A method for the in silico detection of plasmid fragments in environmental samples
- Deep learning - LSTM version available at https://github.com/philippmuench/dna_lstm
- Manuscript draft: https://www.overleaf.com/7758191crzmzwwcxftk
Table of Contents
Prediction
Full Worklow
Basic usage
Installation
Citing
Prediction
If you just want to predict your input sequences, your can use our pre-builded model model.pkl. This model was trained on CAMI dataset.
python plasmidminer/predict.py -i you_file.fasta -m model.pkl -h -s -p
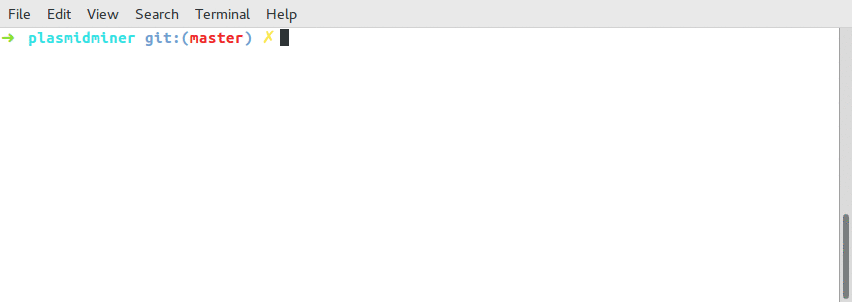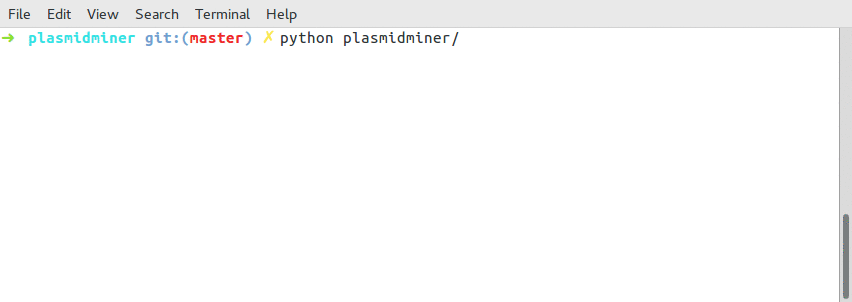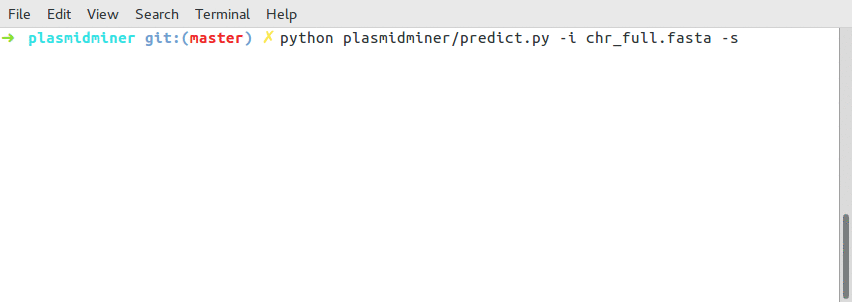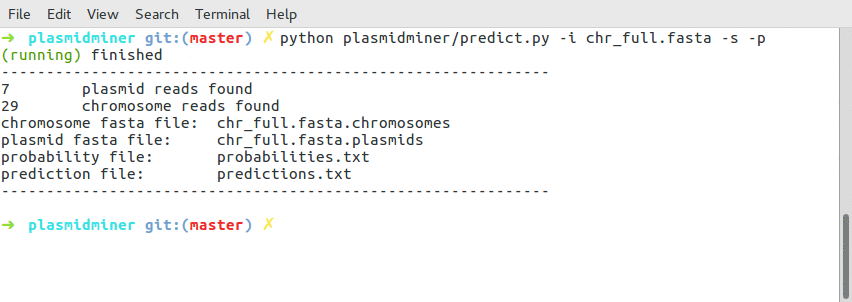
example output:
-------------------------------------------------------------
7 plasmid reads found
29 chromosome reads found
chromosome fasta file: chr_full.fasta.chromosomes
plasmid fasta file: chr_full.fasta.plasmids
probability file: probabilities.txt
prediction file: predictions.txt
-------------------------------------------------------------
Building a model
Step 1a: download learning data from NCBI
- Input: command line parameters
- Output: raw dataset, csv feature matrix and binary object for learning task
We download all E. Coli complete genomes and plasmids from NCBI and randomly sample 10000 reads with the size of 150 nt from both datasets. These randomly sampled reads are even distributed from all genomes in the collection.
