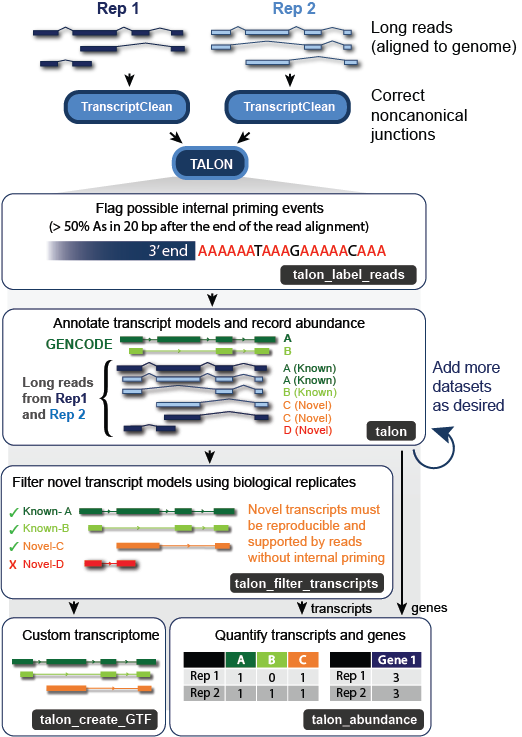
TALON is a Python package for identifying and quantifying known and novel genes/isoforms in long-read transcriptome data sets. TALON is technology-agnostic in that it works from mapped SAM files, allowing data from different sequencing platforms (i.e. PacBio and Oxford Nanopore) to be analyzed side by side.
Reads must be aligned to the reference genome prior to using TALON. We recommend the Minimap2 aligner - please see their GitHub page here for recommended long-read parameters by technology. Please note that TALON requires the SAM MD tag, so Minimap2 should be run with the --MD flag enabled. In principle, you can use any other long-read alignment software provided that an MD tag is generated.
We also recommend correcting the aligned reads with TranscriptClean to fix artifactual noncanonical splice junctions, though this is not strictly necessary for TALON to run.
To learn more about how TALON works, please see our preprint in BioRxiv: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/672931v1
Newer versions of TALON (v4.0+) are designed to be run with Python 3.6+.
To install TALON, simply download the files using Github's "Download ZIP" button, then unzip them in the directory where you would like to store the program. Alternately, you can download a specific version of the program from the Releases tab.
Go to the directory and run pip install .. This will install TALON. You can now run the commands from anywhere.
If the above installation doesn't work, it's likely due to difficulties with MacOS allowing installation of pybedtools. A workaround is to install pybedtools using conda. To do so run conda install -c bioconda pybedtools, then try to pip install . from the TALON directory again.
NOTE: Talon versions 4.2 and lower are not installable. Check the README of those releases to see how you can run the scripts from the install directory, or visit the wiki here.
For a small, self-contained example with all necessary files included, see https://github.com/mortazavilab/TALON/tree/master/example
Current long-read platforms that rely on poly-(A) selection are prone to internal priming artifacts. These occur when the oligo-dT primer binds off-target to A-rich sequences inside an RNA transcript rather than at the end. Therefore, we recommend running the talon_label_reads utility on each of your SAM files separately to record the fraction of As in the n-sized window immediately following each read alignment (reference genome sequence). The default n value is 20 bp, but you can adjust this to match the length of the T sequence in your primer if desired. The output of talon_label_reads is a SAM file with the fraction As recorded in the fA:f custom SAM tag. Non-primary alignments are omitted. This SAM file can now be used as your input to the TALON annotator.
Usage: talon_label_reads [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--f=SAM_FILE SAM file of transcripts
--g=GENOME_FILE Reference genome fasta file
--t=THREADS Number of threads to run
--ar=FRACA_RANGE_SIZE
Size of post-transcript interval to compute fraction
As on. Default = 20
--tmpDir=TMP_DIR Path to directory for tmp files. Default =
tmp_label_reads
--deleteTmp If this option is set, the temporary directory
generated by the program will be removed at the end of
the run.
