This repository contains the code of KNN based term discovery algorithm, implemented for our paper Unsupervised discovery of sign terms by K-nearest neighbours approach (ECCV '20). It contains the necessary scripts to reproduce the results. Contact me via LinkedIn to access the Drive link that contains all the features for OpenPose and DeepHand.
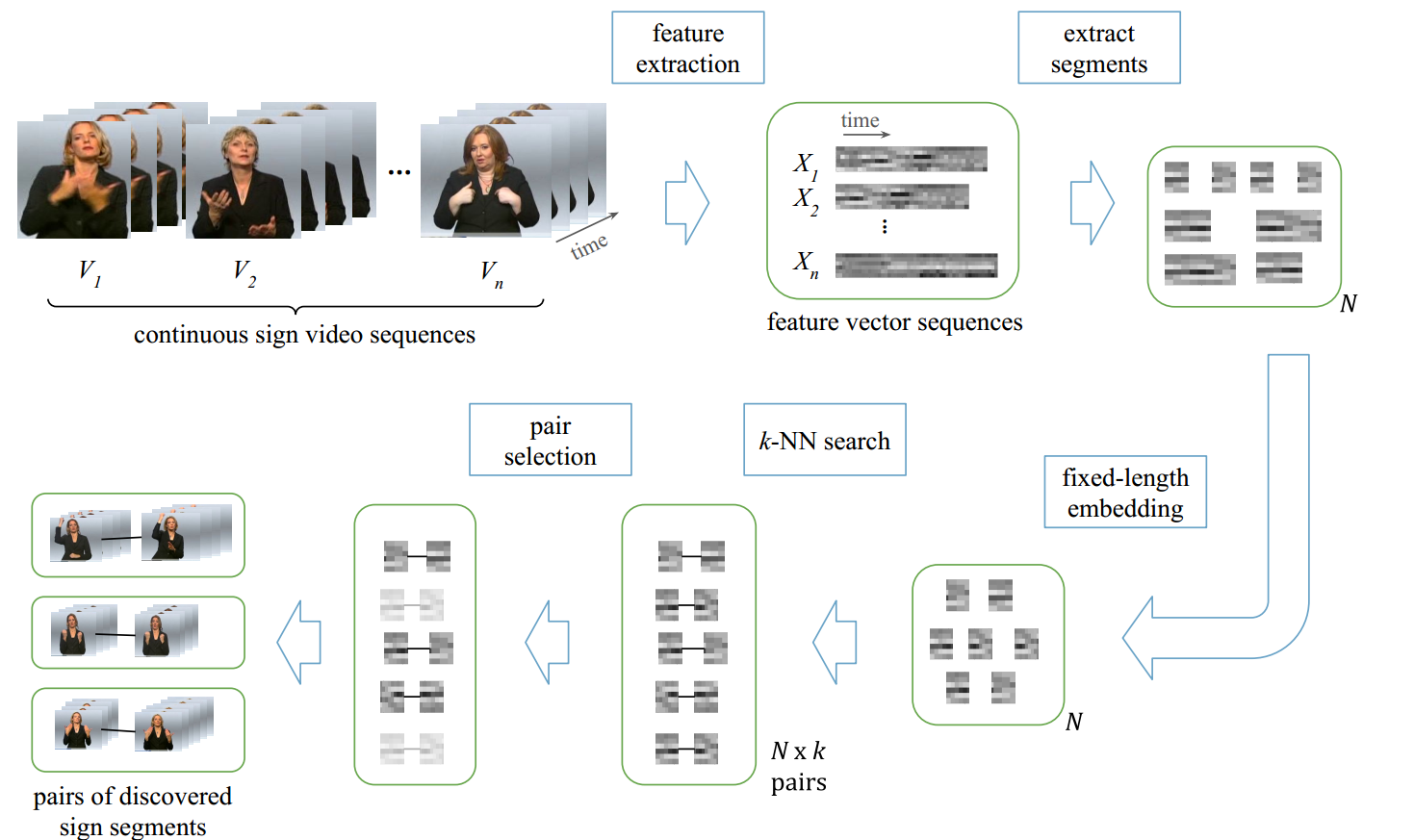
Even though we implemented this algorithm for discovery of sign language terms, this repo is intended for general purpose term (motif) disvovery. Given a set of feature vector sequences, the algorithm outputs pairs of similar segments. The input sequences can be features obtained from speech (MFCC etc), or sign language (skeleton keypoints) or any other type feature that represent a sequence.
Can you spot a common sign among these three sentences ?
These common gestures correspond to words in German sign language. If we humans can notice that there are some common hand gestures among these clips, without any other information but the videos themselves, machines should be able to discover these common patterns as well.
Unsupervised term discovery algorithms aim to find similar repeating segments from an input sequence, without any supervision (hence the name Zero Resource). This problem has been an active research area in speech processing and there are various algorithms that have competed for the Zero Resource Speech Challenges. Our work solves the same problem for sign languages by using visual features instead of speech features. Our implementation closely follows the original algorithm that is proposed by Thual et. al. in A K-nearest neighbours approach to unsupervised spoken term discovery.
Have a look at the notebook to see how you can call the module. The detailed explanations for each parameter are given in the notebook as well. The provided sample data contains the time series features computed from sign language videos.
To reproduce the results in the paper with the exact parameters, refer to this notebook. Here, the parameters are read from csv files provided in data/paper_results.
If you want to perform cross-validated parameter tuning refer to this notebook. You'd need scikit-optimize to run this one.
The main dependency is the FAISS library, which greatly speeds up the KNN search, by utilizing CUDA capable GPU's. If you don't have a CUDA capable GPU, then you can set use_gpuparameter to False.
The other dependencies are common packages such as Numpy, Pandas, Scipy, Numba etc.
A working combination on Ubuntu 16 is:
Python=3.7.4
numba 0.54.1
numpy 1.18.1
faiss 1.7.0
pandas 0.24.2
scikit-optimize 0.9.0
cuda=10.2
If you want to compare discovered pairs to a set of ground truth labels, you can make use of Term Discovery Evaluation toolkit.
Please cite the original paper
@INPROCEEDINGS{8639515,
author={A. {Thual} and C. {Dancette} and J. {Karadayi} and J. {Benjumea} and E. {Dupoux}},
booktitle={2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT)},
title={A K-Nearest Neighbours Approach To Unsupervised Spoken Term Discovery},
year={2018},
pages={491-497},
doi={10.1109/SLT.2018.8639515}}
and our paper
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-030-66096-3_22,
author="Polat, Korhan and Sara{\c{c}}lar, Murat",
title="Unsupervised Discovery of Sign Terms by K-Nearest Neighbours Approach",
booktitle="Computer Vision -- ECCV 2020 Workshops",
year="2020",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="310--321"}
if you use this code in your work.