Dec 12, 2016
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Installation
- 3. Tutorials
- 3.1 Input
- 3.2 Data Summary
- 3.3 Allele Association Analysis
- 3.3.1 Options
- 3.3.1.1 HLA Types File (--input)
- 3.3.1.2 Allele Association Analysis (--assoc)
- 3.3.1.3 Digits resolution (--digit)
- 3.3.1.4 Methods for association test (--test)
- 3.3.1.5 Genetic model to test (--model)
- 3.3.1.6 Minimal allele/allele group frequency (--freq)
- 3.3.1.7 Adjustment for multiple testing (--adjust)
- 3.3.1.8 Output file name (--out)
- 3.3.1.9 Print output to screen (--print)
- 3.3.1.10 Permutation (--perm)
- 3.1.1.11 Random seed (--seed)
- 3.1.1.12 Exclude Alleles (--exclude)
- 3.3.1.13 Covariates file (--covar)
- 3.3.1.14 Covariates name (--covar-name)
- 3.3.2 Allele Association Analysis Examples
- 3.3.1 Options
- 3.4 Amino Acid Alignment
- 3.5 Amino Acid Association
- 3.6 Zygosity Test
- 3.6.1 Options
- 3.6.1.1 HLA Types File (--input)
- 3.6.1.2 Zygosity test (--zygosity)
- 3.6.1.3 Methods for zygosity test (--test)
- 3.6.1.4 Level to test (--level)
- 3.6.1.5 Output file name (--out)
- 3.6.1.6 Print output to screen (--print)
- 3.6.1.7 Consensus sequence (--consensus)
- 3.6.1.8 Digits resolution (--digit)
- 3.6.1.9 Minimal allele/allele group frequency (--freq)
- 3.6.2 Examples
- 3.6.1 Options
- 3.7 Interaction Test
- 3.7.1 Options
- 3.7.1.1 HLA Types File (--input)
- 3.7.1.2 Interaction test (--interaction)
- 3.7.1.3 Test to be used (--test)
- 3.7.1.4 Level to test (--level)
- 3.7.1.5 Output file name (--out)
- 3.7.1.6 Print output to screen (--print)
- 3.7.1.7 Consensus sequence (--consensus)
- 3.7.1.8 Digits resolution (--digit)
- 3.7.1.9 Minimal allele/allele group frequency (--freq)
- 3.7.2 Examples
- 3.7.1 Options
- 4. License
- 5. Citation
- 6. References
Python for HLA analysis: summary, association analysis, zygosity test and interaction test.
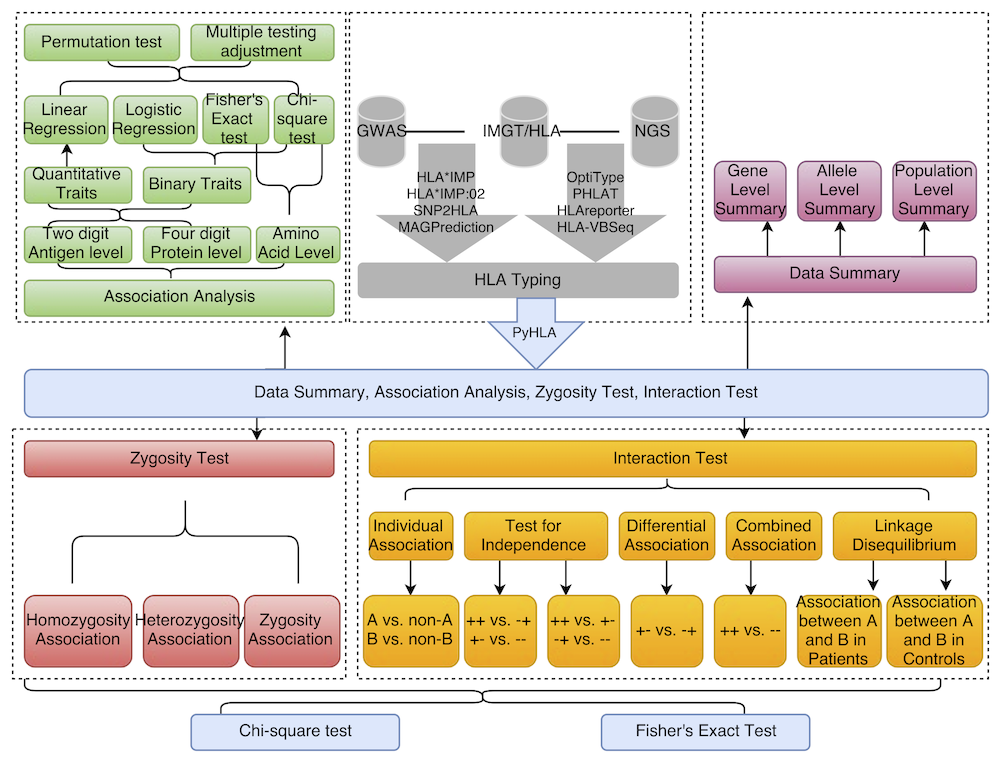
PyHLA uses Python 2 (Python 2.7 or higher) and the following Python modules:
- pandas
- numpy
- SciPy
- StatsModels
- PyQt4 (If you want to use the GUI)
The easiest way to install Python and the required packages: install FREE scientific python distributions such as Anaconda and Enthought Canopy which are already integrated the core scientific analytic and scientific Python packages such as SciPy, pandas, numpy, StatsModels and PyQt4.
