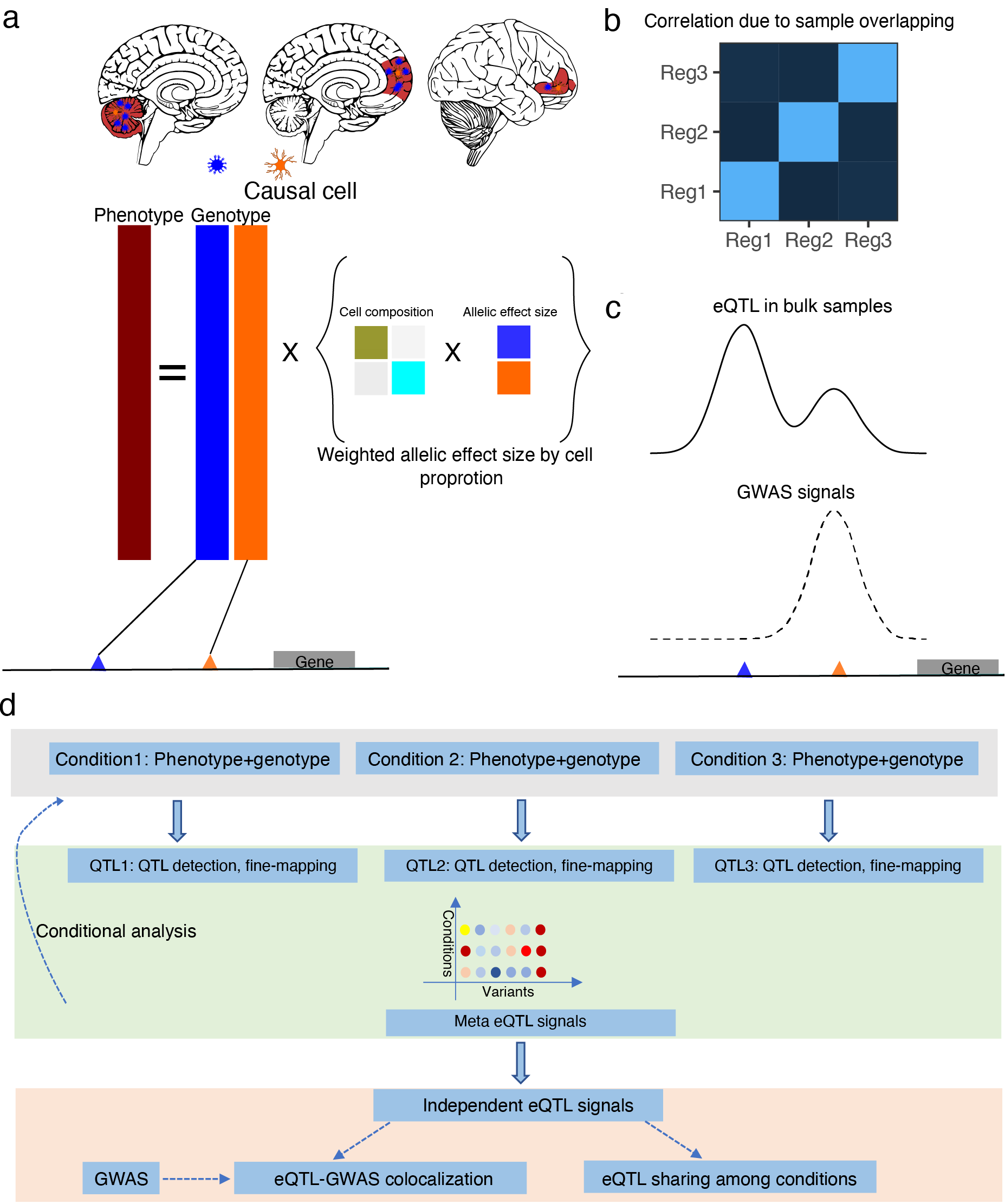
Figure 1. Illustration of mmQTL package. a-c, graphic demonstration of the problem to solve in mmQTL. Upper panel represents three tissue regions, consisting of two cell types, colored in blue for minor cell type and orange for major cell type, with different compositions among regions, and gene expression regulated by cell-type specific eQTL (same color as their regulated target cell types). In the standard colocalization pipeline, we miss the co-localized signal between the eQTL signal and GWAS hit if a minor rare cell type is the causal. b, phenotype correlated due to sample overlapping or polygenetic background in repeat-measurement or multiple-condition experiment design. c, Improvement of fine-mapping in meta-analysis. pp on Y axis means posterior probability in fine-mapping. d, schematic representation of mmQTL steps in meta-eQTL detection. MmQTL disentangles the eQTL profile in the meta-analysis framework (top and middle panel), and evaluates the relationship with phenotype traits through colocalization analysis (down panel).
mmQTL is a flexible software toolkit used to conduct multiple QTL detection with control for population structure and sample overlapping.
