The Quad Tree Builder and Filter allow one to filter 2D data relative to a response value in a spatially aware manner. For example, if one has D data and desires to find Q data with high response values - Q < D - instead of selecting the Q data with the highest responses using the Quad Tree Filter, you can choose the Q data with high response values that are distributed across the entire bounded 2D plane. This is very useful when selecting features for camera-based SLAM systems.
This code was written and validated under the following conditions:
- a linux machine running Ubuntu 16.04.1
- gnu 4.9.4
- CUDA 8.0
NOTES:
- The exact structure of the QuadTree is dependent upon the order in which the data are entered
- Given the variable scheduling on GPUS, the same dataset can result in slightly differenct QuadTrees across runs
make clean && make -j6Efficient-CUDA-Implementation-of-Tree-Based-N-Body-Algorithm
CUDA Example Implementation
https://github.com/jlong29/Nbody-Barnes-Hut-CUDA
OpenCL Example Implementation
https://github.com/jlong29/gpu-nbody
The Problem
Regular Codes: control flow is a predictable function of input size
- e.g. Matrix Multiplication
Irregular Codes: control flow is an unpredictable function of input values
- e.g. Trees
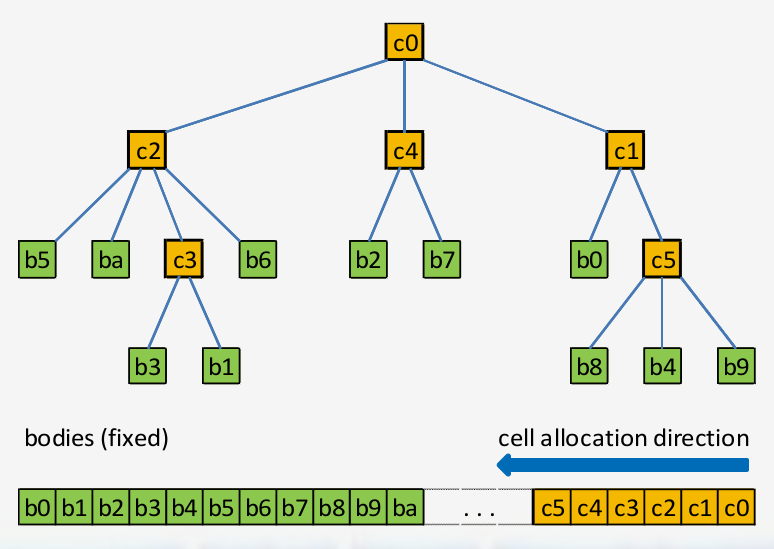
CELLS are in internal nodes in the tree BODIES are leafs
The Tree is stored in a single array
- For N bodies, the bodies are stored from 0...N-1
- The cells are stored from N...Max Nodes
- There is no reason you cannot start allocating cells at N