In case you want to install all package by yourself, you can try the following steps.
If you use Windows OS and you have not install Python 2 yet, you can download the install package from here, the latest version is 2.7.11 (22 April 2016). Download the installer for your machine and install it as any other software.
Linux and Mac OS come with Python 2.7 pre-installed. Open the terminal and type python --version to see the version of Python on your machine. In case Python is not installed on your machine, you can download the installer for Mac and just click it to install it. Users of Ubuntu Linux simply type (untested):
sudo apt-get install build-essential python2.7
Users of RedHat or RedHat-derived distros (Fedora, CentOS) type (untested):
sudo yum groupinstall "Development tools"
sudo yum install python27
If you have Python 2 >=2.7.9, you will already have pip. Open the terminal (or Windows command prompt) and type the following commands to install Python modules.
sudo pip install pandas
sudo pip install numpy
sudo pip install git+http://github.com/scipy/scipy/
sudo pip install statsmodels
Install PyQt4 (optional, for GUI only).
-
Windows OS: Binary installers for Windows for PyQt4 is available here.
-
Mac OS (untested):
brew install pyqt
- Ubuntu Linux (untested):
sudo apt-get install python-qt4
- CentOS and RPM-based Linux (untested):
sudo yum install PyQt4
If you failed to install PyQt4, please follow this guild to install it.
The latest PyHLA is available here.
or, you can clone this repository via the command
git clone https://github.com/felixfan/PyHLA.git
Once you have downloaded PyHLA, typing
$ python PyHLA.py -h
will print a list of all command-line options.
or, typing the following command to start the GUI.
python gPyHLA.py
The input file is a white-space (space or tab) delimited file. The first two columns are mandatory: Individual ID and Phenotype. The Individual IDs are alphanumeric and should uniquely identify a person. The second column is phenotype which can be either a quantitative trait or an affection status. Affection status should be coded as 1 and 2 for unaffected and affected, respectively.
HLA types (column 3 onwards) should also be white-space delimited. Every gene must have two alleles specified. All alleles (see Nomenclature of HLA Alleles) do not need to have the same digits. However, if you want to test association at 4 digits, all alleles should have at least 4 digits resolution. Missing genotype is denoted as NA.
Header line is NOT needed. For example, here are two individuals typed for 6 genes (one row = one person):
0001 2 A*02:07:01 A*11:01:01 B*51:01:01 B*51:01:01 C*14:02:01 C*14:02:01 DQA1*01:04:01 DQA1*01:04:01 DQB1*03:03:02 DQB1*05:02:01 DRB1*07:01:01 DRB1*14:54:01
0002 1 A*24:02:01 A*33:03:01 B*15:25:01 B*58:01:01 C*03:02:02 C*04:03 NA NA DQB1*03:01:01 DQB1*03:01:01 DRB1*03:01:01 DRB1*12:02:01
There are one case and one control. The six genes are: HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1 and HLA-DRB1. Each gene has two columns. Individual 0002 does not have HLA types for HLA-DQA1 (two NA). All alleles have six digits resolution except that one allele of HLA-C of individual 0002 only has four digits resolution. It is fine if we only want to test association at two or four digits resolution.
Note: The allele names in the above example do not have the HLA prefix. Allele names have the HLA prefix can also be used as input. e.g. A*02:07:01 A*11:01:01 is the same as HLA-A*02:07:01 HLA-A*11:01:01. See the example file input0.txt and input1.txt for case-control trait and quantitative trait, respectively.
Alleles to be excluded from analysis. One allele per line.
A*01:01:02
C*01:03
The covariates file is a white-space (space or tab) delimited file. The first row is header. Row 2 onwards contain the individual ID (IID) and measures of several traits. Each row for one individual. The first column is IID and column 2 onwards contain measures of several traits. Each column for one trait.
For example, here are two individuals with three traits:
IID age sex bmi
0001 28 1 20.70
0002 23 0 16.29
Note: Name of trait should not include any white-space. The order of individuals in covariates file does not have to be the same as the genotype input file. The number of individuals in covariates file also does not have to be the same as the genotype input file. Only the common individuals of both files were included in the analysis. See covar.txt for an example.
