This repository contains the files and scripts necessary to reproduce the analyses and generate the graphs shown in the manuscript by Wheeler & Harms entitled "Were Ancestral Proteins Less Specific?" https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.27.120261.
enrichment_files: directory containing enrichment files. This files in this directory are used by all of the jupyter noteboooks used in the analysis.run_whole_pipeline: scripts that will allow re-creation of the files inenrichment_filesfrom the Illumina fastq files uploaded to the NCBI SRA database.fig_2cd-s4: jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figures 2C, 2D and S4 (analysis of peptide enrichment)fig_3jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figure 3 (Venn diagrams and related analyses)fig_4jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figure 4 (change in peptide numbers since ancestor)fig_s2jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figure S2 (identifying minimum read count cutoff)fig_s3jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figure S3D (estimating enrichment from clusters versus indivdual sequences)fig_s4files to reproduce figure S4 (enrichment distribution)fig_s5jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figure S5 (identifying posterior probability for peptide enrichment cutoff)fig_2ef-s6-s7-s8-s9jupyter notebook and files to reproduce figures 2E, 2F, and S6 through S9 (peptide binding experiments)
Throughout this repository, samples are labeled by the following convention PROTEIN_TREATMENT_REPLICATE.
PROTEIN is one of:
- 'hA5' (human S100A5)
- 'hA6' (human S100A6)
- 'aA5A6' (ancA5/A6)
- 'alt' (alternate reconstruction of ancA5/A6).
TREATMENT is one of:
- 'conv' (conventional, no peptide competitor)
- 'comp' (competitor peptide added)
- 'all' (pooled reads from conventional and competitor runs)
REPLICATE is one of:
- '1' (replicate one)
- '2' (replicate two)
- 'pooled' (combined replicates)
- This analysis assumes a modern scientific python computing environment (python 3.x, jupyter, numpy, scipy, matplotlib, and pandas). It will also install a few other dependences (emcee and corner). We have tested this pipeline in linux (Ubuntu 16.4) and macOS (10.15 Catalina). In principle it should work in windows, but we have not tested it.
- Install the hops_enrich package. (Linked v0.1 release is the software used in the publication.)
- Install the venninator package. (Linked v0.1 release is the software used in the publication.)
- If you intend to run our scripts to download our raw sequencing reads from scratch, install and configure the SRA toolkit.
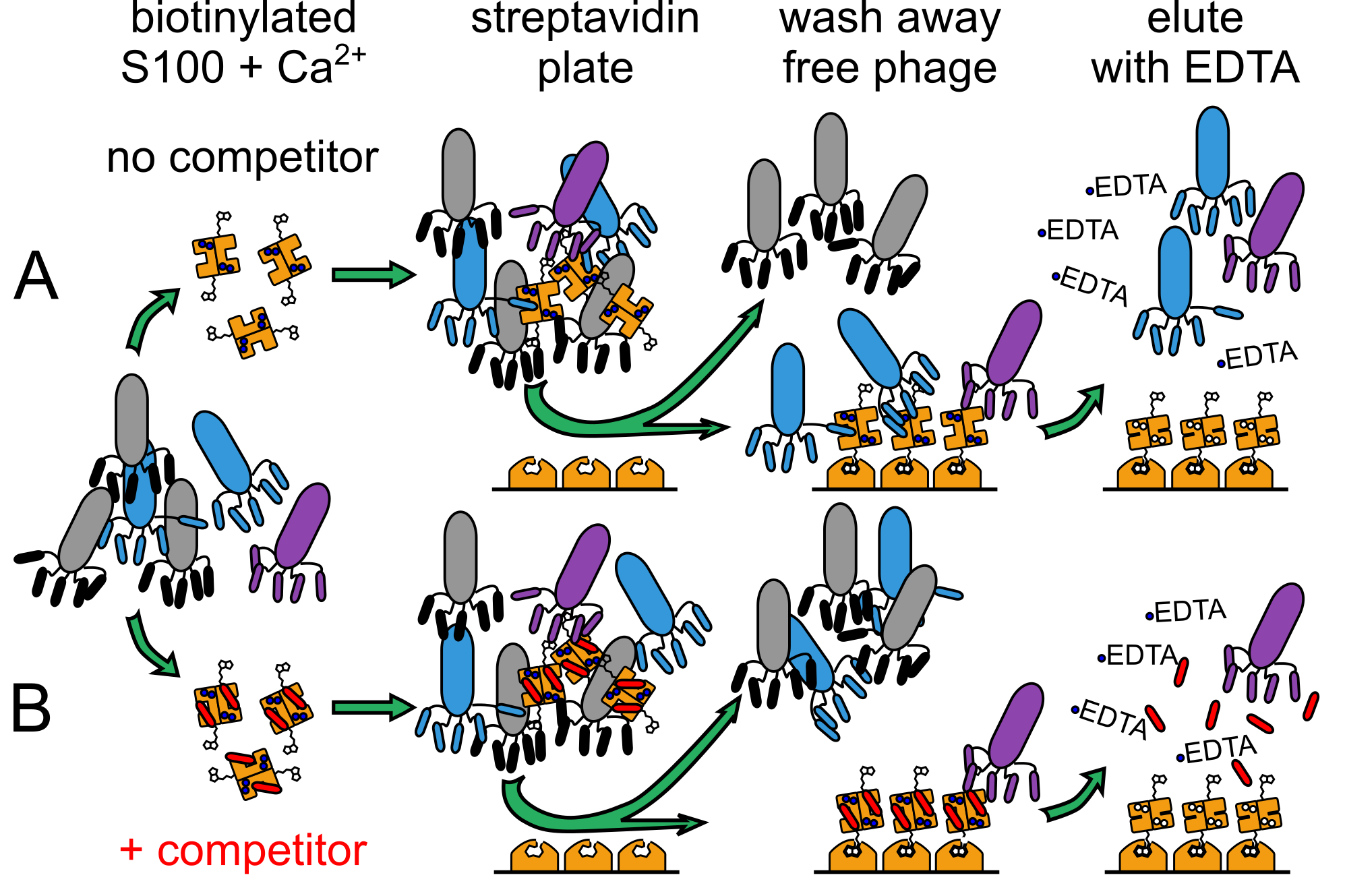
We panned a commercial library of randomized 12-mer peptides expressed as fusions with the M13 phage coat protein. The S100 peptide-binding interface is only exposed upon Ca2+-binding; therefore, we performed phage panning experiments in the presence of Ca2+ and then eluted the bound phage using EDTA. The population of enriched phage will be a mixture of phage that bind at the site of interest and phage that bind adventitiously (blue and purple phage, panel A). Peptides in this latter category enrich in Ca2+-dependent manner through avidity or binding at an alternate site. To separate these populations, we repeated the panning experiment in the presence of a saturating concentration of competitor peptide known to bind at the site of interest (panel B). This should lower enrichment of peptides that bind at the site of interest, while allowing any adventitious interactions to remain. By comparing the competitor and conventional, non-competitor pools, we can distinguish between actual and adventitious binders.