python plasmidminer/getdataset.py -a 10000 -b 10000 --taxa "Escherichia coli" --readsim -N 10000 --save dat/dataset.bin
Step 1b: use personal genome collection (in this case from CAMI project)
- Input: command line parameters,
plasmid.fastaandchromosme.fastalocated indat/folder (downloaded from CAMI website) - Output: raw dataset, csv feature matrix and binary object for learning task
preprocessing:
wget https://s3-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/cami-data-eu/CAMI_low/source_genomes_low.tar.gz
tar xvzf source_genomes_low.tar.gz
rename "s/fna/fasta/" *.fna
renam "s/fna/fasta/" circular_one_repeat/*.fna
cat *.fasta > chromosomes.fasta
cat circular_one_repeat/*.fasta > plasmid.fasta
# move plasmid.fasta and chromosomes.fasta to dat folder
python plasmidminer/getdataset.py --no_download --readsim -N 10000 --save dat/dataset.bin
Step: 2: optimize hyperparameters
- Input: raw data from Step 1
- Output: optimized hyperparameters, model created from training sample for
roc.pyscript
First we have to create a smaller subset of features from the downloaded data.
python plasmidminer/resample.py --data_folder dat --output dat_small -c 150 -s -N 500
We can now find the best parameters for various models using this small subset of the data as train set.
python plasmidminer/findparameters.py --dataset dat_small -i 200 --sobol
This script will try 200 parameters for each model based on sobol number whenever possible and exports the best hyperparameter setting for each model to the cv/ folder. In this example we see that randomforest with an accuracy of 0.81 outperforms all other tested methods.
Currently implementated methods:
- Support Vector Machine
- Relevance vector machine
- Random Forest
- Gradient Boosting Classifier
Step 3: draw a ROC curve
- Input: Folder where pickl objects with trained models are located
- Output: ROC curve, AUC values
We can draw a ROC curve to visualize classification performance. You may want to draw a new random subset instead of using the same data we used for training before.
# move parameter setting file to different folder
mkdir best_parameters && mv cv/*_param_* best_parameters/
# draw ROC using all pickl model files located in cv/
python plasmidminer/roc.py --model_folder cv --data_folder dat_small --cv 3
Step 3: train input data with optimized hyperparameter setting
- Input: pkl object with best hyperparamters and feature file
- Output: final model
We can now use the corresponding pkl file with contains the hyperparameter settings to train a new model with more features as used for the optimization process. For this we first have to resample more reads from our data (in this we resample 100k instances)
python plasmidminer/resample.py -data_folder dat --output dat_big --readsim -N 100000 -c 150 --save dat/dataset_resampled_big.bin
With this bigger dataset and our pikl object containing the parameters we can now build our final model
python plasmidminer/train.py --data_folder dat_big --method cv/best_model.pkl
Basic usage
Scripts for plasmid prediction
Detection of plasmids from FASTA files
usage: predict.py [-h] [-i INPUT] [-m MODEL] [-s] [-p] [--sliding]
[--window WINDOW] [--version]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT, --input INPUT
Path to input FASTA file
-m MODEL, --model MODEL
Path to model (.pkl)
-s, --split split data based on prediction
-p, --probability add probability information to fasta header
--sliding Predict on sliding window
--window WINDOW size of sliding window
--version show program's version number and exit