Summary statistics for the data in three level: gene level, allele level, and population level.
-
Gene level summary: if the sample size is
nand there is no missing data, each gene will appears2ntimes. -
Allele level summary: The number and frequency of each allele.
-
Population level summary: The number and frequency of individuals carry each allele.
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--summary [Mandatory]
--digit 4 [Default]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform data summary analysis.
Summary based on two digits, four digits or six digits. When two was used, alleles such as A*02:01 and A*02:06 will be combined as A*02. Default value is 4.
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --summary --print
Output:
Sample size: 2000
Number of cases: 1158
Number of controls: 842
Gene level summary
------------------------------------------------------------------
Gene CaseCount CtrlCount TotalCount
A 2316 1684 4000
B 2316 1684 4000
C 2316 1684 4000
DQA1 2316 1684 4000
DQB1 2316 1684 4000
DRB1 2316 1684 4000
Allele level summary
------------------------------------------------------------------
Allele CaseCount CtrlCount TotalCount CaseFreq CtrlFreq TotalFreq
A*01:01 25 14 39 0.0108 0.0083 0.0097
A*01:22N 5 4 9 0.0022 0.0024 0.0022
A*01:81 37 22 59 0.0160 0.0131 0.0147
A*02:01 158 98 256 0.0682 0.0582 0.0640
A*02:03 109 85 194 0.0471 0.0505 0.0485
...(truncated)
Population level summary
------------------------------------------------------------------
Allele popCaseCount popCaseFreq popCtrlCount popCtrlFreq
A*01:01 19 0.0164 10 0.0119
A*01:22N 5 0.0043 4 0.0048
A*01:81 37 0.0320 22 0.0261
A*02:01 151 0.1304 96 0.1140
A*02:03 108 0.0933 82 0.0974
...(truncated)
Methods for association analysis between HLA alleles and diseases.
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--assoc [Mandatory]
--digit 4 [Default]
--test fisher [Default]
--model allelic [Default]
--freq 0 [Default]
--adjust FDR [Default]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
--perm N [Optimal]
--seed S [Optimal]
--exclude EXCLUDE.txt [Optimal]
--covar COVAR.txt [Optimal, for logistic and linear regression only]
--covar-name COVARNAME [Optimal, for logistic and linear regression only]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform allele association analysis.
Test of association using two digits, four digits or six digits. When two was used, alleles such as A*02:01 and A*02:06 will be combined as A*02. Default value is 4.
chisq Pearson chi-squared test (For disease traits, 2 x 2 coningency table)
fisher Fisher's exact test (For disease traits, 2 x 2 coningency table)
logistic logistic regression (For disease traits)
linear linear regression (For quantitative traits)
Default value is fisher.
When Pearson chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test was used, three genetic models can be specified.
allelic compares one allele against the others group together
dom compares individuals carry one allele against individuals do not carry it
rec compares individuals carry homozygous of one allele against other individuals
When linear or logistic regression is used, additive, dom and rec can be used. Assume A*01:01 is the test allele, then genotype will be coded as following:
Genotype code (additive model) code (recessive model) code (dominant model)
'A*01:01 A*01:01' 2 1 1
'A*01:01 A*01:02' 1 0 1
'A*01:02 A*01:03' 0 0 0
Default value is allelic.
A value between 0 and 1. Only alleles/allele groups have frequency higher than this threshold will be included in association analysis. Default value is 0.05. When --perm is specified, it is better to set a higher value than 0 to --freq to reduce permutation time.
Bonferroni Bonferroni single-step adjusted p-values
Holm Holm (1979) step-down adjusted p-values
FDR Benjamini & Hochberg (1995) step-up FDR control
FDR_BY Benjamini & Yekutieli (2001) step-up FDR control
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
Number of permutation will be performed.
For each permutation run, a simulated dataset is constructed from the original dataset by randomizing the assignment of phenotype status among individuals. The same individuals are used, maintaining the same LD structure and the original case/control ratio.
Only simulated dataset with the same common alleles between cases and controls as the original dataset will be used. So assign a greater than zero value to --freq can speed up the permutation.
Random seed for permutation. A number used to initialize the basic random number generator. By default, the current system time is used.
Alleles to be excluded. One allele per line.
A*01:01:02
C*01:03
One or more covariates can be included in linear and logistic regression.
The covariates file is a white-space (space or tab) delimited file. The first row is header. Row 2 onwards contain the individual ID (IID) and measures of several traits. Each row for one individual. The first column is IID and column 2 onwards contain measures of several traits. Each column for one trait.
