FinAl-ReSi is a pipeline to find restriction sites conserved among differnt strains/variants of a particular organism. As a proof of concept, we are going to use FinAl-ReSi to find conserved sequences among SARS-CoV-2 variants. Then, the restriction fragments encolsed by two sites of intereset will be used to trigger an EXPAR reaction by the following mechanism:
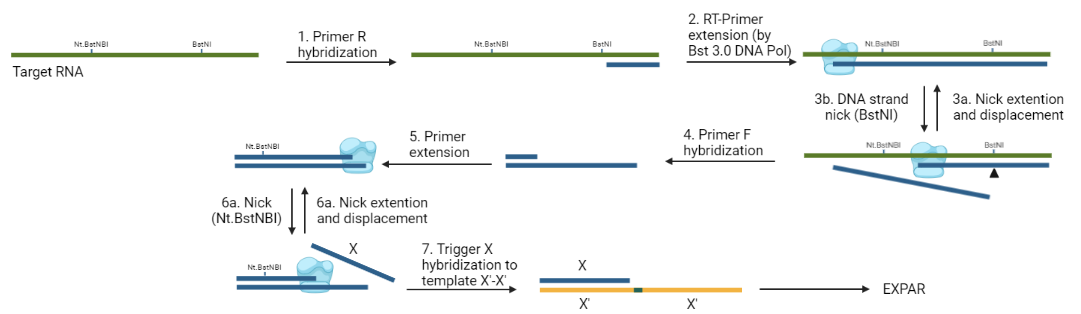
1- A primer hybridizes to the virus RNA, close to a BstNI site.
2- It has been reported that Bst DNA polymerase 3.0 has RT activity (Bekta¸s et al., 2021). Then, this enzyme would extend this primer, creating the first cDNA.
3a- It has been shown that the restriction enzyme BstNI can cut the DNA strand on a DNA:RNA hybrid (Kisiala et al., 2020. Then, the copied BstNI site will be nicked on the DNA strand of the hybrid.
3b- The resulting 3-OH' can now prime a the synthesis of a new cDNA strand. The strand displacement activity of Bst DNA polymerase would displace the cDNA ahead previously copied.
4- The displaced cDNA can now be hybridized by a forward primer, which is upstream from a DNA nicking site (Nt.BstNBI or Nb.BsrDI).
5- The primer is extended and the generated nicking site can be recognized by the nicking enzyme.
6a- The nicking site is nicked
6b- The 3'-OH generated in the nick can now be used by the Bst DNA polymerase to synthesize and displace the strand ahead.
7- This displaced sequence (called the Trigger X) hybridizes to the template X'-X' and starts the EXPAR reaction.
This would create two linear amplification loops -Loop 1 (steps 3a and 3b) : generates various copies of cDNA -Loop 2 (steps 6a and 6b): generates several copies of Trigger X.
Then, the Trigger X will prime the exponential loop given by the EXPAR reaction:
 Mechanism of EXPAR reaction (Obtained from Carter et. al 2021)
Mechanism of EXPAR reaction (Obtained from Carter et. al 2021)
In order to fint these fragments, a python script uses a reference genome (in this case, NC_045512.2) and it searches for the desired restriction sites. In this case, we are looking for fragments flaked by a BstNI site on the 3' and a Nt.BstNBI or Nb.BsrDI (nicking sites) on the 5'.
To make sure that these fragments are conserved among diferent variants of SARS-CoV-2, we downloaded the 224 representative sequences for each Pangolin lineage/sublineage, retrived from the ([COVID-19 Data Portal by the European Nucleic Archive]https://www.covid19dataportal.org/search/sequences?crossReferencesOption=all&overrideDefaultDomain=true&db=representative-sequences&size=1000)).
Then, the fragments found on the previous step are serchead against a database with these representative genomes using blastn (ortho_fragments.py). The resulting hits are then aligned with muscle (align_fragments.py), obtaining a MSA of all the aligned fragments that can be used to assess sequence conservation and primer design.
Further, makebed.py will make a bed file that can be used to create a custom track to visualize the restriction fragments in a genome browser.