survey.pdf |
A curated list of awesome large AI models, or foundation models, for reasoning.
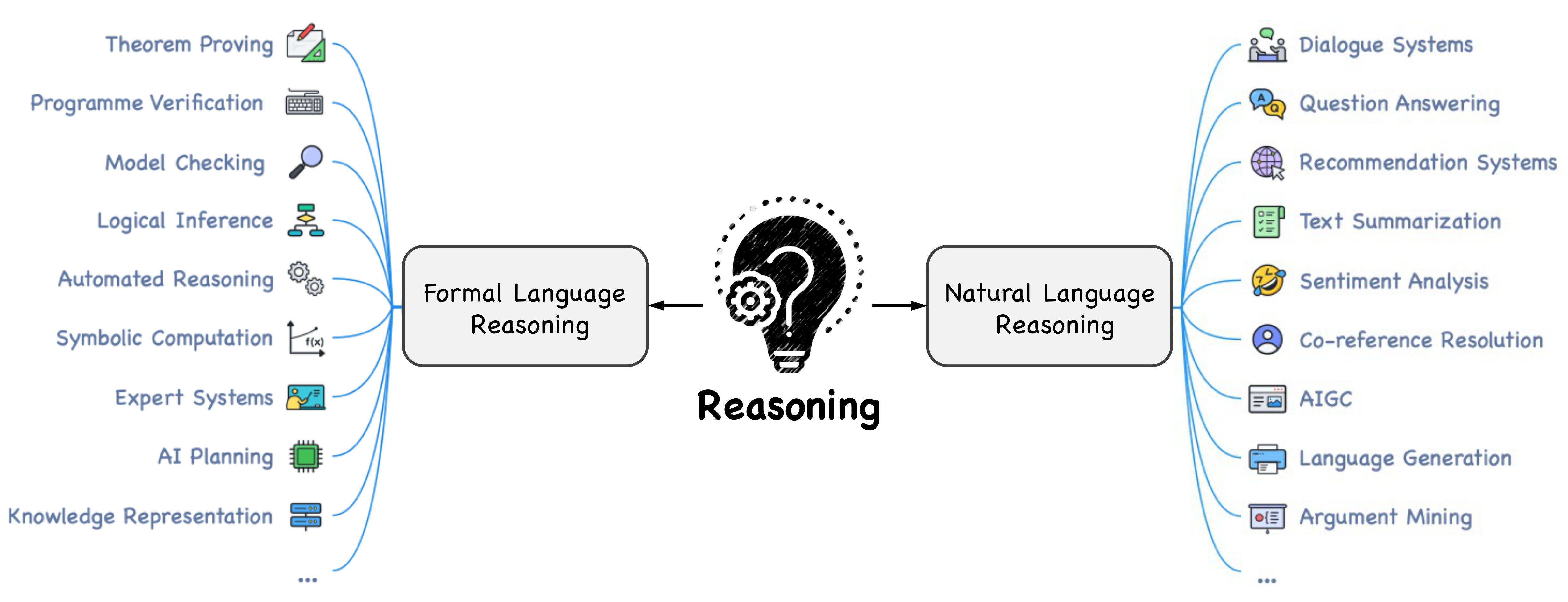
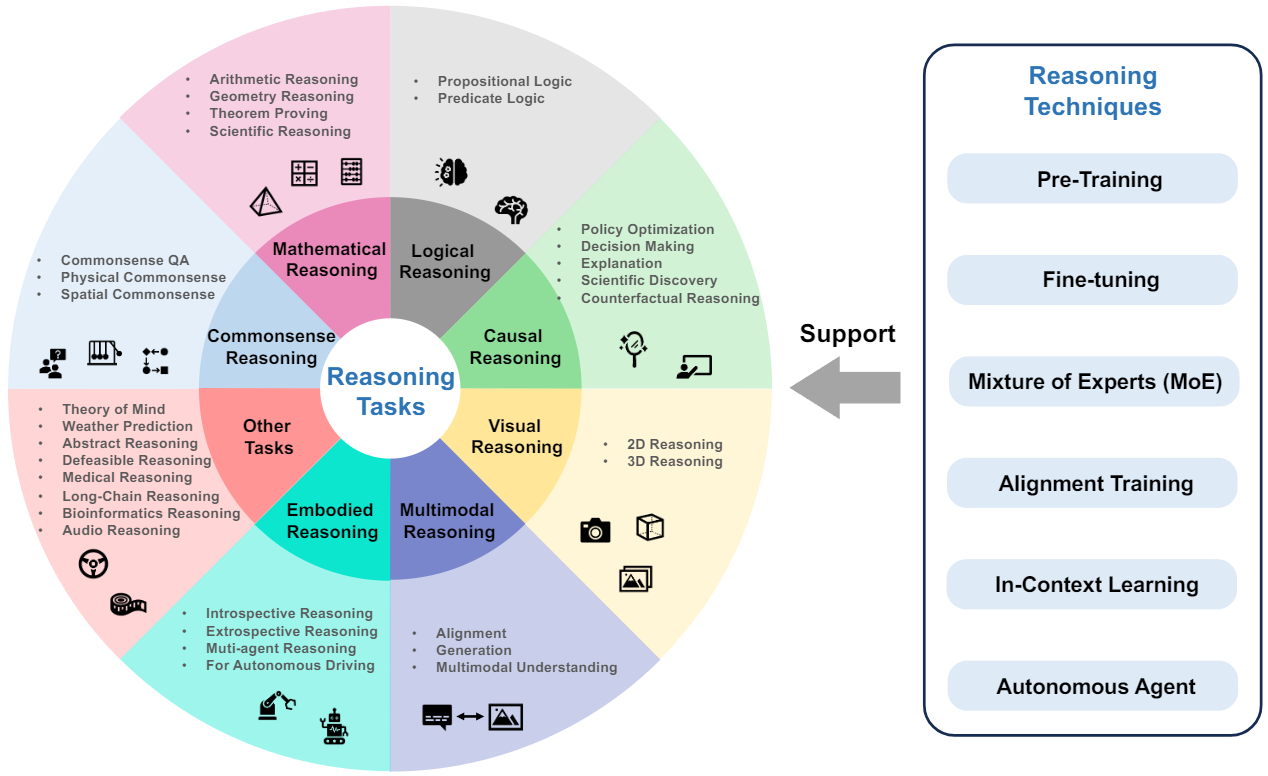
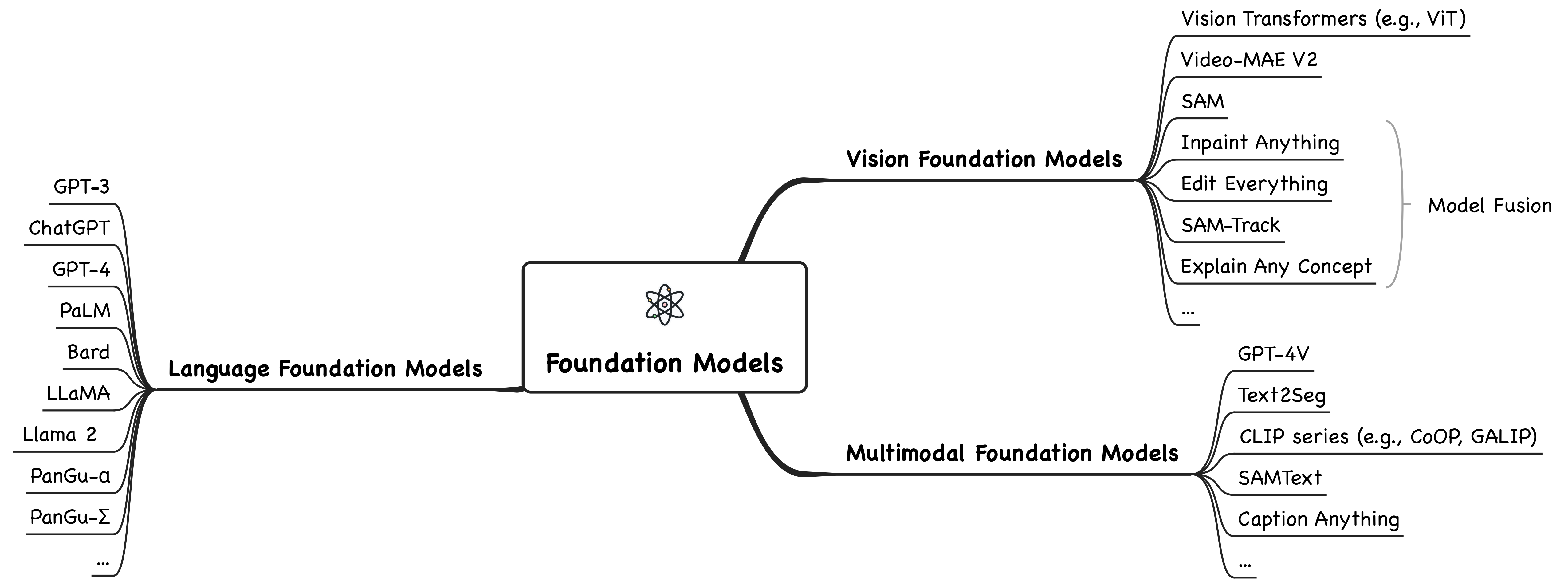
We organize the current foundation models into three categories: language foundation models, vision foundation models, and multimodal foundation models. Further, we elaborate the foundation models in reasoning tasks, including commonsense, mathematical, logical, causal, visual, audio, multimodal, agent reasoning, etc. Reasoning techniques, including pre-training, fine-tuning, alignment training, mixture of experts, in-context learning, and autonomous agent, are also summarized.