For example, here are two individuals with three traits:
IID age sex bmi
0001 28 1 20.70
0002 23 0 16.29
Note: Name of trait should not include any white-space.
Note: --covar only effect when --test linear or --test logistic is specified.
Note: The order of individuals in covariates file does not have to be the same as the genotype input file. The number of individuals in covariates file also does not have to be the same as the genotype input file. Only the common individuals of both files were included in the analysis.
To select a particular subset of covariates, use --covar-name covarnames command.
covarnames is a string of trait names (in the header row of covariates file) concatenate with comma(,).
For example,
--covar cov.txt # use all covariates in cov.txt
--covar cov.txt --covar-name bmi # only use 'bmi'
--covar cov.txt --covar-name age,bmi # use both 'age' and 'bmi'
--covar cov.txt --covar-name age,sex,bmi # use all three covariates
Note: if --covar-name covarnames command is not specified, all covariates in cov.txt will be used.
Output contains several fields depend on which commands were used.
Allele Allele name
Gene Gene name
A_case Count of this allele in cases
B_case Count of other alleles in cases
A_ctrl Count of this allele in controls
B_ctrl Count of other allele in controls
F_case Frequency of this allele in cases
F_ctrl Frequency of this allele in controls
Freq Frequency of this allele in cases and controls
Chisq Chi-square
DF Degree of freedom
P_Chisq P-value for Pearson's chi-squared test
P_FET P-value for Fisher's exact test
P_Logit P-value for logistic regression
P_Linear P-value for linear regression
OR Odds ratio
beta Regression coefficient
L95 Lower bound of 95% confidence interval for odds ratio or regression coefficient
U95 Upper bound of 95% confidence interval for odds ratio or regression coefficient
P_adj Multiple testing adjusted p value
P_perm P-value for permutation test
PermN Number of permutation with statistic larger than the original data
PermNA Number of permutation with NA statistic
Fisher's exact test is the default option.
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --perm 10000
Pearson's chi-squared test
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test chisq
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test chisq --model dom
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test chisq --model rec
For each allele, a 2 X 2 coningency table contains the count of this allele and the count of the other alleles in the same gene in cases and controls was created. The total number of test is the number of alleles have frequency in cases or controls higher the the threshold specified by option --freq.
The output includes: Allele, A_case, B_case, A_ctrl, B_ctrl, F_case, F_ctrl, Freq, OR, L95, U95, P_adj. The output of Pearson's chi-squared test also includes: Chisq, DF, P_Chisq. The output of Fisher's exact test also includes: P_FET. When --perm is used, P_perm, PermN and PermNA are added to the output.
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test logistic --model additive
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test logistic --model additive --perm 10000
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test logistic --model additive --covar example/covar.txt --covar-name age,bmi
The total number of test is the number of alleles have frequency in cases or controls higher the the threshold specified by option --freq.
The output includes: Allele, A_case, B_case, A_ctrl, B_ctrl, F_case, F_ctrl, Freq, L95, U95, P_adj, OR, and P_Logit. When --perm is used, P_perm, PermN and PermNA are added to the output.
python PyHLA.py --input example/input1.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test linear --model additive
python PyHLA.py --input example/input1.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test linear --model additive --perm 10000
python PyHLA.py --input example/input1.txt --assoc --digit 4 --freq 0.05 --adjust FDR --test linear --model additive --covar example/covar.txt --covar-name sex,age,bmi
The total number of test is the number of alleles have frequency higher the the threshold specified by option --freq.
The output includes: Allele, Freq, L95, U95, P_adj, beta, and P_Linear. When --perm is used, P_perm, PermN and PermNA are added to the output.
For each gene, amino acid sequences for all alleles were aligned together. Protein sequence alignments were downloaded from IMGT/HLA, the current release Release 3.23.0, 2016-01-19 was used.
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--align [Mandatory]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
--consensus [Optimal]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform amino acid alignment.
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
When low resolution HLA typing was used in the input file, the program takes the consensus string of all possible high-resolution HLA typings, marking polymorphic amino acid positions as unknown. For example, when C*06:53, which can not be found in the alignment file, was used as input, the consensus sequence of two (it is quite possible larger than two for other alleles) higher-resolution HLA typings C*06:53:01 and C*06:53:02 will be used. If --consensus was not specified, sequence of C*06:53:01 will be used as default.
If there are more than one amino acid in a position, a test will be performed for each amino acid to test whether it is distributed differently between cases and controls.
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--assocAA [Mandatory]
--test [Default]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
--consensus [Optimal]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform amino acid association analysis.
Currently, only --test fisher and --test chisq are available for amino acid association analysis. See section 3.3.1.4 for details about this two tests.
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
See section 3.4.1.5.