--o=OUTPREFIX Prefix for outfiles
The first step in using TALON is to initialize a SQLite database from the GTF annotation of your choice (i.e. GENCODE). This step is done using talon_initialize_database, and only needs to be performed once for your analysis. Keep track of the build and annotation names you choose, as these will be used downstream when running TALON and its utilities.
NOTE: The GTF file you use must contain genes, transcripts, and exons. If the file does not contain explicit gene and/or transcript entries, key tables of the database will be empty and you will experience problems in the downstream analysis. Please see our GTF troubleshooting section for help.
Usage: talon_initialize_database [options]
Options:
-h, --help Show help message and exit
--f GTF annotation file
--g The name of the reference genome build that the annotation describes. Use a short and memorable name since you will need to specify the genome build when you run TALON later.
--a The name of the annotation (for metadata purposes)
--l Minimum required transcript length (default = 0 bp)
--idprefix Prefix for naming novel discoveries in eventual TALON runs (default = 'TALON')
--5p Maximum allowable distance (bp) at the 5' end during annotation (default = 500 bp)
--3p Maximum allowable distance (bp) at the 3' end during annotation (default = 300 bp)
--o Output prefix for the database
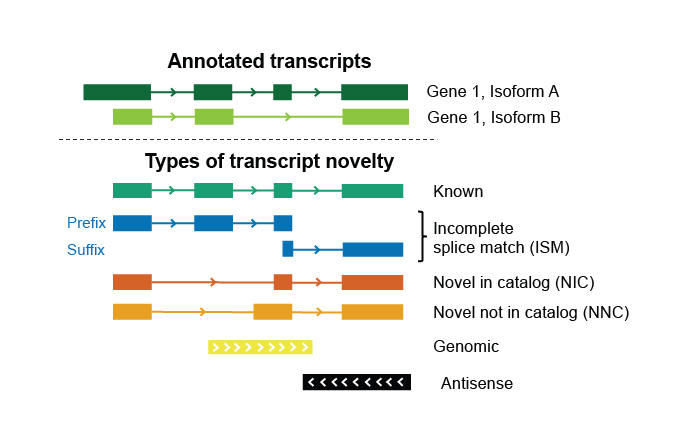
Now that you've initialized your database and checked your reads for evidence of internal priming, you're ready to annotate them. The input database is modified in place to track and quantify transcripts in the provided dataset(s). In a talon run, each input SAM read is compared to known and previously observed novel transcript models on the basis of its splice junctions. This allows us to not only assign a novel gene or transcript identity where appropriate, but to track new transcript models and characterize how they differ from known ones. The types of novelty assigned are shown in this diagram.
To run the talon annotator, create a comma-delimited configuration file with the following four columns: name, sample description, platform, sam file (full path). There should be one line for each dataset, and dataset names must be unique. If you decide later to add more datasets to an existing analysis, you can do so by creating a new config file for this data and running TALON again on the existing database.
Please note that TALON versions 4.4+ can be run in multithreaded fashion for a much faster runtime.
usage: talon [-h] [--f CONFIG_FILE] [--db FILE,] [--build STRING,]
[--threads THREADS] [--cov MIN_COVERAGE]
[--identity MIN_IDENTITY] [--o OUTPREFIX]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--f CONFIG_FILE Dataset config file: dataset name, sample description,
platform, sam file (comma-delimited)
--db FILE, TALON database. Created using
talon_initialize_database
--build STRING, Genome build (i.e. hg38) to use. Must be in the
database.
--threads THREADS, -t THREADS
Number of threads to run program with.
--cov MIN_COVERAGE, -c MIN_COVERAGE
Minimum alignment coverage in order to use a SAM
entry. Default = 0.9
--identity MIN_IDENTITY, -i MIN_IDENTITY
Minimum alignment identity in order to use a SAM
entry. Default = 0.8
--o OUTPREFIX Prefix for output files
TALON generates two output files in the course of a run. The QC log (file with suffix 'QC.log') is useful for tracking why a particular read was or was not included in the TALON analysis.