We welcome contributions to this repository to add more resources. Please submit a pull request if you want to contribute! See CONTRIBUTING.
table of contents
This repository is primarily based on the following paper:
A Survey of Reasoning with Foundation Models
Jiankai Sun, Chuanyang Zheng, Enze Xie, Zhengying Liu, Ruihang Chu, Jianing Qiu, Jiaqi Xu, Mingyu Ding, Hongyang Li, Mengzhe Geng, Yue Wu, Wenhai Wang, Junsong Chen, Zhangyue Yin, Xiaozhe Ren, Jie Fu, Junxian He, Wu Yuan, Qi Liu, Xihui Liu, Yu Li, Hao Dong, Yu Cheng, Ming Zhang, Pheng Ann Heng, Jifeng Dai, Ping Luo, Jingdong Wang, Ji-Rong Wen, Xipeng Qiu, Yike Guo, Hui Xiong, Qun Liu, and Zhenguo Li
If you find this repository helpful, please consider citing:
@article{sun2023survey,
title={A Survey of Reasoning with Foundation Models},
author={Sun, Jiankai and Zheng, Chuanyang and Xie, Enze and Liu, Zhengying and Chu, Ruihang and Qiu, Jianing and Xu, Jiaqi and Ding, Mingyu and Li, Hongyang and Geng, Mengzhe and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11562},
year={2023}
}relevant surveys
-
The Rise and Potential of Large Language Model Based Agents: A Survey - [arXiv] [Link]
-
Multimodal Foundation Models: From Specialists to General-Purpose Assistants - [arXiv] [Tutorial]
-
A Survey on Multimodal Large Language Models - [arXiv] [Link]
-
Self-Supervised Multimodal Learning: A Survey - [arXiv] [Link]
-
Large AI Models in Health Informatics: Applications, Challenges, and the Future - [arXiv] [Paper] [Link]
-
Towards Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Survey - [arXiv] [Paper] [Link]
-
Reasoning with Language Model Prompting: A Survey - [arXiv] [Paper] [Link]
-
Awesome Multimodal Reasoning - [Link]
foundation models
LFMs
-
2023/12|Gemini| Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models - [Paper] -
2023/10|Mistral| Mistral 7B - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/07|Llama 2| Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2023/05|PaLM 2| PaLM 2 Technical Report - -
2023/03|PanGu-Σ| PanGu-Σ: Towards Trillion Parameter Language Model with Sparse Heterogeneous Computing - [Paper] -
2023/03|GPT-4| GPT-4 Technical Report - [Paper] [Blog] -
2023/02|LLaMA| LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2022/11|ChatGPT| Chatgpt: Optimizing language models for dialogue - [Blog] -
2022/04|PaLM| PaLM: Scaling Language Modeling with Pathways - [Paper] [Blog] -
2021/09|FLAN| Finetuned Language Models Are Zero-Shot Learners - -
2021/07|Codex| Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code - -
2021/05|GPT-3| Language Models are Few-Shot Learners - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/04|PanGu-α| PanGu-α: Large-scale Autoregressive Pretrained Chinese Language Models with Auto-parallel Computation - [Paper] [Code] -
2019/08|Sentence-BERT| Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks - -
2019/07|RoBERTa| RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach - -
2018/10|BERT| BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding - [Paper] [Code] [Blog]
VFMs
-
2023/05|SAA+| Segment Any Anomaly without Training via Hybrid Prompt Regularization - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/05|Explain Any Concept| Explain Any Concept: Segment Anything Meets Concept-Based Explanation - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/05|SAM-Track| Segment and Track Anything - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/05|SAMRS| SAMRS: Scaling-up Remote Sensing Segmentation Dataset with Segment Anything Model - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/04|Edit Everything| Edit Everything: A Text-Guided Generative System for Images Editing - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/04|Inpaint Anything| Inpaint Anything: Segment Anything Meets Image Inpainting - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/04|SAM| Segment Anything - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2023/03|VideoMAE V2| VideoMAE V2: Scaling Video Masked Autoencoders with Dual Masking - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/03|Grounding DINO| Grounding DINO: Marrying DINO with Grounded Pre-Training for Open-Set Object Detection - [Paper] [Code] -
2022/03|VideoMAE| VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/12|Stable Diffusion| High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/09|LaMa| Resolution-robust Large Mask Inpainting with Fourier Convolutions - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/03|Swin| Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows - [Paper] [Code] -
2020/10|ViT| An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale - [Paper]
MFMs
-
2023/05|Caption Anything| Caption Anything: Interactive Image Description with Diverse Multimodal Controls - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/05|SAMText| Scalable Mask Annotation for Video Text Spotting - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/04|Text2Seg| Text2Seg: Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation via Text-Guided Visual Foundation Models - [Paper] -
2023/04|MiniGPT-4| MiniGPT-4: Enhancing Vision-Language Understanding with Advanced Large Language Models - -
2023/04|LLaVA| Visual Instruction Tuning - -
2023/04|CLIP Surgery| CLIP Surgery for Better Explainability with Enhancement in Open-Vocabulary Tasks - [Paper] [Code] -
2023/03|UniDiffuser| One Transformer Fits All Distributions in Multi-Modal Diffusion at Scale - -
2023/01|GALIP| GALIP: Generative Adversarial CLIPs for Text-to-Image Synthesis - [Paper] [Code] -
2022/12|Img2Prompt| From Images to Textual Prompts: Zero-shot VQA with Frozen Large Language Models - -
2022/01|BLIP| BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation - -
2021/09|CoOp| Learning to Prompt for Vision-Language Models - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/02|CLIP| Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision - [Paper] [Code] [Blog]
reasoning applications
-
2022/06|Minerva| Solving Quantitative Reasoning Problems with Language Models - [Paper] [Blog] -
2022/06|BIG-bench| Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models - [Paper] [Code] -
2022/05|Zero-shot-CoT| Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners - [Paper] [Code] -
2022/03|STaR| STaR: Bootstrapping Reasoning With Reasoning - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/07|MWP-BERT| MWP-BERT: Numeracy-Augmented Pre-training for Math Word Problem Solving - [Paper] [Code] -
2017/05|AQUA-RAT| Program Induction by Rationale Generation : Learning to Solve and Explain Algebraic Word Problems - [Paper] [Code]
reasoning tasks
commonsense reasoning
-
2023/05|LLM-MCTS| Large Language Models as Commonsense Knowledge for Large-Scale Task Planning - [Paper] [Code] [Project] -
2023/05| Bridging the Gap between Pre-Training and Fine-Tuning for Commonsense Generation - [Paper] [Code] -
2022/11|DANCE| Improving Commonsense in Vision-Language Models via Knowledge Graph Riddles - [Paper] [Code] [Project] -
2022/10|CoCoGen| Language Models of Code are Few-Shot Commonsense Learners - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/10| A Systematic Investigation of Commonsense Knowledge in Large Language Models - [Paper] -
2021/05| Go Beyond Plain Fine-tuning: Improving Pretrained Models for Social Commonsense - [Paper]
-
2019/06|CoS-E| Explain Yourself! Leveraging Language Models for Commonsense Reasoning - [Paper] [Code] -
2018/11|CQA| CommonsenseQA: A Question Answering Challenge Targeting Commonsense Knowledge - [Paper] [Code] [Project] -
2016/12|ConceptNet| ConceptNet 5.5: An Open Multilingual Graph of General Knowledge - [Paper] [Project]
-