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --assoc-AA --consensus
By default, Fisher's exact test was used. Each ID contains three parts: gene, position and residue. A_case and B_case are the number of cases carry and do not carry the residue at this position, respectively. A_ctrl and B_ctrl are the number of controls carry and do not carry the residue at this position, respectively. P denotes the p value of the test. OR is the odds ratio calculated with Haldane's correction of Woolf's method. ACR lists the alleles where the residue is present.
ID A_case B_case A_ctrl B_ctrl P OR ACR
A_9_F 566 592 399 443 0.52589 1.06 A*01:01,A*01:22N,A*01:81,A*02:01,A*02:03,A*02:07,A*02:112,A*02:264,A*02:265,A*02:43N,A*03:01,A*32:01,A*34:08,A*36:01
A_9_S 403 755 291 551 0.92425 1.01 A*23:01,A*24:02,A*24:03,A*24:07,A*24:20,A*24:59,A*30:01,A*30:04
A_9_T 364 794 251 591 0.46171 1.08 A*29:01,A*31:01,A*33:03
...
DRB1_13_C 19 1139 4 838 0.01809 3.19 DRB1*12:20
DRB1_13_F 342 816 244 598 0.80365 1.03 DRB1*01:01,DRB1*01:02,DRB1*09:01,DRB1*09:05,DRB1*09:06,DRB1*09:09,DRB1*09:12,DRB1*09:15,DRB1*09:16,DRB1*10:01
DRB1_13_G 438 720 327 515 0.67497 0.96 DRB1*08:02,DRB1*08:03,DRB1*08:09,DRB1*08:18,DRB1*12:01,DRB1*12:02,DRB1*12:15,DRB1*12:17,DRB1*12:18,DRB1*12:19,DRB1*12:21,DRB1*12:31N,DRB1*14:04
DRB1_13_H 276 882 194 648 0.70858 1.04 DRB1*04:01,DRB1*04:03,DRB1*04:04,DRB1*04:05,DRB1*04:06,DRB1*04:08,DRB1*04:10,DRB1*04:23,DRB1*04:71
DRB1_13_R 378 780 258 584 0.35570 1.10 DRB1*15:01,DRB1*15:02,DRB1*15:30,DRB1*15:58,DRB1*16:01,DRB1*16:02
DRB1_13_S 510 648 388 454 0.38704 0.92 DRB1*03:01,DRB1*04:66,DRB1*11:01,DRB1*11:04,DRB1*11:06,DRB1*11:54,DRB1*13:01,DRB1*13:02,DRB1*13:12,DRB1*13:13,DRB1*13:19,DRB1*13:47,DRB1*14:03,DRB1*14:05,DRB1*14:54
DRB1_13_Y 97 1061 75 767 0.68689 0.93 DRB1*07:01,DRB1*09:07
...
When an allele or residual was associated (p < 0.05) with the disease, three tests are performed here to identify whether a homozygote or heterozygote condition differentiates susceptibility to the disease.
| Table 1. Homozygosity association | ||
| category | class1 | class2 |
|---|---|---|
| case | hom | absent |
| control | hom | absent |
| Table 2. Heterozygosity association | ||
| category | class1 | class2 |
|---|---|---|
| case | het | absent |
| control | het | absent |
| Table 3. Zygosity association | ||
| category | class1 | class2 |
|---|---|---|
| case | hom | het |
| control | hom | het |
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--zygosity [Mandatory]
--test [Default]
--level [Default]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
--consensus [Optimal, for residual level only]
--digit [Default, for allele level only]
--freq [Default, for allele level only]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform zygosity test.
Currently, only --test fisher and --test chisq are available for zygosity test. See section 3.3.1.4 for details about this two tests.
Two levels --level residue and --level allele for amino acid and allele test, respectively. Default is --level residue.
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
For residual level only. When low resolution HLA typing was used in the input file, the program takes the consensus string of all possible high-resolution HLA typings, marking polymorphic amino acid positions as unknown. See section 3.4.1.5.
For allele level only. Test of association using two digits, four digits or six digits. When two was used, alleles such as A*02:01 and A*02:06 will be combined as A*02. Default value is 4.
For allele level only. A value between 0 and 1. Only alleles/allele groups have frequency higher than this threshold will be included in association analysis. Default value is 0.05.
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --zygosity --consensus
By default, Fisher's exact test was used. Each ID contains three parts: gene, position and residue. Hom_P, Het_P and Zyg_P is the p-value for testing homozygosity association, herterozygosity association and zygosity association, respectively. Hom_OR, Het_OR and Zyg_OR is odds ratio for testing homozygosity association, herterozygosity association and zygosity association, respectively. OR is the odds ratio calculated with Haldane's correction of Woolf's method.