Any bugs, please contact biao.zeng@mssm.edu or jxzb1988@gmail.com
Currently, mmQTL is supported for 64-bit Linux platforms.
-
Control for population structure;
-
Control for sample overlapping;
-
Meta-analysis to integrate QTL signal among conditions;
-
Conditional analysis to find independent QTL signals.
Some new features are included in current version.
-
A license file is attached;
-
An option to adjust random-effect model by Han & Eksin method is introduced;
-
The default function to estimate covariance structure is switched to cor instead of cov;
-
P-value cutoff to determine QTL signal and Z-score to determine non-significant variants can be set;
-
Conditional analysis can be swithched off, and users can set the maximum number of independent QTL to report;
-
Bugs are fixed.
To install mmQTL you can
-
Download the precompiled binaries (64-bit Linux only);
-
Compile mmQTL from source.
After downloading the precompiled mmQTL code, run the command
chmod +x MMQTL26
to change the mode.
To get mmQTL running options, you can type
MMQTL26 -h
Example code
MMQTL26 -b -P pheno_file.txt -Z geno_file.txt -R GRM_file.txt -a feature_annotation.bed -A random -gene gene_name
Given that we have 5 tissues/conditions, named as condition1, condition2, condition3, condition4, condition5.
For phenotype, the phenotype files ((g+1)x(n+1) matrix, g is the number of explored genes, and n is the sample size. Both column and row names should be included) are named as phenotype_file_1, phenotype_file2, phenotype_file3, phentoype_file4, phenotype_file5;
For genotype, the binary plink-format genotype files are named as genotype_file_1, genotype_file_2, genotype_file_3, genotype_file_4, genotype_file_5; To speed up mmQTL running, split genotype into chromosomes.
You need an annotation file for the exploed features in bed format: chr start end feature_name;
Make sure that position information in genotype matches with those in annotation, and name chromosomes with digits.
Optional, to apply mixed linear model to control for population strucutre, you need to provide GRM files, named as GRM_file_1, GRM_file_2, GRM_file_3, GRM_file_4, GRM_file_5.
explanation for parameters:
-P: specify the location of the file containing the location of phenotype files for each tissue/condition;
This file should be:
path/to/phenotype_file_1
path/to/phenotype_file_2
path/to/phenotype_file_3
path/to/phenotype_file_4
path/to/phenotype_file_5
-Z: specify the location of the file containing the location of genotype files for each tissue/condition. The format for the genotype should be in PLINK format.
This file should be:
path/to/genotype_file_1
path/to/genotype_file_2
path/to/genotype_file_3
path/to/genotype_file_4
path/to/genotype_file_5
-R: specify the location of the file containing the location of genetic relatedness matrix files for each tissue/condtional.
This file should be:
path/to/GRM_file_1
path/to/GRM_file_2
path/to/GRM_file_3
path/to/GRM_file_4
path/to/GRM_file_5
The GRM file can be created with packages, like GEMMA, GCTA. For example, run command "gemma -bfile plink_bfile_format -gk 2", which will create a *.sXX.txt file used in QTL detection.
If there is an issue of population structure or cryptic relatedness for partial tissues/conditions, set the path as "NA" for those tissues/conditions without GRM files.
-A: run mmQTL in random-effect or fixed-effect model when performing meta-analysis.
-a: Specify the feature annotation, which should be bed format.
-gene: Specify the gene/feature for which that you want to detect eQTL, which is a required parameter.
We have prepared a test dataset, which is deposited in google drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1G8ccfR9vPliMs_KKxAdW1CnA2C8bniZy/view?usp=sharing. Note: In this test dataset, we simulated phenotypes in 5 tissues on the same set of individuals, so you should set the same genotype and GRM file paths for the 5 tissues
When covariate information are available, -C can be used to specify the covariate file path, just like -Z and -P
mmQTL can also use summary results to perform meta-analysis. Set -D or -cis_summary to tell mmQTL to run QTL with summary results, and put the files containing QTL summary results in path files set by -P.
The source codes should be compiled in src folder.
Before compiling, please change the directionaries for the libraries, and unzip "armadillo-9.400.3.zip". Then type
make
Currently mmQTL takes PLINK format for genotype, and text for phenotype
Biao Zeng, Jaroslav Bendl, Roman Kosoy, John F Fullard, Gabriel E Hoffman, Panos Roussos. Multi-ancestry eQTL meta-analysis of human brain identifies candidate causal variants for brain-related traits. Nat Genet (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-021-00987-9
Biao Zeng, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
1470 Madison Ave
The Leon and Norma Hess Center for Science and Medicine
New York, NY 10029