2023/10|NEWTON| NEWTON: Are Large Language Models Capable of Physical Reasoning? - [Paper] [Code] [Project] -
2022/03|PACS| PACS: A Dataset for Physical Audiovisual CommonSense Reasoning - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/10|VRDP| Dynamic Visual Reasoning by Learning Differentiable Physics Models from Video and Language - [Paper] [Code] -
2020/05|ESPRIT| ESPRIT: Explaining Solutions to Physical Reasoning Tasks - [Paper] [Code] -
2019/11|PIQA| PIQA: Reasoning about Physical Commonsense in Natural Language - [Paper] [Project]
-
2022/03| Things not Written in Text: Exploring Spatial Commonsense from Visual Signals - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/06|PROST| PROST: Physical Reasoning of Objects through Space and Time - [Paper] [Code] -
2019/02|GQA| GQA: A New Dataset for Real-World Visual Reasoning and Compositional Question Answering - [Paper] [Project]
-
2023/06|CConS| Probing Physical Reasoning with Counter-Commonsense Context - -
2023/05|SummEdits| LLMs as Factual Reasoners: Insights from Existing Benchmarks and Beyond - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/03|RAINBOW| UNICORN on RAINBOW: A Universal Commonsense Reasoning Model on a New Multitask Benchmark - -
2020/11|ProtoQA| ProtoQA: A Question Answering Dataset for Prototypical Common-Sense Reasoning - [Paper] -
2020/10|DrFact| Differentiable Open-Ended Commonsense Reasoning -
2019/11|CommonGen| CommonGen: A Constrained Text Generation Challenge for Generative Commonsense Reasoning -
2019/08|Cosmos QA| Cosmos QA: Machine Reading Comprehension with Contextual Commonsense Reasoning -
2019/08|αNLI| Abductive Commonsense Reasoning - -
2019/08|PHYRE| PHYRE: A New Benchmark for Physical Reasoning - -
2019/07|WinoGrande| WinoGrande: An Adversarial Winograd Schema Challenge at Scale - -
2019/05|MathQA| MathQA: Towards Interpretable Math Word Problem Solving with Operation-Based Formalisms - -
2019/05|HellaSwag| HellaSwag: Can a Machine Really Finish Your Sentence? - -
2019/04|Social IQa| SocialIQA: Commonsense Reasoning about Social Interactions - [Paper] -
2018/08|SWAG| SWAG: A Large-Scale Adversarial Dataset for Grounded Commonsense Inference - -
2002/07|BLEU| BLEU: a Method for Automatic Evaluation of Machine Translation - [Paper]
mathematical reasoning
-
2022/11| Tokenization in the Theory of Knowledge - [Paper] -
2022/06|MultiHiertt| MultiHiertt: Numerical Reasoning over Multi Hierarchical Tabular and Textual Data -
2021/04|MultiModalQA| MultiModalQA: Complex Question Answering over Text, Tables and Images -
2017/05| Program Induction by Rationale Generation : Learning to Solve and Explain Algebraic Word Problems -
2014/04| Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview - [Paper] -
2004| Wittgenstein on philosophy of logic and mathematics - [Paper] -
1989|CLP| Connectionist Learning Procedures - [Paper]
-
2022/09|PromptPG| Dynamic Prompt Learning via Policy Gradient for Semi-structured Mathematical Reasoning -
2022/01| Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2021/03|SVAMP| Are NLP Models really able to Solve Simple Math Word Problems? - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/03|MATH| Measuring Mathematical Problem Solving With the MATH Dataset - -
2016/08| How well do Computers Solve Math Word Problems? Large-Scale Dataset Construction and Evaluation - [Paper] -
2015/09| Learn to Solve Algebra Word Problems Using Quadratic Programming - [Paper] -
2014/06|Alg514| Learning to Automatically Solve Algebra Word Problems - [Paper]
-
2022/12|UniGeo/Geoformer| UniGeo: Unifying Geometry Logical Reasoning via Reformulating Mathematical Expression -
2021/05|GeoQA/NGS| GeoQA: A Geometric Question Answering Benchmark Towards Multimodal Numerical Reasoning -
2021/05|Geometry3K/Inter-GPS| Inter-GPS: Interpretable Geometry Problem Solving with Formal Language and Symbolic Reasoning -
2015/09|GeoS| Solving Geometry Problems: Combining Text and Diagram Interpretation - [Paper]
-
2020/10|Prover| LEGO-Prover: Neural Theorem Proving with Growing Libraries - -
2023/09|Lyra| Lyra: Orchestrating Dual Correction in Automated Theorem Proving -
2023/06|DT-Solver| DT-Solver: Automated Theorem Proving with Dynamic-Tree Sampling Guided by Proof-level Value Function - [Paper] -
2023/05| Decomposing the Enigma: Subgoal-based Demonstration Learning for Formal Theorem Proving -
2023/03|Magnushammer| Magnushammer: A Transformer-based Approach to Premise Selection -
2022/10|DSP| Draft, Sketch, and Prove: Guiding Formal Theorem Provers with Informal Proofs - -
2022/05| Autoformalization with Large Language Models - [Paper] -
2022/05|HTPS| HyperTree Proof Search for Neural Theorem Proving -
2022/05|Thor| Thor: Wielding Hammers to Integrate Language Models and Automated Theorem Provers - -
2022/02| Formal Mathematics Statement Curriculum Learning - -
2021/07|Lean 4| The Lean 4 Theorem Prover and Programming Language - -
2021/02|TacticZero| TacticZero: Learning to Prove Theorems from Scratch with Deep Reinforcement Learning - -
2021/02|PACT| Proof Artifact Co-training for Theorem Proving with Language Models - -
2020/09|GPT-f|Generative Language Modeling for Automated Theorem Proving - -
2019/07| Formal Verification of Hardware Components in Critical Systems - [Paper] -
2019/06|Metamath| A Computer Language for Mathematical Proofs - [Paper] -
2019/05|CoqGym| Learning to Prove Theorems via Interacting with Proof Assistants -
2018/12|AlphaZero| A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play - [Paper] -
2018/04|TacticToe| TacticToe: Learning to Prove with Tactics -
2015/08|Lean| The Lean Theorem Prover (system description) - [Paper] -
2010/07| Three Years of Experience with Sledgehammer, a Practical Link between Automatic and Interactive Theorem Provers - [Paper] -
2010/04| Formal Methods at Intel - An Overview - [Slides] -
2005/07| Combining Simulation and Formal Verification for Integrated Circuit Design Validation - [Paper] -
2003| Extracting a Formally Verified, Fully Executable Compiler from a Proof Assistant - [Paper] -
1996|Coq| The Coq Proof Assistant-Reference Manual - [Project] -
1994|Isabelle| Isabelle: A Generic Theorem Prover - [Paper]
-
2023/07|SciBench| SciBench: Evaluating College-Level Scientific Problem-Solving Abilities of Large Language Models - -
2022/09|ScienceQA| Learn to Explain: Multimodal Reasoning via Thought Chains for Science Question Answering -
2022/03|ScienceWorld| ScienceWorld: Is your Agent Smarter than a 5th Grader? -
2012| Current Topics in Children's Learning and Cognition - [Book]
-
2023/08|Math23K-F/MAWPS-F/FOMAS| Guiding Mathematical Reasoning via Mastering Commonsense Formula Knowledge - [Paper] -
2023/07|ARB| ARB: Advanced Reasoning Benchmark for Large Language Models - -
2023/05|SwiftSage| SwiftSage: A Generative Agent with Fast and Slow Thinking for Complex Interactive Tasks - -
2023/05|TheoremQA| TheoremQA: A Theorem-driven Question Answering dataset - -
2022/10|MGSM| Language Models are Multilingual Chain-of-Thought Reasoners - [Paper] [Code] -
2021/10|GSM8K| Training Verifiers to Solve Math Word Problems - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2021/10|IconQA| IconQA: A New Benchmark for Abstract Diagram Understanding and Visual Language Reasoning - -
2021/09|FinQA| FinQA: A Dataset of Numerical Reasoning over Financial Data - -
2021/08|MBPP/MathQA-Python| Program Synthesis with Large Language Models -
2021/08|HiTab/EA| HiTab: A Hierarchical Table Dataset for Question Answering and Natural Language Generation -
2021/07|HumanEval/Codex| Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code - -
2021/06|ASDiv/CLD| A Diverse Corpus for Evaluating and Developing English Math Word Problem Solvers - -