ID Hom_P Het_P Zyg_P Hom_OR Het_OR Zyg_OR
A_57_P 1.0000 1.0000 0.0131 1.3833 0.0909 15.2161
A_57_R 1.0000 1.0000 0.0131 0.0909 1.3833 0.0657
B_45_T 0.0428 0.1309 0.0078 1.9192 0.8610 2.2291
B_62_G 0.4933 0.0598 0.3149 1.8058 0.7937 2.2750
B_65_R 0.4933 0.0598 0.3149 1.8058 0.7937 2.2750
B_66_N 0.4933 0.0598 0.3149 1.8058 0.7937 2.2750
B_67_M 0.4933 0.0598 0.3149 1.8058 0.7937 2.2750
B_67_Y 0.2916 0.0191 0.9075 1.3092 1.2547 1.0434
B_70_Q 0.2916 0.0191 0.9075 1.3092 1.2547 1.0434
B_70_S 0.4933 0.0598 0.3149 1.8058 0.7937 2.2750
B_74_D 0.3947 0.0229 0.8511 1.1900 1.2407 0.9591
B_77_S 0.1520 0.1292 0.0149 0.8678 1.2379 0.7011
B_80_I 0.0889 0.0302 0.0356 2.2191 0.7994 2.7760
B_80_N 0.4483 0.0712 0.0240 0.9223 1.2692 0.7267
B_82_R 0.4483 0.0712 0.0240 0.9223 1.2692 0.7267
B_83_G 0.4483 0.0712 0.0240 0.9223 1.2692 0.7267
B_152_V 0.0156 0.0037 0.3312 1.2808 1.4701 0.8712
C_1_G 1.0000 0.0464 1.0000 4.3333 5.9962 0.7227
C_165_E 1.0000 0.0464 1.0000 4.3333 5.9962 0.7227
DQA1_25_Y 0.6999 0.0247 0.0360 0.9623 0.6726 1.4308
DQB1_14_M 0.1584 0.0020 0.0096 0.8634 0.4410 1.9576
DQB1_53_L 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_84_Q 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_85_L 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_86_E 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_87_L 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_89_T 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_90_T 0.4933 0.0354 0.1100 0.9339 0.7434 1.2563
DQB1_116_I 1.0000 0.0117 1.0000 5.0000 6.9270 0.7218
DQB1_125_S 1.0000 0.0117 1.0000 5.0000 6.9270 0.7218
DQB1_126_H 1.0000 0.0117 1.0000 5.0000 6.9270 0.7218
DQB1_133_Q 1.0000 0.0117 1.0000 5.0000 6.9270 0.7218
DQB1_135_D 1.0000 0.0327 1.0000 2.0769 2.8857 0.7197
DRB1_11_A 1.0000 0.0334 1.0000 0.3623 0.4906 0.7386
DRB1_13_C 1.0000 0.0181 1.0000 0.2308 0.3136 0.7358
DRB1_73_A 1.0000 0.0391 0.0421 0.9951 0.4925 2.0206
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --zygosity --level allele --freq 0.05
By default, Fisher's exact test and 4 digit allele was used.
ID Hom_P Het_P Zyg_P Hom_OR Het_OR Zyg_OR
B*58:01 0.4925 0.0830 0.3151 1.8212 0.8034 2.2669
DQA1*02:01 0.1676 0.3188 0.0602 0.5688 1.1873 0.4791
When an allele or residual was associated (p < 0.05) with the disease, tests for independence, difference in association, combined action, interaction and linkage disequilibrium (LD) are used to determine the strongest association.
Table 1 Number of individuals with/without (+/-) factor A and/or factor B.
| Factor A | Factor B | Number of Cases | Number of Controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | + | x1 | y1 |
| + | - | x2 | y2 |
| - | + | x3 | y3 |
| - | - | x4 | y4 |
Table 2 Summary of the ten tests (2x2 Tables)
| Comparison | a | b | c | d | Test [Number] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A vs. non-A | x1+x2 | x3+x4 | y1+y2 | y3+y4 | [1] A associated? |
| B vs. non-B | x1+x3 | x2+x4 | y1+y3 | y2+y4 | [2] B associated? |
| ++ vs. -+ | x1 | x3 | y1 | y3 | [3] A associated in B-positives? |
| +- vs. -- | x2 | x4 | y2 | y4 | [4] A associated in B-negatives? |
| ++ vs. +- | x1 | x2 | y1 | y2 | [5] B associated in A-positives? |
| -+ vs. -- | x3 | x4 | y3 | y4 | [6] B associated in A-negatives? |
| +- vs. -+ | x2 | x3 | y2 | y3 | [7] Difference between A and B association? |
| ++ vs. -- | x1 | x4 | y1 | y4 | [8] Combined A-B association? |
| Association A and B in Cases | x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | [9] Linkage disequilibrium in cases |
| Association A and B in Controls | y1 | y2 | y3 | y4 | [10] Linkage disequilibrium in controls |
Both test 3 and test 4 are significant: A is associated with the disease independently of B.
