A real-time slosh-free tracking method for robotic manipulators.
| Slosh-free reference (sim) | Slosh-free tracking (sim) | Slosh-free motions (real) |
|---|---|---|
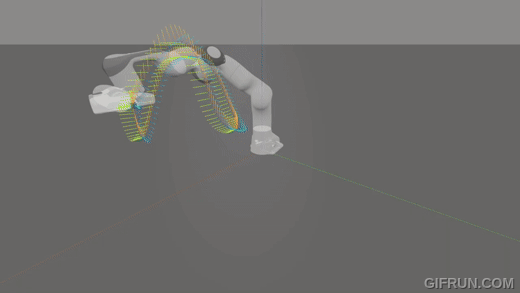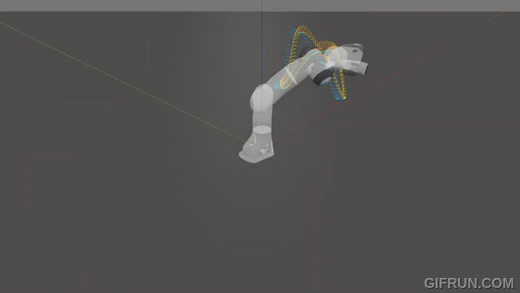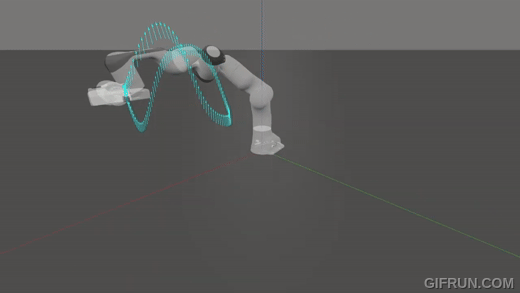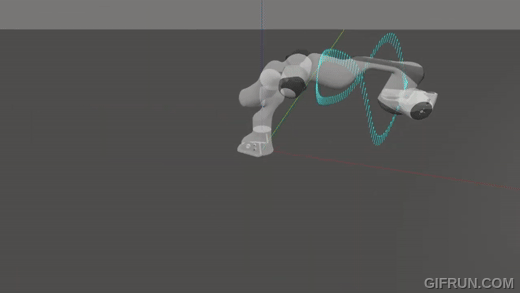 |
 |
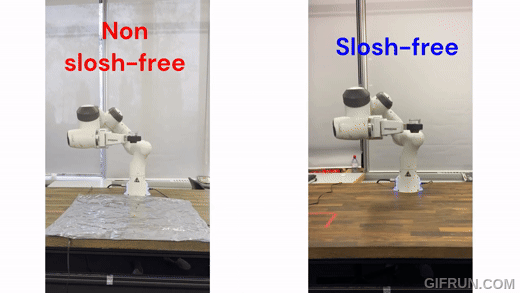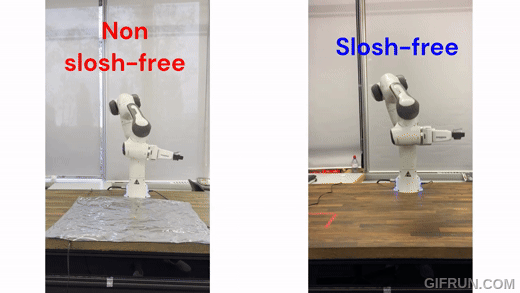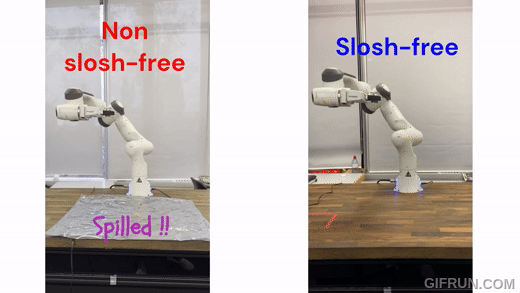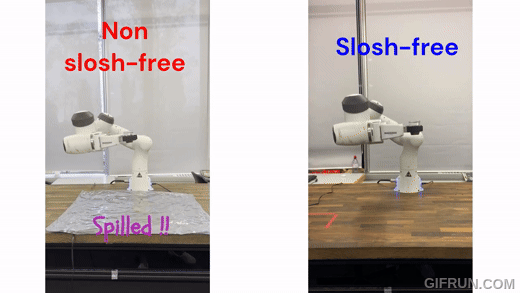 |
For the implementation details, please check the paper and/or watch the video. If you use this framework please cite our work:
@misc{arrizabalaga2024geometric,
title={Geometric Slosh-Free Tracking for Robotic Manipulators},
author={Jon Arrizabalaga and Lukas Pries and Riddhiman Laha and Runkang Li and Sami Haddadin and Markus Ryll},
year={2024},
eprint={2402.05197},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO}
}
Initialize git submodules with
git submodule init
git submodule update
Install the specific versions of every package from requirements.txt in a new conda environment:
conda create --name gsft python=3.9
conda activate gsft
pip install -r requirements.txt
To ensure that Python paths are properly defined, update the ~/.bashrc by adding the following lines
export GSFT_PATH=/path_to_gsfc
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/$GSFT_PATH
To run an example, execute this file. For example,
python main.py --t_nav 6.5 --case h
runs the helix case study for a navigation time of 6.5 s. The other two case studies are b (backflip, named "loop" in the paper) or l (lissajous). You can also add the --no_visualization and --nsf (non slosh-free) flags when running the command. Other seettings can be modified from the configuration file