2021/06|AIT-QA| AIT-QA: Question Answering Dataset over Complex Tables in the Airline Industry - -
2021/05|APPS| Measuring Coding Challenge Competence With APPS - -
2021/05|TAT-QA| TAT-QA: A Question Answering Benchmark on a Hybrid of Tabular and Textual Content in Finance -
2021/03|SVAMP| Are NLP Models really able to Solve Simple Math Word Problems? - -
2021/01|TSQA/MAP/MRR| TSQA: Tabular Scenario Based Question Answering -
2020/10|HMWP| Semantically-Aligned Universal Tree-Structured Solver for Math Word Problems - -
2020/04|HybridQA| HybridQA: A Dataset of Multi-Hop Question Answering over Tabular and Textual Data -
2019/03|DROP| DROP: A Reading Comprehension Benchmark Requiring Discrete Reasoning Over Paragraphs - -
2019|NaturalQuestions| Natural Questions: A Benchmark for Question Answering Research - [Paper] -
2018/09|HotpotQA| HotpotQA: A Dataset for Diverse, Explainable Multi-hop Question Answering - -
2018/09|Spider| Spider: A Large-Scale Human-Labeled Dataset for Complex and Cross-Domain Semantic Parsing and Text-to-SQL Task - -
2018/03|ComplexWebQuestions| The Web as a Knowledge-base for Answering Complex Questions - -
2017/12|MetaQA| Variational Reasoning for Question Answering with Knowledge Graph - -
2017/09|GEOS++| From Textbooks to Knowledge: A Case Study in Harvesting Axiomatic Knowledge from Textbooks to Solve Geometry Problems - [Paper] -
2017/09|Math23k| Deep Neural Solver for Math Word Problems - [Paper] -
2017/08|WikiSQL/Seq2SQL| Seq2SQL: Generating Structured Queries from Natural Language using Reinforcement Learning - -
2017/08| Learning to Solve Geometry Problems from Natural Language Demonstrations in Textbooks - [Paper] -
2017/05|TriviaQA| TriviaQA: A Large Scale Distantly Supervised Challenge Dataset for Reading Comprehension - -
2017/05|GeoShader| Synthesis of Solutions for Shaded Area Geometry Problems - [Paper] -
2016/09|DRAW-1K| Annotating Derivations: A New Evaluation Strategy and Dataset for Algebra Word Problems - -
2016/08|WebQSP| The Value of Semantic Parse Labeling for Knowledge Base Question Answering - [Paper] -
2016/06|SQuAD| SQuAD: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text - -
2016/06|WikiMovies| Key-Value Memory Networks for Directly Reading Documents - -
2016/06|MAWPS| MAWPS: A Math Word Problem Repository - [Paper] -
2015/09|Dolphin1878| Automatically Solving Number Word Problems by Semantic Parsing and Reasoning - [Paper] -
2015/08|WikiTableQA| Compositional Semantic Parsing on Semi-Structured Tables - -
2015|SingleEQ| Parsing Algebraic Word Problems into Equations - [Paper] -
2015|DRAW| DRAW: A Challenging and Diverse Algebra Word Problem Set - [Paper] -
2014/10|Verb395| Learning to Solve Arithmetic Word Problems with Verb Categorization - [Paper] -
2013/10|WebQuestions| Semantic Parsing on Freebase from Question-Answer Pairs - [Paper] -
2013/08|Free917| Large-scale Semantic Parsing via Schema Matching and Lexicon Extension - [Paper] -
2002/04|NMI| Cluster Ensembles - A Knowledge Reuse Framework for Combining Multiple Partitions - [Paper] -
1990|ATIS| The ATIS Spoken Language Systems Pilot Corpus - [Paper]
logical reasoning
-
2023/10|LogiGLUE| Towards LogiGLUE: A Brief Survey and A Benchmark for Analyzing Logical Reasoning Capabilities of Language Models - -
2023/05|Logic-LM| Logic-LM: Empowering Large Language Models with Symbolic Solvers for Faithful Logical Reasoning - -
2023/03|LEAP| Explicit Planning Helps Language Models in Logical Reasoning - -
2023/03| Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4 - -
2022/10|Entailer| Entailer: Answering Questions with Faithful and Truthful Chains of Reasoning - -
2022/06|NeSyL| Weakly Supervised Neural Symbolic Learning for Cognitive Tasks - [Paper] -
2022/05|NeuPSL| NeuPSL: Neural Probabilistic Soft Logic - -
2022/05|NLProofS| Generating Natural Language Proofs with Verifier-Guided Search - -
2022/05|Least-to-Most Prompting| Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2022/05|SI| Selection-Inference: Exploiting Large Language Models for Interpretable Logical Reasoning - -
2022/03| Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thought Reasoning in Language Models - -
2021/11|NSPS| Neuro-Symbolic Program Search for Autonomous Driving Decision Module Design - [Paper] -
2021/09|DeepProbLog| Neural probabilistic logic programming in DeepProbLog - [Paper] -
2021/08|GABL| Abductive Learning with Ground Knowledge Base - [Paper] -
2020/02|RuleTakers| Transformers as Soft Reasoners over Language - -
2019/12|NMN-Drop| Neural Module Networks for Reasoning over Text - -
2019/04|NS-CL| The Neuro-Symbolic Concept Learner: Interpreting Scenes, Words, and Sentences From Natural Supervision - -
2012| Logical Reasoning and Learning - [Paper]
2022/09| Propositional Reasoning via Neural Transformer Language Models - [Paper]
-
2021/06|ILP| Inductive logic programming at 30 - [Paper] -
2011| Statistical Relational Learning - [Paper]
-
2022/10|PrOntoQA| Language Models Are Greedy Reasoners: A Systematic Formal Analysis of Chain-of-Thought - -
2022/09|FOLIO| FOLIO: Natural Language Reasoning with First-Order Logic - -
2020/12|ProofWriterProofWriter: Generating Implications, Proofs, and Abductive Statements over Natural Language -
causal reasoning
-
2023/08| Causal Parrots: Large Language Models May Talk Causality But Are Not Causal -
2023/07| Causal Discovery with Language Models as Imperfect Experts - -
2023/06|Corr2Cause| Can Large Language Models Infer Causation from Correlation? - -
2023/05|Code-LLMs| The Magic of IF: Investigating Causal Reasoning Abilities in Large Language Models of Code - -
2023/04| Understanding Causality with Large Language Models: Feasibility and Opportunities - -
2023/04| Causal Reasoning and Large Language Models: Opening a New Frontier for Causality - -
2023/03| Can large language models build causal graphs? - -
2023/01| Causal-Discovery Performance of ChatGPT in the context of Neuropathic Pain Diagnosis - -
2022/09| Probing for Correlations of Causal Facts: Large Language Models and Causality - [Paper] -
2022/07| Can Large Language Models Distinguish Cause from Effect? - [Paper] -
2021/08| Learning Faithful Representations of Causal Graphs - [Paper] -
2021/05|InferBERT| InferBERT: A Transformer-Based Causal Inference Framework for Enhancing Pharmacovigilance - [Paper] -
2021/02| Towards Causal Representation Learning - -
2020/05|CausaLM| CausaLM: Causal Model Explanation Through Counterfactual Language Models - -
2019/06| Neuropathic Pain Diagnosis Simulator for Causal Discovery Algorithm Evaluation - -
2017| Elements of Causal Inference: Foundations and Learning Algorithms - [Book] -
2016| Actual Causality - [Book] -
2013| Causal Reasoning - [Paper]
-
2023/05| Counterfactual reasoning: Testing language models' understanding of hypothetical scenarios - -
2007| The Rational Imagination: How People Create Alternatives to Reality - [Paper] -
1986| Norm theory: Comparing reality to its alternatives - [Paper]
-
2021/12|CRASS| CRASS: A Novel Data Set and Benchmark to Test Counterfactual Reasoning of Large Language Models - -
2021/08|Arctic sea ice| Benchmarking of Data-Driven Causality Discovery Approaches in the Interactions of Arctic Sea Ice and Atmosphere - [Paper] -
2014/12|CauseEffectPairs| Distinguishing cause from effect using observational data: methods and benchmarks -
visual reasoning
-
2022/11|G-VUE| Perceive, Ground, Reason, and Act: A Benchmark for General-purpose Visual Representation - -
2021/03|VLGrammar| VLGrammar: Grounded Grammar Induction of Vision and Language - -
2020/12| Attention over learned object embeddings enables complex visual reasoning -
