Quick links
The Excite-O-Meter (EoM) is a package that extends a standalone Unity project with functionalities to easily record users' data in experimental sessions. It captures heart and motion activity, automatically extracts relevant data features, and visualizes the data post data collection directly in your compiled desktop application. Suitable for Unity developers wanting to analyze body responses in users or researchers conducting empirical studies in XR.
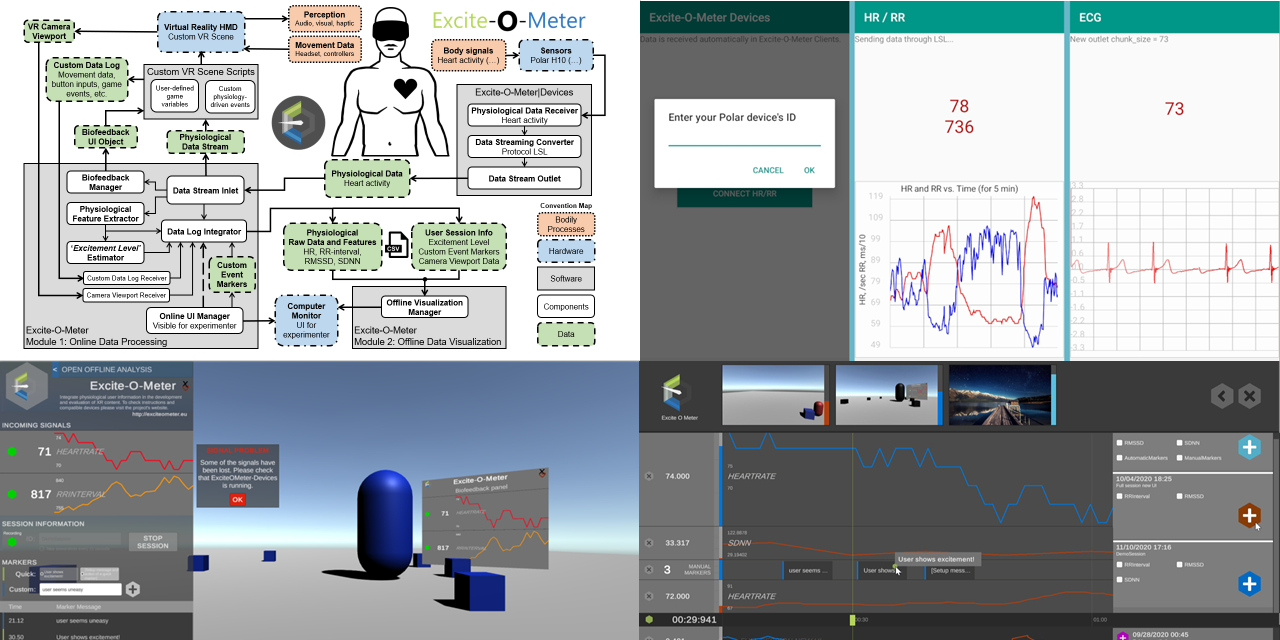
The EoM enables the integation of heart activity and movement analysis in any standalone application created with Unity, intended for Extended Reality (XR). This plugin contains all the logic to record data from external wearable sensors, log into persistent files, and visualize the captured data without leaving the Unity Editor.
The tool is simple to use and doesn't require coding. The EoM is particularly suitable in two use cases: 1) for hobbyists or Unity developers wanting to measure the body responses that your application induces on your users. 2) for researcher running scientific experiments (e.g., psychology or behavioral research) in XR and wanting to easily collect data using a Unity environment that you created or found online.
The EoM may be used without external wearable sensors. However, the tool's main advantage is the easy integration with body sensors compatible with LSL. Currently, it is compatible with the chest strap sensor Polar H10 to capture heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability data (HRV), (see top-right image). It also records movement from any object in the scene, useful to record head movement from Virtual Reality (VR) headsets record headsets. Additionally, screenshots and manual string markers can be added to label specific events occurring while users interact with your XR environment. Finally, it includes a data visualizer to review the session of the user offline (see bottom-right image), showing in synchrony all the time-series data, screenshots, and markers. Everything works in the Unity Editor and in the final compiled application.
