Stock Market Basic Influencing Factor:
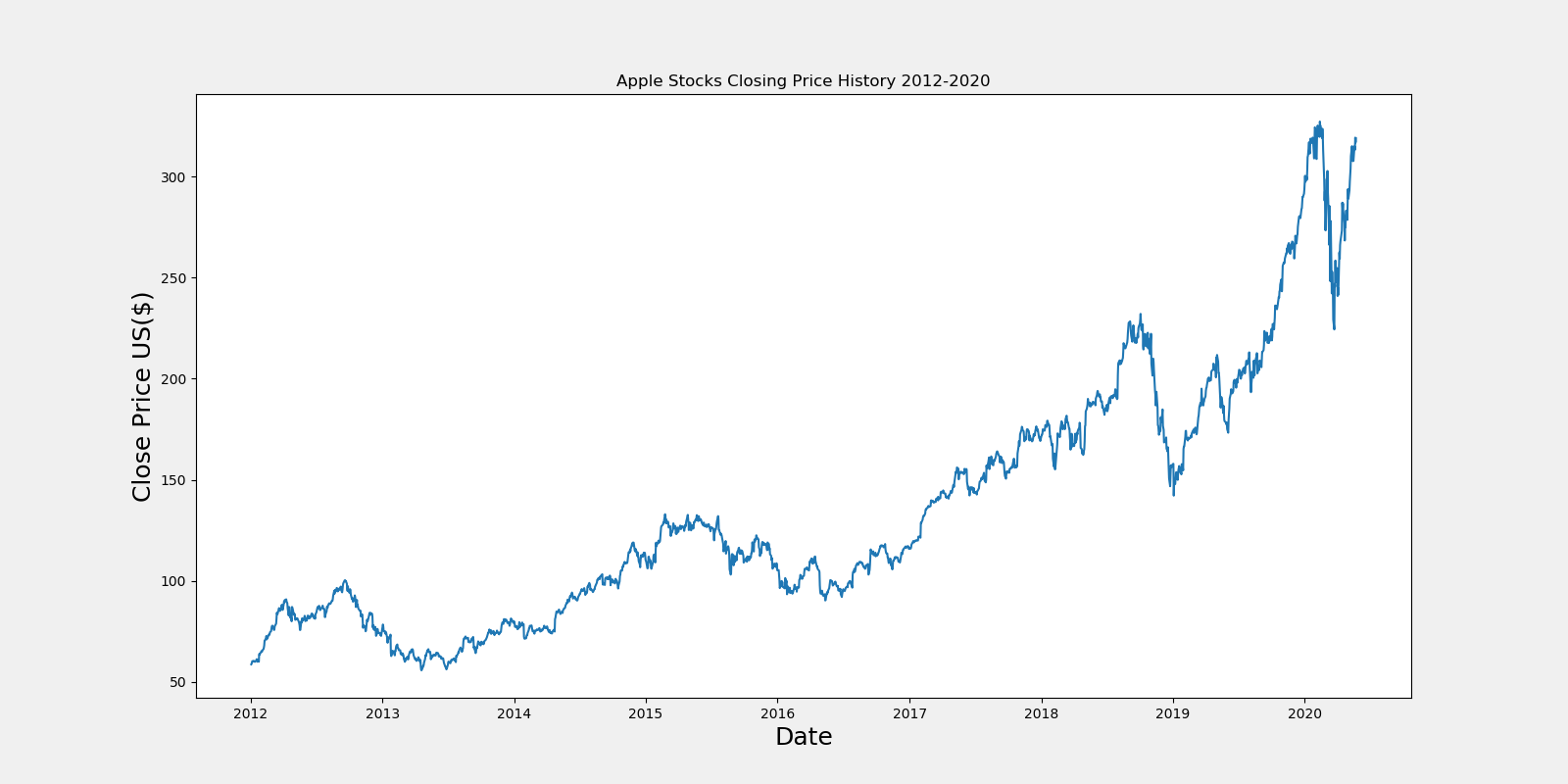
- Closing Price
- Opening Price
- After-Hour Trading
Libraries
- Pandas
- Scikit-learn
- Matplotlib
- Numpy
- Pandas_datareader.data
- Seaborn
- OS
Coding
- Dataset Import
pandas_datareader library allows us to connect to the website and extract data directly from internet sources, in this case we are extracting data from Yahoo Finance API. I have kept APPL.csv file too (if anyone wants to play with it.)