-
2023/08|PointLLM| PointLLM: Empowering Large Language Models to Understand Point Clouds - -
2023/08|3D-VisTA| 3D-VisTA: Pre-trained Transformer for 3D Vision and Text Alignment - -
2023/07|3D-LLM| 3D-LLM: Injecting the 3D World into Large Language Models - -
2022/10|SQA3D| SQA3D: Situated Question Answering in 3D Scenes -
-
2021/12|PTR| PTR: A Benchmark for Part-based Conceptual, Relational, and Physical Reasoning - -
2019/05|OK-VQA| OK-VQA: A Visual Question Answering Benchmark Requiring External Knowledge - -
2016/12|CLEVR| CLEVR: A Diagnostic Dataset for Compositional Language and Elementary Visual Reasoning -
audio reasoning
-
2022/03|SUPERB-SG| SUPERB-SG: Enhanced Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark for Semantic and Generative Capabilities - -
2022/02|Data2Vec| data2vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language - -
2021/10|WavLM| WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing - -
2021/06|HuBERT| HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units - -
2021/05|SUPERB| SUPERB: Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark - -
2020/10|Speech SIMCLR| Speech SIMCLR: Combining Contrastive and Reconstruction Objective for Self-supervised Speech Representation Learning - -
2020/06|Wav2Vec 2.0| wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations - -
2020/05|Conformer| Conformer: Convolution-augmented Transformer for Speech Recognition - -
2019/10|Mockingjay| Mockingjay: Unsupervised Speech Representation Learning with Deep Bidirectional Transformer Encoders - -
2019/04|APC| An Unsupervised Autoregressive Model for Speech Representation Learning - -
2018/07|CPC| Representation Learning with Contrastive Predictive Coding - -
2018/04|Speech-Transformer| Speech-Transformer: A No-Recurrence Sequence-to-Sequence Model for Speech Recognition - [Paper] -
2017/11|VQ-VAE| Neural Discrete Representation Learning - -
2017/08| Large-Scale Domain Adaptation via Teacher-Student Learning -
-
2022/03|SUPERB-SG| SUPERB-SG: Enhanced Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark for Semantic and Generative Capabilities - -
2021/11|VoxPopuli/XLS-R| XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale - -
2021/05|SUPERB| SUPERB: Speech processing Universal PERformance Benchmark - -
2020/12|Multilingual LibriSpeech| MLS: A Large-Scale Multilingual Dataset for Speech Research - -
2020/05|Didi Dictation/Didi Callcenter| A Further Study of Unsupervised Pre-training for Transformer Based Speech Recognition - -
2019/12|Libri-Light| Libri-Light: A Benchmark for ASR with Limited or No Supervision - -
2019/12|Common Voice| Common Voice: A Massively-Multilingual Speech Corpus -
multimodal reasoning
2023/01|BLIP-2| BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models -
-
2023/10|DALL·E 3| Improving Image Generation with Better Captions - [Paper] [Project] -
2023/06|Kosmos-2| Kosmos-2: Grounding Multimodal Large Language Models to the World - -
2023/05|BiomedGPT| BiomedGPT: A Unified and Generalist Biomedical Generative Pre-trained Transformer for Vision, Language, and Multimodal Tasks - -
2023/03|Visual ChatGPT| Visual ChatGPT: Talking, Drawing and Editing with Visual Foundation Models - -
2023/02|Kosmos-1| Language Is Not All You Need: Aligning Perception with Language Models - -
2022/07|Midjourney- [Project] -
2022/04|Flamingo| Flamingo: a Visual Language Model for Few-Shot Learning - -
2021/12|MAGMA| MAGMA -- Multimodal Augmentation of Generative Models through Adapter-based Finetuning -
-
2023/09|Q-Bench| Q-Bench: A Benchmark for General-Purpose Foundation Models on Low-level Vision - -
2023/05|DetGPT| DetGPT: Detect What You Need via Reasoning - -
2023/03|Vicuna| Vicuna: An Open-Source Chatbot Impressing GPT-4 with 90%* ChatGPT Quality - [Blog] -
2022/12|DePlot| DePlot: One-shot visual language reasoning by plot-to-table translation - -
2022/12|MatCha| MatCha: Enhancing Visual Language Pretraining with Math Reasoning and Chart Derendering -
-
2023/06|LVLM-eHub| LVLM-eHub: A Comprehensive Evaluation Benchmark for Large Vision-Language Models - -
2023/06|LAMM| LAMM: Language-Assisted Multi-Modal Instruction-Tuning Dataset, Framework, and Benchmark - -
2023/05|AttackVLM| On Evaluating Adversarial Robustness of Large Vision-Language Models - -
2023/05|POPE| Evaluating Object Hallucination in Large Vision-Language Models - -
2023/05|MultimodalOCR| On the Hidden Mystery of OCR in Large Multimodal Models - -
2022/10|ObjMLM| Plausible May Not Be Faithful: Probing Object Hallucination in Vision-Language Pre-training -
2022/06|RAVEN/ARC| Evaluating Understanding on Conceptual Abstraction Benchmarks - -
2021/06|LARC| Communicating Natural Programs to Humans and Machines - -
2014/11|CIDEr/PASCAL-50S/ABSTRACT-50S| CIDEr: Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation -
agent reasoning
-
2023/11|OpenFlamingo| Vision-Language Foundation Models as Effective Robot Imitators - -
2023/07|RT-2| RT-2: Vision-Language-Action Models Transfer Web Knowledge to Robotic Control - -
2023/05|RAP| Reasoning with Language Model is Planning with World Model - -
2022/12|RT-1| RT-1: Robotics Transformer for Real-World Control at Scale -
2022/10| Skill Induction and Planning with Latent Language - -
2022/05|Gato| A Generalist Agent - -
2022/04|SMs| Socratic Models: Composing Zero-Shot Multimodal Reasoning with Language - -
2022/02| | Pre-Trained Language Models for Interactive Decision-Making - -
2022/01|Language-Planner| Language Models as Zero-Shot Planners: Extracting Actionable Knowledge for Embodied Agents - -
2021/11| Value Function Spaces: Skill-Centric State Abstractions for Long-Horizon Reasoning - -
2020/09| Visually-Grounded Planning without Vision: Language Models Infer Detailed Plans from High-level Instructions - -
2016/01|AlphaGo| Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search - [Paper] -
2014/05| Gesture in reasoning: An embodied perspective - [Paper]
-
2022/11|PAL| PAL: Program-aided Language Models - -
2022/09|ProgPrompt| ProgPrompt: Generating Situated Robot Task Plans using Large Language Models - -
2022/09|Code as Policies| Code as Policies: Language Model Programs for Embodied Control - -
2022/04|SayCan| Do As I Can, Not As I Say: Grounding Language in Robotic Affordances - -
2012| Introspective Learning and Reasoning - [Paper]
-
2023/06|Statler| Statler: State-Maintaining Language Models for Embodied Reasoning - -
2023/02|Planner-Actor-Reporter| Collaborating with language models for embodied reasoning - -
2023/02|Toolformer| Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools - -
2022/12|LLM-Planner| LLM-Planner: Few-Shot Grounded Planning for Embodied Agents with Large Language Models - -
2022/10|ReAct| ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models - -
2022/10|Self-Ask| Measuring and Narrowing the Compositionality Gap in Language Models - -
2022/07|Inner Monologue| Inner Monologue: Embodied Reasoning through Planning with Language Models -
-
2023/07|Federated LLM| Federated Large Language Model: A Position Paper - -
2023/07| Self-Adaptive Large Language Model (LLM)-Based Multiagent Systems - -
2023/07|Co-LLM-Agents| Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models - -
2023/05| Improving Factuality and Reasoning in Language Models through Multiagent Debate - -
2017/02|FIoT| FIoT: An agent-based framework for self-adaptive and self-organizing applications based on the Internet of Things - [Paper] -
2004| A Practical Guide to the IBM Autonomic Computing Toolkit - [Book]
-
2023/10| Driving through the Concept Gridlock: Unraveling Explainability Bottlenecks in Automated Driving - -