QC log format
Columns:
- dataset
- read_ID
- passed_QC (1/0)
- primary_mapped (1/0)
- read_length
- fraction_aligned
- Identity
The second output file (suffix 'read_annot.tsv') appears at the very end of the run and contains a line for every read that was successfully annotated.
Read annotation file format
Columns:
- Name of individual read
- Name of dataset the read belongs to
- Name of genome build used in TALON run
- Chromosome
- Read start position (1-based). This refers to the 5' end start, so for reads on the - strand, this number will be larger than the read end (col 6).
- Read end position (1-based). This refers to the 3' end stop, so for reads on the - strand, this will be smaller than the read start (col 5).
- Strand (+ or -)
- Number of exons in the transcript
- Read length (soft-clipped bases not included)
- Gene ID (issued by TALON, integer)
- Transcript ID (issued by TALON, integer)
- Annotation gene ID
- Annotation transcript ID
- Annotation gene name (human-readable gene symbol)
- Annotation transcript name (human-readable transcript symbol)
- Gene novelty: one of "Known", "Antisense", or "Intergenic".
- Transcript novelty: one of "Known", "ISM", "NIC", "NNC", "Antisense", "Intergenic", or "Genomic".
- ISM subtype. If transcript novelty is not ISM, this field will be 'None'. If the transcript is an ISM, then this field can be 'Prefix', 'Suffix', 'Both', or 'None'.
- fraction_As: From the talon_label_reads step. Records the fraction of As present in the n bases after the read alignment.
- Custom_label: If the user provided a custom SAM flag (lC:Z), the value will be shown here.
- Allelic_label: If the user provided a custom SAM flag (lA:Z) to denote which allele a read came from, the value will be shown here.
- Start_support: If the user provided a custom SAM flag (tS:Z) to denote external evidence for the start site of a read, the value will be shown here.
- End_support: If the user provided a custom SAM flag (tE:Z to denote external evidence for the end site of a read, the value will be shown here.
It is also possible to obtain this file from a TALON database at any time by running the talon_fetch_reads utility.
Usage: talon_fetch_reads [-h] [--db FILE,] [--build STRING,]
[--datasets STRING,] [--o OUTPREFIX]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--db FILE, TALON database
--build STRING, Genome build (i.e. hg38) to use. Must be in the
database.
--datasets STRING, Optional: Comma-delimited list of datasets to include.
Default behavior is to include all datasets in the
database.
--o OUTPREFIX Prefix for output files
The talon_abundance module can be used to extract a raw or filtered transcript count matrix from your TALON database. Each row of this file represents a transcript detected by TALON in one or more of your datasets. To generate a file suitable for gene expression analysis, skip the --whitelist option (i.e. make an unfiltered abundance file). To generate a file for isoform-level analysis, please see the next section to generate a whitelist file to use.
Usage: talon_abundance [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--db=FILE TALON database
-a ANNOT, --annot=ANNOT
Which annotation version to use. Will determine which
annotation transcripts are considered known or novel
relative to. Note: must be in the TALON database.
--whitelist=FILE Whitelist file of transcripts to include in the
output. First column should be TALON gene ID,
second column should be TALON transcript ID
-b BUILD, --build=BUILD
Genome build to use. Note: must be in the TALON
database.
-d FILE, --datasets=FILE
Optional: A file indicating which datasets should be
included (one dataset name per line). Default is to
include all datasets.
--o=FILE Prefix for output file
Please note to run this utility, you must provide genome build (-b) and annotation (-a) names that match those provided for the talon_initialize_database, otherwise it will not run.
Abundance file format
The columns in the abundance file are as follows:
- TALON gene ID
- TALON transcript ID
- Gene ID from your annotation of choice. If the gene is novel relative to that annotation, this will be the TALON-derived name.
- Transcript ID from your annotation of choice. If the transcript is novel relative to that annotation, this will be the TALON-derived name.
- Gene name from your annotation of choice (makes the file a bit more human-readable!). If the transcript is novel relative to that annotation, this will be the TALON-derived name.
- Transcript name from your annotation of choice. If the transcript is novel relative to that annotation, this will be the TALON-derived name.
