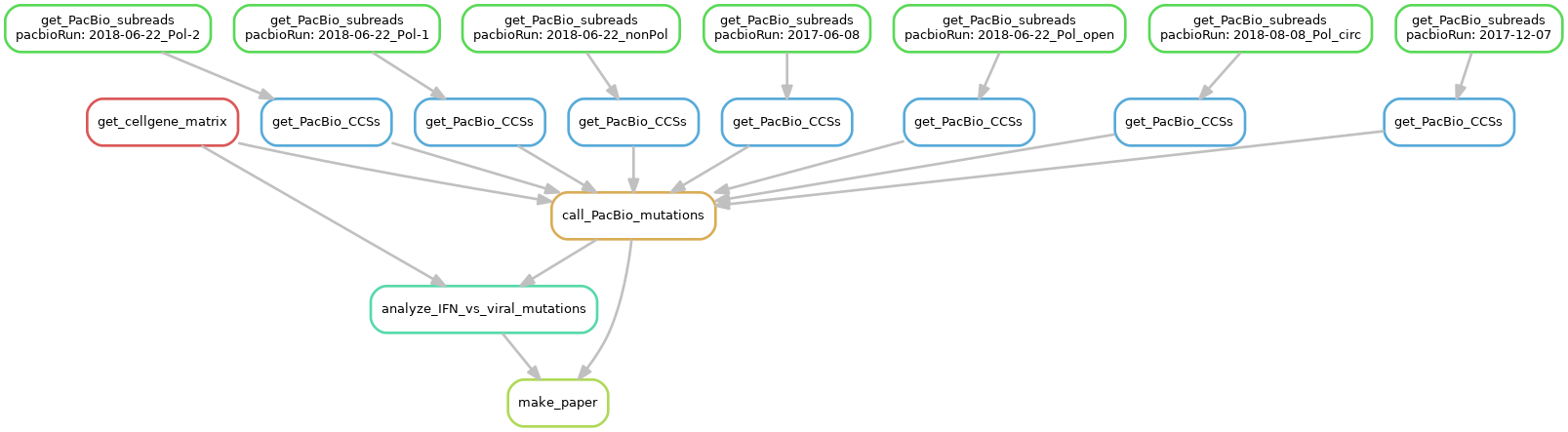
Here is a visualization of the pipeline in Snakefile created in the file workflow.png with:
snakemake --forceall --dag | dot -Tpng > workflow.png
Results are written to a ./results/ subdirectory, which is not included as part of this GitHub repository.
The figures and the final paper describing the findings and conclusions are in the ./paper/ subdirectory.
Note that the automatically generated figures required for the paper are included as part of this repository, so if you simply run snakemake it will not re-run the full analysis since the required figures already exist.
If you want to delete the figures and re-run the analysis from the top, first run:
snakemake --delete-all-output
which deletes the existing output.
The analysis involves the following major steps:
The Python notebook align_and_annotate.ipynb demultiplexes and aligns the reads, annotates the flu synonymous barcodes, and generates the cell-gene matrix.
It requires installation of cellranger, which performs the demultiplexing and alignment.
It also uses custom Python and bash scripts found in the ./scripts/ subdirectory, and requires installation of a few common Python modules.
The notebook describes the software versions used.
The end result of this notebook is an annotated cell-gene matrix that is stored in ./results/cellgenecounts/.
There are separate matrices for the human cells with flu reads (humanplusflu) and the canine reads (canine):
results/cellgenecounts/merged_canine_cells.tsv
results/cellgenecounts/merged_canine_genes.tsv
results/cellgenecounts/merged_canine_matrix.mtx
results/cellgenecounts/merged_humanplusflu_cells.tsv
results/cellgenecounts/merged_humanplusflu_genes.tsv
results/cellgenecounts/merged_humanplusflu_matrix.mtx
Snakefile runs the PacBio ccs program to build circular consensus sequences.
These are placed in the directory ./results/pacbio/ccs/.
The Python notebook pacbio_analysis.ipynb analyzes the PacBio CCSs to identify mutations present in viruses infecting individual cells. Numerous plots and a detailed analysis are included in this notebook. In addition, the notebook creates an annotated version of the cell descriptor for the cell-gene matrix that contains information about the mutations that can be called by the PacBio sequencing. This is the created file:
results/cellgenecounts/PacBio_annotated_merged_humanplusflu_cells.tsv
The R notebook monocle_analysis.ipynb analyzes the cell-gene matrix to look for viral features associated with IFN induction. The analysis makes substantial use of the Monocle package, and the results are described within the notebook.
The ./paper/ subdirectory contains the LaTex source for the paper and manually created figures. Figures related to the single-cell sequencing are created automatically and placed into this directory.
The ./data/ subdirectory contains input data used by the analysis:
-
./data/PacBio_runs.csv contains a list of the PacBio runs and the locations of their corresponding subreads files on the Hutch computing cluster.
-
The subdirectory ./data/flu_sequences/ contains the influenza genomes for both the wildtype A/WSN/1933 virus and the variants with double synonymous barcodes. See the README in that directory for more details.
-
The subdirectory ./data/images/ contains some schematic images used in the Jupyter notebooks.