2023/10| Vision Language Models in Autonomous Driving and Intelligent Transportation Systems - -
2023/10|DriveGPT4| DriveGPT4: Interpretable End-to-end Autonomous Driving via Large Language Model - -
2023/09|MotionLM| MotionLM: Multi-Agent Motion Forecasting as Language Modeling - -
2023/06| End-to-end Autonomous Driving: Challenges and Frontiers - -
2023/04| Graph-based Topology Reasoning for Driving Scenes - -
2022/09| Delving into the Devils of Bird's-eye-view Perception: A Review, Evaluation and Recipe - -
2021/11| Artificial intelligence: A powerful paradigm for scientific research - [Paper]
-
2023/09|NuPrompt/PromptTrack| Language Prompt for Autonomous Driving - -
2023/08|DriveLM| Drive on Language: Unlocking the future where autonomous driving meets the unlimited potential of language - [Code] -
2023/07|LCTGen| Language Conditioned Traffic Generation -
2023/05|NuScenes-QA| NuScenes-QA: A Multi-modal Visual Question Answering Benchmark for Autonomous Driving Scenario - -
2022/06|BEHAVIOR-1K| BEHAVIOR-1K: A Benchmark for Embodied AI with 1,000 Everyday Activities and Realistic Simulation - -
2021/08|iGibson| iGibson 2.0: Object-Centric Simulation for Robot Learning of Everyday Household Tasks - -
2021/06|Habitat 2.0| Habitat 2.0: Training Home Assistants to Rearrange their Habitatz - -
2020/04|RoboTHOR| RoboTHOR: An Open Simulation-to-Real Embodied AI Platform - -
2019/11|HAD| Grounding Human-to-Vehicle Advice for Self-driving Vehicles - -
2019/04|Habitat| Habitat: A Platform for Embodied AI Research - -
2018/08|Gibson| Gibson Env: Real-World Perception for Embodied Agents - -
2018/06|VirtualHome| VirtualHome: Simulating Household Activities via Programs -
other tasks and applications
2023/02|ToM| Theory of Mind Might Have Spontaneously Emerged in Large Language Models -
-
2022/09|MetNet-2| Deep learning for twelve hour precipitation forecasts - [Paper] -
2023/07|Pangu-Weather| Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks - [Paper]
-
2023/06|BoardgameQA| BoardgameQA: A Dataset for Natural Language Reasoning with Contradictory Information - -
2021/10|CURIOUS| Think about it! Improving defeasible reasoning by first modeling the question scenario - -
2020/11|Defeasible NLI/δ-NLI| Thinking Like a Skeptic: Defeasible Inference in Natural Language - [Paper] -
2020/04|KACC| KACC: A Multi-task Benchmark for Knowledge Abstraction, Concretization and Completion - -
2009/01| A Recursive Semantics for Defeasible Reasoning - [Paper]
-
2023/10|GPT4V-Medical-Report| Multimodal ChatGPT for Medical Applications: an Experimental Study of GPT-4V - -
2023/10|VisionFM| VisionFM: a Multi-Modal Multi-Task Vision Foundation Model for Generalist Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence - -
2023/09| The Dawn of LMMs: Preliminary Explorations with GPT-4V(ision) - -
2023/09|RETFound| A foundation model for generalizable disease detection from retinal images - [Paper] -
2023/08|ELIXR| ELIXR: Towards a general purpose X-ray artificial intelligence system through alignment of large language models and radiology vision encoders - -
2023/07|Med-PaLM M| Towards Generalist Biomedical AI - -
2023/06|LLaVA-Med| LLaVA-Med: Training a Large Language-and-Vision Assistant for Biomedicine in One Day - -
2023/05|Med-PaLM 2| Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models -
-
2023/07|Prot2Text| Prot2Text: Multimodal Protein's Function Generation with GNNs and Transformers - -
2023/07|Uni-RNA| Uni-RNA: Universal Pre-Trained Models Revolutionize RNA Research - -
2023/07|RFdiffusion| De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion - [Paper] -
2023/06|HyenaDNA| HyenaDNA: Long-Range Genomic Sequence Modeling at Single Nucleotide Resolution - -
2023/06|DrugGPT| DrugGPT: A GPT-based Strategy for Designing Potential Ligands Targeting Specific Proteins - -
2023/04|GeneGPT| GeneGPT: Augmenting Large Language Models with Domain Tools for Improved Access to Biomedical Information - -
2023/04| Drug discovery companies are customizing ChatGPT: here’s how - [News] -
2023/01|ProGen| Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families - [Paper] -
2022/06|ProGen2| ProGen2: Exploring the Boundaries of Protein Language Models - -
2021/07|AlphaFold| Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold - [Paper]
-
2022/12|Fine-tune-CoT| Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers - -
2021/09|PlaTe| PlaTe: Visually-Grounded Planning with Transformers in Procedural Tasks -
reasoning techniques
pre-training
-
2023/07|peS2o| peS2o (Pretraining Efficiently on S2ORC) Dataset - [Code] -
2023/05|ROOTS/BLOOM| The BigScience ROOTS Corpus: A 1.6TB Composite Multilingual Dataset - -
2023/04|RedPajama| RedPajama: an Open Dataset for Training Large Language Models - [Code] -
2020/12|The Pile| The Pile: An 800GB Dataset of Diverse Text for Language Modeling - -
2020/04|Reddit| Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot - -
2020/04|CLUE| CLUE: A Chinese Language Understanding Evaluation Benchmark - -
2019/10|C4| Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer - -
2013/10|Gutenberg| Complexity of Word Collocation Networks: A Preliminary Structural Analysis
-
2023/06|I2E/MOFI| MOFI: Learning Image Representations from Noisy Entity Annotated Images - -
2022/01|SWAGRevisiting Weakly Supervised Pre-Training of Visual Perception Models - -
2021/04|ImageNet-21K| ImageNet-21K Pretraining for the Masses - -
2017/07|JFT| Revisiting Unreasonable Effectiveness of Data in Deep Learning Era - -
2014/09|ImageNet| ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge -
-
2023/09|Point-Bind| Point-Bind & Point-LLM: Aligning Point Cloud with Multi-modality for 3D Understanding, Generation, and Instruction Following - -
2023/05|ImageBind| ImageBind: One Embedding Space To Bind Them All - -
2023/04|DataComp| DataComp: In search of the next generation of multimodal datasets - -
2022/10|LAION-5B| LAION-5B: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models - -
2022/08|Shutterstock| Quality Not Quantity: On the Interaction between Dataset Design and Robustness of CLIP - -
2022/08|COYO-700M| COYO-700M: Image-Text Pair Dataset - [Code] -
2022/04|M3W| Flamingo: a Visual Language Model for Few-Shot Learning - -
2021/11|RedCaps| RedCaps: web-curated image-text data created by the people, for the people - -
2021/11|LAION-400M| LAION-400M: Open Dataset of CLIP-Filtered 400 Million Image-Text Pairs - -
2021/03|WIT| WIT: Wikipedia-based Image Text Dataset for Multimodal Multilingual Machine Learning - -
2011/12|Im2Text/SBU| Im2Text: Describing Images Using 1 Million Captioned Photographs -
2023/04| Decoder-Only or Encoder-Decoder? Interpreting Language Model as a Regularized Encoder-Decoder -
-
2019/10|BART| BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension - -
2019/10|T5| Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer - -
2018/10|BERT| BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2017/06|Transformer| Attention Is All You Need -
-
2023/07|Llama 2| Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2023/02|LLaMA| LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models - [Paper] [Code] [Blog] -
2022/11|BLOOM| BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model - -
2022/10|GLM| GLM-130B: An Open Bilingual Pre-trained Model - -
2022/05|OPT| OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models - -
2021/12|Gopher| Scaling Language Models: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Training Gopher - -
2021/05|GPT-3| Language Models are Few-Shot Learners - [Paper] [Code] -
2019/02|GPT-2| Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners - [Paper] -
2018/06|GPT-1| Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training - [Paper]