Using following code:
df = web.DataReader("AAPL", 'yahoo', start, end)
Where:
start = datetime.datetime(2012, 1, 1)
end = datetime.datetime(2020, 5, 22)
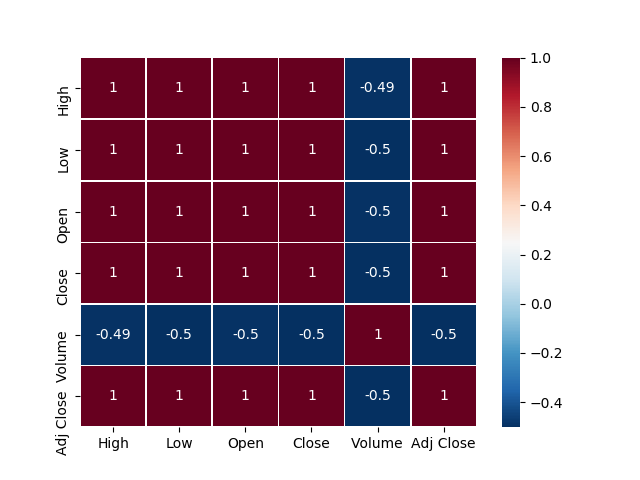
- Checking Correlation
Correlation is a measure of association or dependency between two features i.e. how much Y will vary with a variation in X. The correlation method that we will use is the Pearson Correlation.
Using Pearson Correlation coefficient:
corr=df.corr(method='pearson')
Pearson Correlation Coefficient is the most popular way to measure correlation, the range of values varies from -1 to 1. In mathematics/physics terms it can be understood as if two features are positively correlated then they are directly proportional and if they share negative correlation then they are inversely proportional.
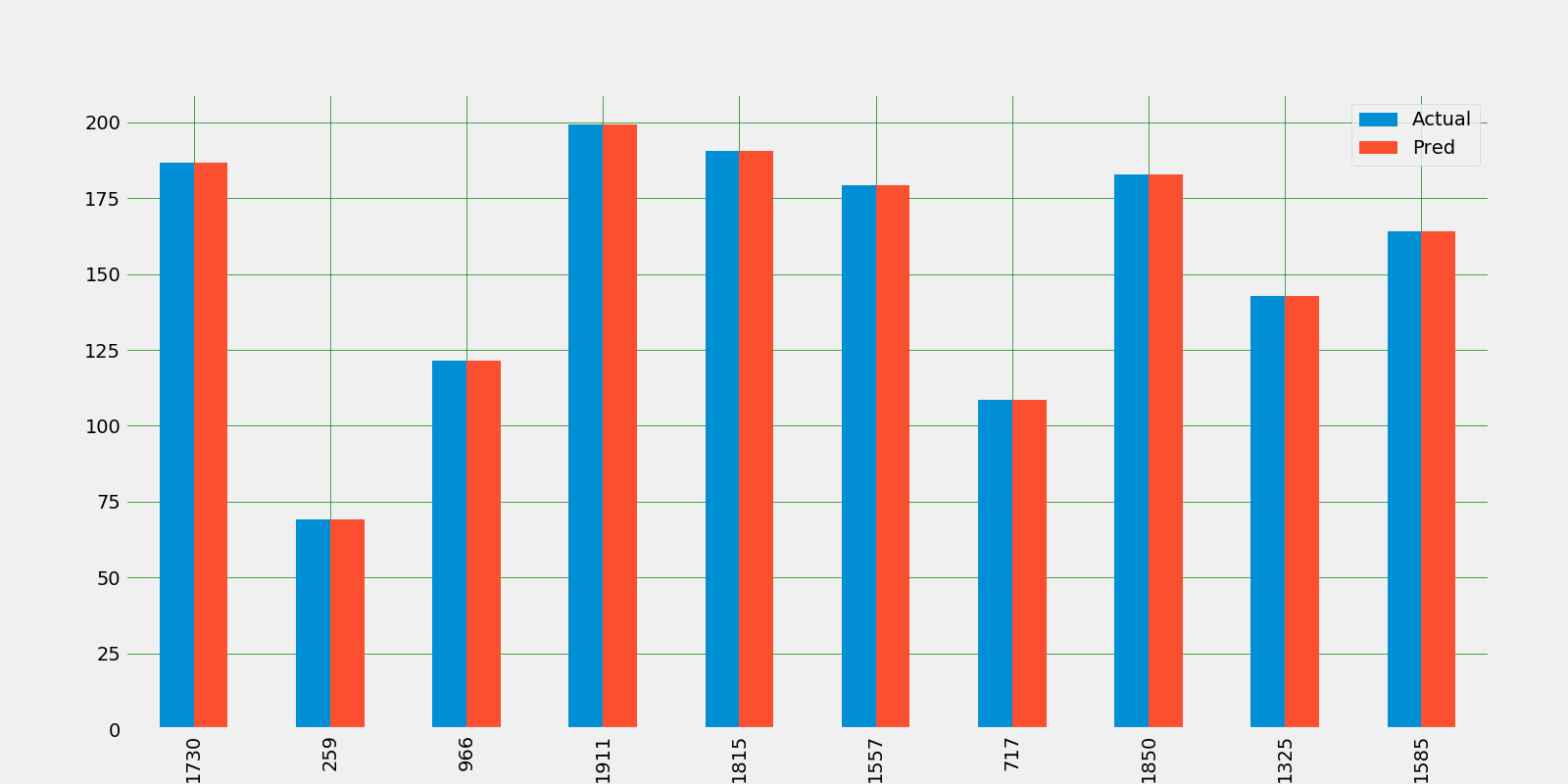
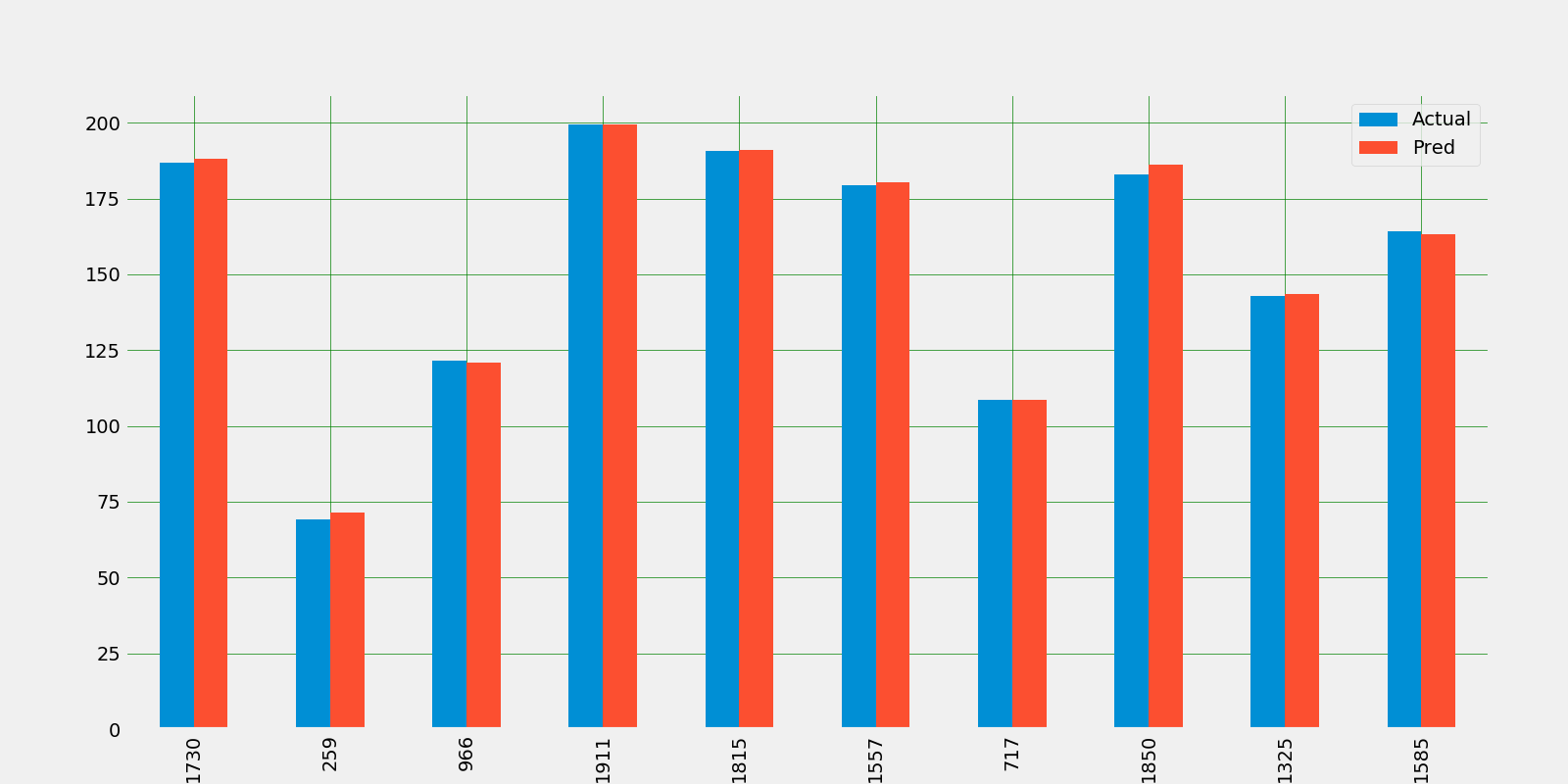
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2012 year
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2020 year
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2012 year
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2020 year
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2012 year
Let's take a look at the bar plot of top 50 data which is from 2020 year
Linear Model Cross-Validation:
Basically Cross Validation is a technique using which Model is evaluated on the dataset on which it is not trained i.e. it can be a test data or can be another set as per availability or feasibility.
number of splits: 20
Accuracy: 99.99743780203187
k neighbors = 4
Accuracy: 99.91435220285842
Accuracy: 99.99301338392715
Root Mean Square Error is the Standard Deviation of residuals, which are a measure of how far data points are from the regression. Or in simple terms how concentrated the data points are around the best fit line.
Linear Model RMSE: 3.0534992716871643e-14
KNN Model RMSE: 1.191675778610913
SVM Model RMSE: 0.5182098703394772
R-Squared score varies between 0 to 100%.
Mathematical Formula for R-squared score:(y_test[i] — y_pred[i]) **2
Linear R-Squared: 1.0
KNN R-Squared: 0.999629726665711
SVM R-Squared: 0.9999299807307482