Both test 5 and test 6 are significant: B is associated with the disease independently of A.
Both test 3 and test 5 are significant: A and B show interaction.
Test 7 is significant: Difference between A and B is associated with the disease.
Test 8 is significant: A and B have combined action.
Test 9 is significant: A and B are in LD in cases.
Test 10 is significant: A and B are in LD in controls.
--input input0.txt [Mandatory]
--interaction [Mandatory]
--test [Default]
--level [Default]
--out output.txt [Default]
--print [Optimal]
--consensus [Optimal, for residual level only]
--digit [Default, for allele level only]
--freq [Default, for allele level only]
See section 3.1.1.
This option tells PyHLA perform interaction test.
Only --test fisher and --test chisq can be used here. Default is --test fisher.
Two levels --level residue and --level allele for amino acid and allele test, respectively. Default is --level residue.
Default value is output.txt.
Specify --print will print all results to screen (still write results to the output file).
For residual level only. When low resolution HLA typing was used in the input file, the program takes the consensus string of all possible high-resolution HLA typings, marking polymorphic amino acid positions as unknown. See section 3.4.1.5.
For allele level only. Test of association using two digits, four digits or six digits. When two was used, alleles such as A*02:01 and A*02:06 will be combined as A*02. Default value is 4.
For allele level only. A value between 0 and 1. Only alleles/allele groups have frequency higher than this threshold will be included in association analysis. Default value is 0.05.
####3.7.2.1 Residue level
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --interaction --consensus
By default, Fisher's exact test was used. Each ID contains three parts: gene, position and residue. OR is the odds ratio calculated with Haldane's correction of Woolf's method. P3-P10 and OR3-OR10 are the p-value and odds ratio for tests listed in table 2, respectively.
ID1 ID2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 OR3 OR4 OR5 OR6 OR7 OR8 OR9 OR10
A_57_P B_45_T 0.3897 0.0365 0.0456 1.0000 0.4365 0.0234 1.0000 1.0000 4.71 11.64 1.21 3.00 3.88 14.14 0.58 1.44
A_57_P B_62_G 1.0000 0.0148 0.0473 1.0000 1.0000 0.0076 1.0000 1.0000 1.69 14.61 1.27 11.00 1.33 18.59 0.23 1.97
A_57_P B_65_R 1.0000 0.0148 0.0473 1.0000 1.0000 0.0076 1.0000 1.0000 1.69 14.61 1.27 11.00 1.33 18.59 0.23 1.97
A_57_P B_66_N 1.0000 0.0148 0.0473 1.0000 1.0000 0.0076 1.0000 1.0000 1.69 14.61 1.27 11.00 1.33 18.59 0.23 1.97
A_57_P B_67_M 1.0000 0.0148 0.0473 1.0000 1.0000 0.0076 1.0000 1.0000 1.69 14.61 1.27 11.00 1.33 18.59 0.23 1.97
A_57_P B_67_Y 0.2025 0.0646 0.0330 1.0000 0.1607 0.0913 1.0000 1.0000 6.14 10.49 0.82 1.40 7.49 8.59 0.61 1.04
A_57_P B_70_Q 0.2025 0.0646 0.0330 1.0000 0.1607 0.0913 1.0000 1.0000 6.14 10.49 0.82 1.40 7.49 8.59 0.61 1.04
A_57_P B_70_S 1.0000 0.0148 0.0473 1.0000 1.0000 0.0076 1.0000 1.0000 1.69 14.61 1.27 11.00 1.33 18.59 0.23 1.97
A_57_P B_74_D 0.1988 0.0636 0.0363 1.0000 0.1590 0.0888 1.0000 1.0000 6.24 10.59 0.82 1.40 7.56 8.73 0.78 1.33
A_57_P B_77_S 0.0146 1.0000 0.0490 1.0000 0.0071 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 14.67 1.74 0.77 0.09 19.13 1.33 5.57 0.66
A_57_P B_80_I 1.0000 0.0162 0.0148 1.0000 1.0000 0.0080 1.0000 0.3334 1.65 14.16 1.28 11.00 1.29 18.12 0.46 3.98
A_57_P B_80_N 0.0346 0.3667 0.0279 1.0000 0.0186 0.4307 1.0000 0.5405 11.91 5.22 0.76 0.33 15.65 3.97 4.53 1.98
A_57_P B_82_R 0.0346 0.3667 0.0279 1.0000 0.0186 0.4307 1.0000 0.5405 11.91 5.22 0.76 0.33 15.65 3.97 4.53 1.98
A_57_P B_83_G 0.0346 0.3667 0.0279 1.0000 0.0186 0.4307 1.0000 0.5405 11.91 5.22 0.76 0.33 15.65 3.97 4.53 1.98
A_57_P B_152_V 0.0347 0.3631 0.0228 1.0000 0.0179 0.4312 1.0000 0.5309 11.89 5.30 0.75 0.33 15.89 3.96 4.59 2.04
A_57_P C_1_G 1.0000 0.0129 0.0243 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 0.23 15.31 0.17 11.00 1.39 2.54 0.00 0.09
A_57_P C_165_E 1.0000 0.0129 0.0243 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 0.23 15.31 0.17 11.00 1.39 2.54 0.00 0.09
A_57_P DQA1_25_Y 0.0120 1.0000 0.0219 1.0000 0.0599 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 15.72 0.98 1.46 0.09 10.74 1.43 12.88 0.80
A_57_P DQB1_14_M 0.0123 1.0000 0.0046 1.0000 0.1487 1.0000 1.0000 1.0000 15.58 0.69 2.06 0.09 7.57 1.42 42.74 1.89
A_57_P DQB1_53_L 0.0287 0.4765 0.0488 1.0000 0.0528 0.4110 1.0000 0.5746 12.91 3.32 1.30 0.33 9.96 4.30 6.97 1.79
...