-
2023/05|LaCLIP| Improving CLIP Training with Language Rewrites - -
2023/04|DetCLIPv2| DetCLIPv2: Scalable Open-Vocabulary Object Detection Pre-training via Word-Region Alignment - -
2022/12|FLIP| Scaling Language-Image Pre-training via Masking - -
2022/09|DetCLIP| DetCLIP: Dictionary-Enriched Visual-Concept Paralleled Pre-training for Open-world Detection - -
2022/04|K-LITE| K-LITE: Learning Transferable Visual Models with External Knowledge - -
2021/11|FILIP| FILIP: Fine-grained Interactive Language-Image Pre-Training - -
2021/02|CLIP| Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision - [Paper] [Code] [Blog]
-
2023/09|StreamingLLM| Efficient Streaming Language Models with Attention Sinks - -
2023/07|RetNet| Retentive Network: A Successor to Transformer for Large Language Models - -
2023/07| | LongNet: Scaling Transformers to 1,000,000,000 Tokens - -
2023/05|RWKV| RWKV: Reinventing RNNs for the Transformer Era - -
2023/02|Hyena| Hyena Hierarchy: Towards Larger Convolutional Language Models - -
2022/12|H3| Hungry Hungry Hippos: Towards Language Modeling with State Space Models - -
2022/06|GSS| Long Range Language Modeling via Gated State Spaces - -
2022/03|DSS| Diagonal State Spaces are as Effective as Structured State Spaces - -
2021/10|S4| Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces -
fine-tuning
-
2023/09|MetaMath| MetaMath: Bootstrap Your Own Mathematical Questions for Large Language Models - -
2023/09|MAmmoTH| MAmmoTH: Building Math Generalist Models through Hybrid Instruction Tuning - -
2023/08|WizardMath| WizardMath: Empowering Mathematical Reasoning for Large Language Models via Reinforced Evol-Instruct - -
2023/08|RFT| Scaling Relationship on Learning Mathematical Reasoning with Large Language Models - -
2023/05|PRM800K/ `` | Let's Verify Step by Step - -
2023/05|Distilling Step-by-Step| Distilling Step-by-Step! Outperforming Larger Language Models with Less Training Data and Smaller Model Sizes - -
2023/01| Specializing Smaller Language Models towards Multi-Step Reasoning - -
2022/12|Fine-tune-CoT| Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers - -
2022/12| Teaching Small Language Models to Reason - -
2022/10| Large Language Models Can Self-Improve - -
2022/10| Explanations from Large Language Models Make Small Reasoners Better -
-
2023/03|LLaMA-Adapter| LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-tuning of Language Models with Zero-init Attention - -
2022/05|AdaMix| AdaMix: Mixture-of-Adaptations for Parameter-efficient Model Tuning - -
2021/10| Towards a Unified View of Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning - -
2021/06|Compacter| Compacter: Efficient Low-Rank Hypercomplex Adapter Layers - -
2020/04|MAD-X| MAD-X: An Adapter-Based Framework for Multi-Task Cross-Lingual Transfer - -
2019/02|Adapter| Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for NLP -
-
2023/05|QLoRA| QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs - -
2023/03|AdaLoRA| Adaptive Budget Allocation for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning - -
2022/12|KronA| KronA: Parameter Efficient Tuning with Kronecker Adapter - -
2022/10|DyLoRA| DyLoRA: Parameter Efficient Tuning of Pre-trained Models using Dynamic Search-Free Low-Rank Adaptation - -
2021/06|LoRA| LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models -
-
2021/10|P-Tuning v2| P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks - -
2021/04|Prompt Tuning| The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning - -
2021/04|OptiPrompt| Factual Probing Is [MASK]: Learning vs. Learning to Recall - -
2021/03|P-Tuning| GPT Understands, Too - -
2021/01|Prefix-Tuning| Prefix-Tuning: Optimizing Continuous Prompts for Generation -
-
2023/04|DiffFit| DiffFit: Unlocking Transferability of Large Diffusion Models via Simple Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning - -
2022/10|SSF| Scaling & Shifting Your Features: A New Baseline for Efficient Model Tuning - -
2021/09|Child-Tuning| Raise a Child in Large Language Model: Towards Effective and Generalizable Fine-tuning - -
2021/06|BitFit| BitFit: Simple Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning for Transformer-based Masked Language-models -
-
2023/10|LLaVA-1.5| Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning - -
2023/05|MMA/LaVIN| Cheap and Quick: Efficient Vision-Language Instruction Tuning for Large Language Models - -
2023/04|LLaMA-Adapter V2| LLaMA-Adapter V2: Parameter-Efficient Visual Instruction Model - -
2023/04|LLaVA| Visual Instruction Tuning - -
2023/02|RepAdapter| Towards Efficient Visual Adaption via Structural Re-parameterization -
alignment training
-
2023/06|Dolly| Free Dolly: Introducing the World's First Truly Open Instruction-Tuned LLM - [Code] -
2023/04|LongForm| LongForm: Optimizing Instruction Tuning for Long Text Generation with Corpus Extraction - -
2023/04|COIG| Chinese Open Instruction Generalist: A Preliminary Release - -
2023/04|OpenAssistant Conversations| OpenAssistant Conversations -- Democratizing Large Language Model Alignment - -
2023/01|Flan 2022| The Flan Collection: Designing Data and Methods for Effective Instruction Tuning - -
2022/11|xP3| Crosslingual Generalization through Multitask Finetuning - -
2022/04|Super-NaturalInstructions| Super-NaturalInstructions: Generalization via Declarative Instructions on 1600+ NLP Tasks - -
2021/11|ExT5| ExT5: Towards Extreme Multi-Task Scaling for Transfer Learning - -
2021/10|MetaICL| MetaICL: Learning to Learn In Context - -
2021/10|P3| Multitask Prompted Training Enables Zero-Shot Task Generalization - -
2021/04|CrossFit| CrossFit: A Few-shot Learning Challenge for Cross-task Generalization in NLP - -
2021/04|NATURAL INSTRUCTIONS| Cross-Task Generalization via Natural Language Crowdsourcing Instructions - -
2020/05|UnifiedQA| UnifiedQA: Crossing Format Boundaries With a Single QA System -
-
2023/08|Instruction Backtranslation| Self-Alignment with Instruction Backtranslation - -
2023/05|Dynosaur| Dynosaur: A Dynamic Growth Paradigm for Instruction-Tuning Data Curation - -
2023/05|UltraChat| Enhancing Chat Language Models by Scaling High-quality Instructional Conversations - -
2023/05|CoT Collection| The CoT Collection: Improving Zero-shot and Few-shot Learning of Language Models via Chain-of-Thought Fine-Tuning - -
2023/05|CoEdIT| CoEdIT: Text Editing by Task-Specific Instruction Tuning - -
2023/04|LaMini-LM| LaMini-LM: A Diverse Herd of Distilled Models from Large-Scale Instructions - -
2023/04|GPT-4-LLM| Instruction Tuning with GPT-4 - -
2023/04|Koala| Koala: A Dialogue Model for Academic Research - [Blog] -
2023/03|Alpaca| Alpaca: A Strong, Replicable Instruction-Following Model - [Blog] -
2023/03|GPT4All| GPT4All: Training an Assistant-style Chatbot with Large Scale Data Distillation from GPT-3.5-Turbo - [Code] -
2022/12|OPT-IML/OPT-IML Bench| OPT-IML: Scaling Language Model Instruction Meta Learning through the Lens of Generalization - -
2022/12|Self-Instruc| Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Models with Self-Generated Instructions - -
2022/12|Unnatural Instructions| Unnatural Instructions: Tuning Language Models with (Almost) No Human Labor -
-
2023/06|APA| Fine-Tuning Language Models with Advantage-Induced Policy Alignment - -
2023/04|RAFT| RAFT: Reward rAnked FineTuning for Generative Foundation Model Alignment - -
2022/03|InstructGPT/RLHF| Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback -
-
2023/06|PRO| Preference Ranking Optimization for Human Alignment - -
2023/05|DPO| Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model - -
2023/04|RRHF| RRHF: Rank Responses to Align Language Models with Human Feedback without tears - -