- Number of exons in the transcript
- Length of transcript model (nucleotides). Note: For known transcripts, this will be the length of the model as defined in the annotation. The actual reads that matched it may not be that length. For actual read lengths, see the read_annot output file.
- Gene novelty (Known, Antisense, Intergenic)
- Transcript status (Known, ISM, NIC, NNC, Antisense, Intergenic)
- ISM subtype (Both, Prefix, Suffix, None)
---------------------------- Remaining columns -----------------------------
One column per dataset, with a count indicating how many times the current transcript was observed in that dataset.
Before quantifying your results on the isoform level, it is important to filter the novel transcript models because long-read platforms are prone to several forms of artifacts. The most effective experimental design for filtering is to use biological replicates. Some limited filtering is possible even for singlet datasets, but keep in mind that this is likely to be far less effective.
The talon_filter_transcripts module generates a whitelist of transcripts that are either:
a) Known
b) Observed at least n times in each of k datasets.
The default value for n is 5 and the default for k is the total number of datasets you provide for filtering. In addition, the filter requires that all n reads used to support a novel transcript must not have evidence of internal priming (default: internal priming defined as > 0.5 fraction As). If you wish to disregard internal priming, set --maxFracA to 1 (not generally recommended).
Usage: talon_filter_transcripts [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--db=FILE TALON database
-a ANNOT, --annot=ANNOT
Which annotation version to use. Will determine which
annotation transcripts are considered known or novel
relative to. Note: must be in the TALON database.
--datasets=DATASETS Datasets to include. Can be provided as a comma-
delimited list on the command line, or as a file with
one dataset per line. If this option is omitted, all
datasets will be included.
--maxFracA=MAX_FRAC_A
Maximum fraction of As to allow in the window located
immediately after any read assigned to a novel
transcript (helps to filter out internal priming
artifacts). Default = 0.5. Use 1 if you prefer to not
filter out internal priming.
--minCount=MIN_COUNT Number of minimum occurrences required for a novel
transcript PER dataset. Default = 5
--minDatasets=MIN_DATASETS
Minimum number of datasets novel transcripts must be
found in. Default = all datasets provided
--allowGenomic If this option is set, transcripts from the Genomic
novelty category will be permitted in the output
(provided they pass the thresholds). Default behavior
is to filter out genomic transcripts since they are
unlikely to be real novel isoforms.
--o=FILE Outfile name
The columns in the resulting output file are:
- TALON gene ID (an integer). This is the same type of ID found in column 1 of TALON abundance files.
- TALON transcript ID (an integer). This is the same type of ID found in column 2 of TALON abundance files.
You can use the talon_create_GTF utility to extract a GTF-formatted annotation from the TALON database.
Usage: talon_create_GTF [options]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--db=FILE TALON database
-b BUILD, --build=BUILD
Genome build to use. Note: must be in the TALON
database.
-a ANNOT, --annot=ANNOT
Which annotation version to use. Will determine which
annotation transcripts are considered known or novel
relative to. Note: must be in the TALON database.
--whitelist=FILE Whitelist file of transcripts to include in the
output. First column should be TALON gene ID,
second column should be TALON transcript ID
--observed If this option is set, the GTF file will only
include transcripts that were observed in at least one
dataset (redundant if dataset file provided).
-d FILE, --datasets=FILE
Optional: A file indicating which datasets should be
included (one dataset name per line). Default is to
include all datasets.
--o=FILE Prefix for output GTF
Please note to run this utility, you must provide genome build (-b) and annotation (-a) names that match those provided for the talon_initialize_database, otherwise it will not run.
Please cite our preprint when using TALON:
A technology-agnostic long-read analysis pipeline for transcriptome discovery and quantification. Dana Wyman, Gabriela Balderrama-Gutierrez, Fairlie Reese, Shan Jiang, Sorena Rahmanian, Weihua Zeng, Brian Williams, Diane Trout, Whitney England, Sophie Chu, Robert C. Spitale, Andrea J. Tenner, Barbara J. Wold, Ali Mortazavi bioRxiv 672931; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/672931
MIT, see LICENSE