python PyHLA.py --input example/input0.txt --interaction --level allele --freq 0.01
By default, Fisher's exact test and 4 digit allele was used.
ID1 ID2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 OR3 OR4 OR5 OR6 OR7 OR8 OR9 OR10
A*11:77 B*35:01 1.0000 0.0793 1.0000 0.0595 0.7396 0.4127 0.6210 1.0000 0.39 0.67 0.35 0.59 1.13 0.23 0.44 0.76
A*11:77 B*58:01 0.8144 0.0493 0.3127 0.0879 0.0072 1.0000 0.1053 0.6684 0.87 0.61 1.79 1.25 0.49 1.09 1.83 1.28
A*11:77 DQA1*02:01 0.5562 0.1022 0.7598 0.1128 0.6857 0.2500 0.4217 0.3392 0.66 0.68 0.75 0.78 0.87 0.51 1.49 1.54
A*11:77 DRB1*04:66 0.2609 0.1014 1.0000 0.0209 0.0033 0.4209 0.6364 0.5004 0.11 0.69 0.35 2.18 0.32 0.24 0.35 2.20
B*35:01 DQA1*02:01 1.0000 0.0359 1.0000 0.0851 0.3555 0.6945 0.5018 1.0000 0.92 0.56 1.24 0.76 0.74 0.70 1.52 0.92
B*35:01 DRB1*04:66 0.2609 0.0813 1.0000 0.0209 0.0027 0.4214 1.0000 0.3831 0.11 0.62 0.39 2.18 0.28 0.24 0.58 3.20
B*58:01 DQA1*02:01 0.1916 0.1199 1.0000 0.0622 0.0091 0.6062 0.2718 1.0000 1.69 1.23 0.99 0.72 1.70 1.22 1.37 0.99
B*58:01 DRB1*04:66 0.4124 0.0413 1.0000 0.0192 0.1095 1.0000 0.8205 0.3967 0.51 1.29 0.94 2.39 0.54 1.21 0.86 2.19
DQA1*02:01 DRB1*04:66 0.1732 0.1198 1.0000 0.0144 0.0045 0.6998 1.0000 0.1343 0.30 0.79 0.92 2.39 0.33 0.72 1.17 3.05
This project is licensed under GNU GPL v2.
Yanhui Fan, You-Qiang Song. (2016) PyHLA: tests for association between HLA alleles and diseases. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. 18:90
-
Sham PC, Curtis D: Monte Carlo tests for associations between disease and alleles at highly polymorphic loci. Ann Hum Genet 1995, 59:97-105.
-
Lancaster AK, Single RM, Solberg OD, Nelson MP, Thomson G: PyPop update – a software pipeline for large-scale multilocus population genomics. Tissue Antigens 2007, 69:192-197.
-
Kanterakis S, Magira E, Rosenman KD, Rossman M, Talsania K, Monos DS: SKDM human leukocyte antigen (HLA) tool: A comprehensive HLA and disease associations analysis software. Human Immunology 2008, 69(8):522-525.
-
El Galta R, Hsu L, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ: Methods to test for association between a disease and a multi-allelic marker applied to a candidate region. BMC Genetics 2005, 6:S101-S101.
-
Svejgaard A, Ryder LP: HLA and disease associations: Detecting the strongest association. Tissue Antigens 1994, 43(1):18-27.