2022/09|SLiC| Calibrating Sequence likelihood Improves Conditional Language Generation -
mixture of experts
-
2023/06| An Efficient General-Purpose Modular Vision Model via Multi-Task Heterogeneous Training - -
2023/03|MixedAE| Mixed Autoencoder for Self-supervised Visual Representation Learning - -
2022/12|Mod-Squad| Mod-Squad: Designing Mixture of Experts As Modular Multi-Task Learners - -
2022/04|MoEBERT| MoEBERT: from BERT to Mixture-of-Experts via Importance-Guided Adaptation - -
2021/12|GLaM| GLaM: Efficient Scaling of Language Models with Mixture-of-Experts - -
2021/07|WideNet| Go Wider Instead of Deeper - -
2021/01|Switch Transformers| Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity - -
2020/06|GShard| GShard: Scaling Giant Models with Conditional Computation and Automatic Sharding - -
2017/01|Sparsely-Gated Mixture-of-Experts| Outrageously Large Neural Networks: The Sparsely-Gated Mixture-of-Experts Layer - -
1991/03| Adaptive Mixtures of Local Experts - [Paper]
in-context learning
-
2022/10|FLAN-T5| Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models - -
2021/05|GPT-3| Language Models are Few-Shot Learners - [Paper] [Code]
-
2022/12| Diverse Demonstrations Improve In-context Compositional Generalization - -
2022/11| Complementary Explanations for Effective In-Context Learning - -
2022/10|Auto-CoT| Automatic Chain of Thought Prompting in Large Language Models - -
2022/10|Complex CoT| Complexity-Based Prompting for Multi-Step Reasoning - -
2022/10|EmpGPT-3| Does GPT-3 Generate Empathetic Dialogues? A Novel In-Context Example Selection Method and Automatic Evaluation Metric for Empathetic Dialogue Generation - [Paper] -
2022/09| Selective Annotation Makes Language Models Better Few-Shot Learners - -
2021/01| What Makes Good In-Context Examples for GPT-3? -
-
2023/10|DQ-LoRe| DQ-LoRe: Dual Queries with Low Rank Approximation Re-ranking for In-Context Learning - -
2023/07|LLM-R| Learning to Retrieve In-Context Examples for Large Language Models - -
2023/05|Dr.ICL| Dr.ICL: Demonstration-Retrieved In-context Learning - -
2023/02|LENS| Finding Support Examples for In-Context Learning - -
2023/02|CEIL| Compositional Exemplars for In-context Learning - -
2021/12| Learning To Retrieve Prompts for In-Context Learning -
-
2023/05|Plan-and-Solve| Plan-and-Solve Prompting: Improving Zero-Shot Chain-of-Thought Reasoning by Large Language Models - -
2022/05|Zero-shot-CoT| Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners - [Paper] [Code]
-
2023/07|SoT| Skeleton-of-Thought: Large Language Models Can Do Parallel Decoding - -
2023/05|Code Prompting| Code Prompting: a Neural Symbolic Method for Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2023/05|GoT| Beyond Chain-of-Thought, Effective Graph-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2023/05|ToT| Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models - -
2023/03|MathPrompter| MathPrompter: Mathematical Reasoning using Large Language Models - -
2022/11|PoT| Program of Thoughts Prompting: Disentangling Computation from Reasoning for Numerical Reasoning Tasks - -
2022/11|PAL| PAL: Program-aided Language Models - -
2022/10|Auto-CoT| Automatic Chain of Thought Prompting in Large Language Models - -
2022/10|Complex CoT| Complexity-Based Prompting for Multi-Step Reasoning - -
2022/05|Least-to-Most Prompting| Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2022/01| Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models -
-
2023/05|RAP| Reasoning with Language Model is Planning with World Model - -
2023/05| Automatic Model Selection with Large Language Models for Reasoning - -
2023/05|AdaptiveConsistency| Let's Sample Step by Step: Adaptive-Consistency for Efficient Reasoning and Coding with LLMs - -
2023/05|ToT| Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models - -
2023/05|ToT| Large Language Model Guided Tree-of-Thought - -
2023/05| Self-Evaluation Guided Beam Search for Reasoning - -
2022/10|Complex CoT| Complexity-Based Prompting for Multi-Step Reasoning - -
2022/06|DIVERSE| Making Large Language Models Better Reasoners with Step-Aware Verifier - -
2022/03| Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thought Reasoning in Language Models -
-
2023/02|LLM-Augmenter| Check Your Facts and Try Again: Improving Large Language Models with External Knowledge and Automated Feedback - -
2022/10|Self-Correction| Generating Sequences by Learning to Self-Correct - -
2022/08|PEER| PEER: A Collaborative Language Model - -
2022/04|R3| Read, Revise, Repeat: A System Demonstration for Human-in-the-loop Iterative Text Revision - -
2021/10|CURIOUS| Think about it! Improving defeasible reasoning by first modeling the question scenario - -
2020/05|DrRepair| Graph-based, Self-Supervised Program Repair from Diagnostic Feedback -
-
2023/06|InterCode| InterCode: Standardizing and Benchmarking Interactive Coding with Execution Feedback - -
2023/06| Is Self-Repair a Silver Bullet for Code Generation? - -
2023/05| Improving Factuality and Reasoning in Language Models through Multiagent Debate - -
2023/05|CRITIC| CRITIC: Large Language Models Can Self-Correct with Tool-Interactive Critiquing - -
2023/05|GPT-Bargaining| Improving Language Model Negotiation with Self-Play and In-Context Learning from AI Feedback - -
2023/05|Self-Edit| Self-Edit: Fault-Aware Code Editor for Code Generation - -
2023/04|PHP| Progressive-Hint Prompting Improves Reasoning in Large Language Models - -
2023/04|Self-collaboration| Self-collaboration Code Generation via ChatGPT - -
2023/04|Self-Debugging| Teaching Large Language Models to Self-Debug - -
2023/04|REFINER| REFINER: Reasoning Feedback on Intermediate Representation - -
2023/03|Self-Refine| Self-Refine: Iterative Refinement with Self-Feedback -
autonomous agent
-
2023/10|planning tokens| Guiding Language Model Reasoning with Planning Tokens - -
2023/09|AutoAgents| AutoAgents: A Framework for Automatic Agent Generation - -
2023/06|AssistGPT| AssistGPT: A General Multi-modal Assistant that can Plan, Execute, Inspect, and Learn - -
2023/05|SwiftSage| SwiftSage: A Generative Agent with Fast and Slow Thinking for Complex Interactive Tasks - -
2023/05|MultiTool-CoT| MultiTool-CoT: GPT-3 Can Use Multiple External Tools with Chain of Thought Prompting - -
2023/05|Voyager| Voyager: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models - -
2023/05|ChatCoT| ChatCoT: Tool-Augmented Chain-of-Thought Reasoning on Chat-based Large Language Models - -
2023/05|CREATOR| CREATOR: Tool Creation for Disentangling Abstract and Concrete Reasoning of Large Language Models - -
2023/05|TRICE| Making Language Models Better Tool Learners with Execution Feedback - -
2023/05|ToolkenGPT| ToolkenGPT: Augmenting Frozen Language Models with Massive Tools via Tool Embeddings - -
2023/04|Chameleon| Chameleon: Plug-and-Play Compositional Reasoning with Large Language Models - -
2023/04|OpenAGI| OpenAGI: When LLM Meets Domain Experts - -
2023/03|CAMEL| CAMEL: Communicative Agents for "Mind" Exploration of Large Language Model Society - -
2023/03|HuggingGPT| HuggingGPT: Solving AI Tasks with ChatGPT and its Friends in Hugging Face - -
2023/03|Reflexion| Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning - -
2023/03|ART| ART: Automatic multi-step reasoning and tool-use for large language models - -
2023/03|Auto-GPT| Auto-GPT: An Autonomous GPT-4 Experiment - [Code] -
2023/02|Toolformer| Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools - -
2022/11|VISPROG| Visual Programming: Compositional visual reasoning without training - -
2022/10|ReAct| ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models -