Note: The description below is a summary of the complete step-by-step user manual available in this link.
The EoM includes two parts:
- The (
Excite-O-Meter|Devices), a compiled software (versions for Android and Win10) that interfaces the physical sensor with Unity.
- Download the Windows Application from the store: https://www.microsoft.com/store/apps/9NW9MSXHTQ5M
- The code to compile the Android application that transforms Bluetooth stream into LSL is available in this repo: https://github.com/luisqtr/exciteometer-devices-android/
- The code to compile the Windows UWP application that transforms Bluetooth stream into LSL is available in this repo: https://github.com/luisqtr/exciteometer-devices-UWP/
- The
EoMUnity package that integrates the functionalities in your custom standalone Unity project. - The script
EoM_DataReceiver.cscan be attached to any existing scene to read the values from physiological data and custom markers and be processed as desired.
The EoM package already ships the library dependencies LSL for collecting time series, and UI Extensions to visualize time series as lines in the Unity UI. In addition, your Unity project requires the package Text Mesh PRO (TMPro).
Read about installation and setup in this document, the middleware software interfaces the Polar H10 sensor with Unity.
The Excite-O-Meter|Devices can be downloaded from the latest release branch.
You can import the project in two ways depending on whether you use git or not. The simplest way is downloading the .unitypackage from the latest release branch.
If you prefer to clone the git in your own project, either to obtain the latest version or to contribute, you can use clone the main branch as a submodule: git add submodule https://github.com/luisqtr/exciteometer.git. Read more details in the user manual.
A description of the example is available in this link. The example scene Scenes/Example_withURP_NewInputSystem.unity shows the integration of the EoM in an existing Unity project.
If the EoM is useful for your research, please consider citing the following paper:
Quintero L, Muñoz JE, de Mooji J, Gaebler M. Excite-O-Meter: Software Framework to Integrate Heart Activity in Virtual Reality. In: IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR). Bari, Italy; 2021. p. 357–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR52148.2021.00052
@inproceedings{Quintero2021_EoM,
author = {Quintero, Luis and Mu{\~{n}}oz, John E and de Mooji, Jeroen and Gaebler, Michael},
booktitle = {IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR)},
doi = {10.1109/ISMAR52148.2021.00052},
pages = {357--366},
title = {{Excite-O-Meter: Software Framework to Integrate Heart Activity in Virtual Reality}},
year = {2021}
}Scientific disclaimer: The EoM includes an algorithm that estimates 'excitement level' from cardiac data. It MUST be considered considered on early stages and not as an objective scientifically validated measure. Please read the full disclaimer at the end of this document.
Please read the guidelines about the CODE OF CONDUCT and CONTRIBUTION.
The project's website (http://exciteometer.eu/) contains additional information. Although it gets updated less often than the GitHub repository (https://github.com/luisqtr/exciteometer).
- The project is currently maintained by Luis Quintero, part of his PhD project at the Data Science Group at Stockholm University, Sweden.
- The project leader was Michael Gaebler, who conceptualized the project and led the work from the first publication, as found in the branch
release_v1.0.1. John Muñoz and Jeroen de Mooij also heavily contributed in the conceptualization and UI development of the EoM, respectively. - Acknowledgements:
- The authors wish to thank Anna Francová and Jessica Gärtner for their support in the empirical evaluation of the first version of the
EoM; as well as Johanne Tromp, Felix Klotzsche, Mert Akbal, and Alexander Masurovsky for helping in the conceptualization of the project on its first stage. - This project received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme through the XR4ALL project with grant agreement N° 825545.
- Thanks to all contributors from other libraries: LSL, UI Extensions.