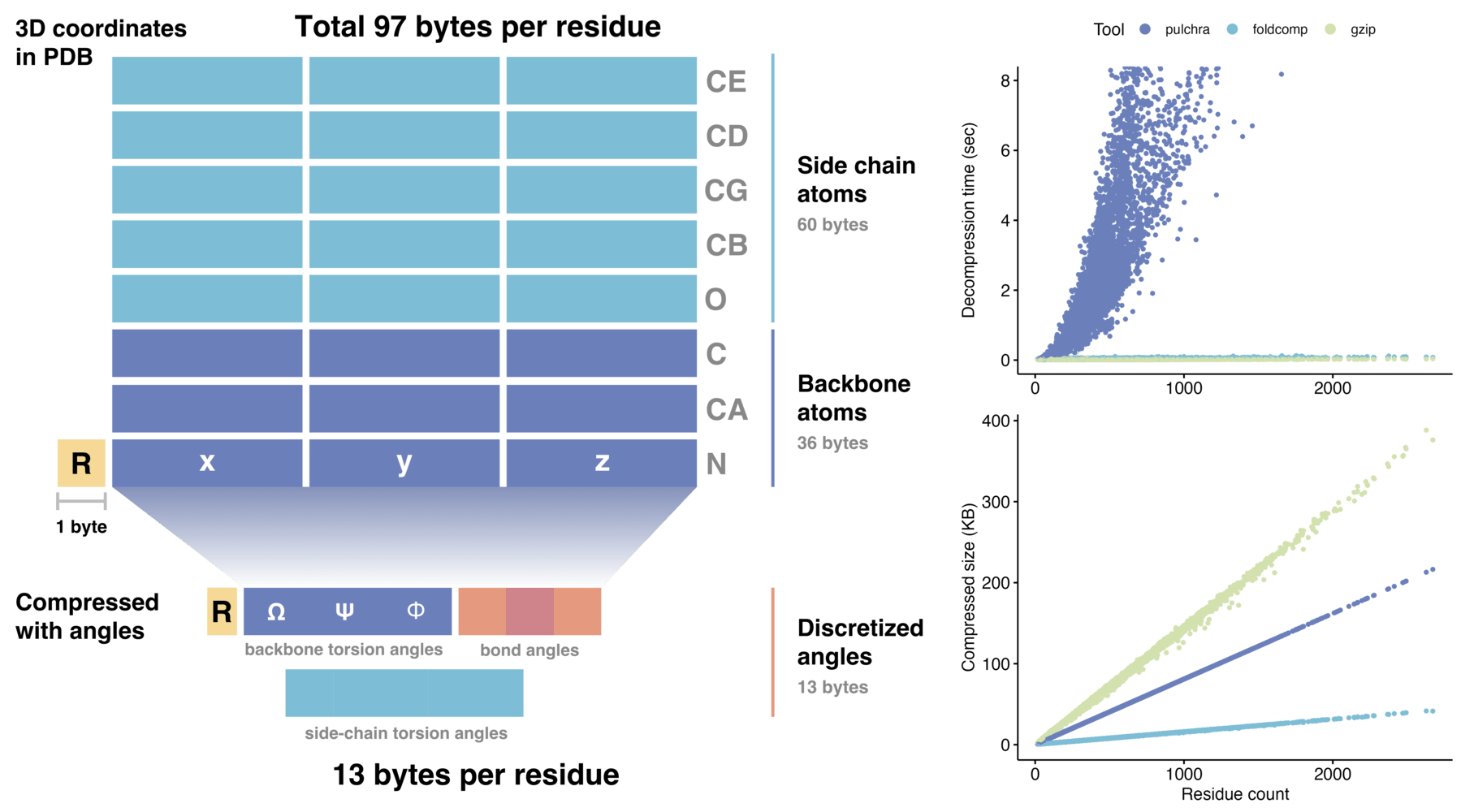
Foldcomp efficient compressed format stores protein structures requiring only 13 bytes per residue, which reduces the required storage space by an order of magnitude compared to saving 3D coordinates directly. We achieve this reduction by encoding the torsion angles of the backbone as well as the side-chain angles in a compact binary file format (FCZ).
Foldcomp currently only supports compression of single chain PDB files
# Install Foldcomp Python package
pip install foldcomp
# Download static binaries for Linux
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldcomp/foldcomp-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
# Download static binaries for Linux (ARM64)
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldcomp/foldcomp-linux-arm64.tar.gz
# Download binary for macOS
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldcomp/foldcomp-macos-universal.tar.gz
# Compression
foldcomp compress <pdb_file|cif_file> [<fcz_file>]
foldcomp compress [-t number] <pdb_dir|cif_dir> [<fcz_dir>]
# Decompression
foldcomp decompress <fcz_file> [<pdb_file>]
foldcomp decompress [-t number] <fcz_dir> [<pdb_dir>]
# Extraction of sequence or pLDDT
foldcomp extract [--plddt|--fasta] <fcz_file> [<txt_file|fasta_file>]
foldcomp extract [--plddt|--fasta] [-t number] <fcz_dir|tar> [<output_dir>]
# Check
foldcomp check <fcz_file>
foldcomp check [-t number] <fcz_dir|tar>
# RMSD
foldcomp rmsd <pdb1|cif1> <pdb2|cif2>
# Options
-h, --help print this help message
-t, --threads threads for (de)compression of folders/tar files [default=1]
-a, --alt use alternative atom order [default=false]
-b, --break interval size to save absolute atom coordinates [default=25]
-z, --tar save as tar file [default=false]
--plddt extract pLDDT score (only for extraction mode)
--fasta extract amino acid sequence (only for extraction mode)
--no-merge do not merge output files (only for extraction mode)
You can find more in-depth examples of using Foldcomp's Python interface in the example notebook:
import foldcomp
# 01. Handling a FCZ file
# Open a fcz file
with open("test/compressed.fcz", "rb") as fcz:
fcz_binary = fcz.read()
# Decompress
(name, pdb) = foldcomp.decompress(fcz_binary) # pdb_out[0]: file name, pdb_out[1]: pdb binary string
# Save to a pdb file
with open(name, "w") as pdb_file:
pdb_file.write(pdb)
# Get data as dictionary (v0.0.3)
data_dict = foldcomp.get_data(fcz_binary) # foldcomp.get_data(pdb) also works
# Keys: phi, psi, omega, torsion_angles, residues, bond_angles, coordinates
data_dict["phi"] # phi angles (C-N-CA-C)
data_dict["psi"] # psi angles (N-CA-C-N)
data_dict["omega"] # omega angles (CA-C-N-CA)
data_dict["torsion_angles"] # torsion angles of the backbone as list (phi + psi + omega)
data_dict["bond_angles"] # bond angles of the backbone as list
data_dict["residues"] # amino acid residues as string
data_dict["coordinates"] # coordinates of the backbone as list
# 02. Iterate over a database of FCZ files
# Open a foldcomp database
ids = ["d1asha_", "d1it2a_"]
with foldcomp.open("test/example_db", ids=ids) as db:
# Iterate through database
for (name, pdb) in db:
# save entries as seperate pdb files
with open(name + ".pdb", "w") as pdb_file:
pdb_file.write(pdb)