-
Obtain the fastq files (for example,
hA5_conv_1.fastq.gzandhA5_comp_1.fastq.gz) -
Count the number of times each peptide is seen in the fastq file (
hA5_conv_1.countsandhA5_comp_1.countsfor example) -
Create clusters of peptides seen in the counts files (
hA5_1.cluster) -
Calculate enrichments for each peptide by comparing counts in conventional and competitor experiments (
hA5_1.enrich)
To download the fastq files from the NCBI:
cd run_whole_pipeline
bash download-sra.sh sra-files.txt
In 2020, this script took about 3 hours to run on a 100 Mbit residential connection with a 2018 macbook pro. It will create about 10 Gb of fastq.gz files.
To calculate enrichments from the fastq files:
cd run_whole_pipeline
bash fastq-to-enrichment.sh
This script took about 4 hours to run on a 2018 macbook pro.
The raw reads associated with this analysis are available as BioProject PRJNA646756. The samples are:
| Accession | Sample |
|---|---|
| SRR12244639 | hA6_conv_1 |
| SRR12244813 | hA6_comp_1 |
| SRR12244638 | hA6_conv_2 |
| SRR12244812 | hA6_comp_2 |
| SRR12244629 | hA5_conv_1 |
| SRR12244637 | hA5_comp_1 |
| SRR12244628 | hA5_conv_2 |
| SRR12244636 | hA5_comp_2 |
| SRR12244543 | aA5A6_conv_1 |
| SRR12244560 | aA5A6_comp_1 |
| SRR12244542 | aA5A6_conv_2 |
| SRR12244559 | aA5A6_comp_2 |
| SRR12244562 | alt_conv_1 |
| SRR12244584 | alt_comp_1 |
| SRR12244561 | alt_conv_2 |
| SRR12244583 | alt_comp_2 |
Calculate the the number of time each peptide is seen in the relavent .fastq.gz file using hops_count. This script applies some quality control:
- Is the sequence translatable in-frame, without stops or nonsensical codons?
- Is the average PHRED score above a cutoff (15 as we ran the analysis)?
- Is the flanking phage region correct to within one base across the whole sequence?
hops_count hA5.fastq.gz -o hA5.counts
-
Create a file containing all sequences observed in all experiments with a given protein.
awk '{print $1}' hA5_conv_1.counts > tmp awk '{print $1}' hA5_comp_1.counts >> tmp sort tmp | uniq > hA5_1_all-seq.txt rm -f tmp -
Cluster all sequences by Hamming distance using dbscan. In the manuscript, we used a neighborhood value (epsilon) equal to one, meaning the algorithm only looks one amino acid step away when constructing the clusters. We also set the minimum cluster size to 2. The following call will reproduce this for hA5 replicate 1.
hops_cluster hA5_1_all-seq.txt -s 2 -e 1 -d simple -o hA5_1.cluster
Calculate enrichment in the conventional versus competitor experiment using hops_enrich. Only include samples where the number of counts is six or great.
hops_enrich hA5_conv_1.counts hA5_comp_1.counts -f hA5_1.cluster -m 6 -o hA5_1.enrich
Each figure directory contains data files, jupyter notebooks, and scripts necessary to reproduce the indicated figures.