Scripts for training and validation
Download training samples
usage: getdataset.py [-h] [--save SAVE] [--output DATA] [-t TAXA] [-a PLANUM]
[-b CHRNUM] [-c CHUNKSIZE] [-s] [-N SIMNUM] [-e EMAIL]
[--multi] [--no_download] [--screen] [--version]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--save SAVE Save dataset as msg pack object
--output DATA path to output folder for raw data without tailing
backslash
-t TAXA, --taxa TAXA Taxonomic name for downloaded samples
-a PLANUM, --planum PLANUM
Number of plasmids to be downloaded
-b CHRNUM, --chrnum CHRNUM
Number of chromosomes to be downloaded
-c CHUNKSIZE, --chunksize CHUNKSIZE
Chunk size in nt
-s, --readsim use read simluation based on wgsim instead of sliding
window
-N SIMNUM, --simnum SIMNUM
number of reads to simulate with wgsim
-e EMAIL, --email EMAIL
Email adress needed for ncbi file download
--multi Prepare data in multi feature format (taxonomic column
in train/test samples)
--no_download use dataset stored in data folder
--screen Screen downloaded chr for plasmid specific domains and
remove them
--version show program's version number and exit
Generate a new set of training samples from raw data
usage: resample.py [-h] [--data_folder DATA_FOLDER] [--output DATA]
[--save SAVE] [-c CHUNKSIZE] [-s] [-N SIMNUM] [--version]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--data_folder DATA_FOLDER
Input data folder which should be processed without
tailing backslash
--output DATA output data folder without tailing backslash
--save SAVE Save dataset as msg pack object
-c CHUNKSIZE, --chunksize CHUNKSIZE
Chunk size in nt
-s, --readsim use read simluation based on wgsim instead of sliding
window
-N SIMNUM, --simnum SIMNUM
number of reads to simulate with wgsim
--version show program's version number and exit
Hyperparameter optimization
usage: findparameters.py [-h] [-d DATASET] [-t TEST_SIZE] [-i ITER] [--sobol]
[--version]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DATASET, --dataset DATASET
path to dataset .pkl object
-t TEST_SIZE, --test_size TEST_SIZE
size of test set
-i ITER, --iterations ITER
number of random iterationsfor hyperparameter
optimization
--sobol use sobol sequence for random search
--version show program's version number and exit
ROC Curve
usage: roc.py [-h] [-m MODEL] [-d DATA] [-t TEST_SIZE] [-c CV] [--version]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-m MODEL, --model_folder MODEL
path to folder where .pkl models are located
-d DATA, --data_folder DATA
path to file foulder
-t TEST_SIZE, --test_size TEST_SIZE
size of test set from whole dataset in percent
-c CV, --cv CV cross validation size (e.g. 10 for 10-fold cross
validation)
--version show program's version number and exit
Installation
make sure you have installed the dependencies
libpq-dev libboost-all-dev libmysqlclient-dev python-dev build-essential libssl-dev libffi-dev python-tk
on some systems libboost-all-dev cannot be installed via apt-get install, so you can install it directly
wget http://launchpadlibrarian.net/153613169/libboost1.54-dev_1.54.0-2ubuntu3_amd64.deb
sudo dpkg -i --force-overwrite libboost1.54-dev_1.54.0-2ubuntu3_amd64.deb
and binaries of hmmer and prodigal in your PATH variable
Installation workflow with virtualenv:
virtualenv env
source env/bin/activate
git clone https://github.com/philippmuench/plasmidminer.git
cd plasmidminer
pip install numpy cython pysam
pip install https://github.com/AmazaspShumik/sklearn_bayes/archive/master.zip
pip install -r requirements.txt
python setup.py install
Citing
$bibtex item