This ROS package includes the necessary code to replicate the results in our paper Asymmetric Dual-Arm Task Execution using an Extended Relative Jacobian.
In particular, it defines generic velocity controllers that implement different strategies for modeling the differential Kinematics of a dual-arm robotic manipulator, and the necessary configuration files to setup a numerical simulation of the different methods.
We implement controllers that make use of:
- The Cooperative Task Space (CTS)
- The Extended CTS
- A relative Jacobian formulation
- Our extended relative Jacobian
Our code requires a working ROS installation (tested on full ROS Kinetic and Melodic installations). In addition, we have dependencies on the following packages:
- generic_control_toolbox
- baxter_description (required only to replicate our article's results. You should be able to configure this package to use your own robot's URDF).
- robot_kinematic_simulation
- object_server
- rviz_visual_tools
You can setup a workspace with the required packages to run this work by inputting the following commands on a terminal:
$ mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src && cd ~/catkin_ws/src
$ catkin_init_workspace
$ wstool init && wstool merge https://raw.githubusercontent.com/diogoalmeida/asymmetric_manipulation/master/.rosinstall
$ wstool up
$ cd ~/catkin_ws
$ catkin_make
You can setup a simulation of a RethinkRobotics' Baxter by running the experiments launch file,
$ roslaunch asymmetric_manipulation experiments.launch
This will launch a kinematic simulation of Baxter. If you open RViz, you can load the configuration file config/display.rviz
to visualize the robot. This will add two interactive markers which represent object frames, rigidly linked to the robot's end-effectors.
The relative motion task of the provided controllers is to align these frames.
We provide an actionlib server to interact with the different methods. This can be called through the axclient.py GUI,
$ rosrun actionlib axclient.py /coordination_controller/coordination_control
- The argument
control_mode/controllersets the method used in executing the relative motion task. Your options are:- 0: Reset to the initial state
- 1: Uses the ECTS method
- 2: Uses our extended Relative Jacobian
- 3: Uses the relative Jacobian with a secondary task which regulates Baxter's left arm pose. The target for the secondary task can be set by regulating the 'Secondary Task' display in RViz
- You can set a maximum simulation time with the argument
max_time - The
alphaparameter sets the corresponding value for the ECTS and our methods (between 0 and 1) - If you set
use_asymmetric_l_onlywe will not project our Jacobian's solution in the nullspace of the symmetric relative Jacobian.
The script run_simulations.py runs the simulations from which the article's results were obtained. Launch Baxter's simulation by using the experiments launch file,
$ roslaunch asymmetric_manipulation experiments.launch
then, on a separate terminal
$ rosrun asymmetric_manipulation run_simulations.py
You can now open RViz and import the display.rviz file in the config/ directory (by pressing CTRL + o and navigating to the directoy where the package is installed). You should see the following view
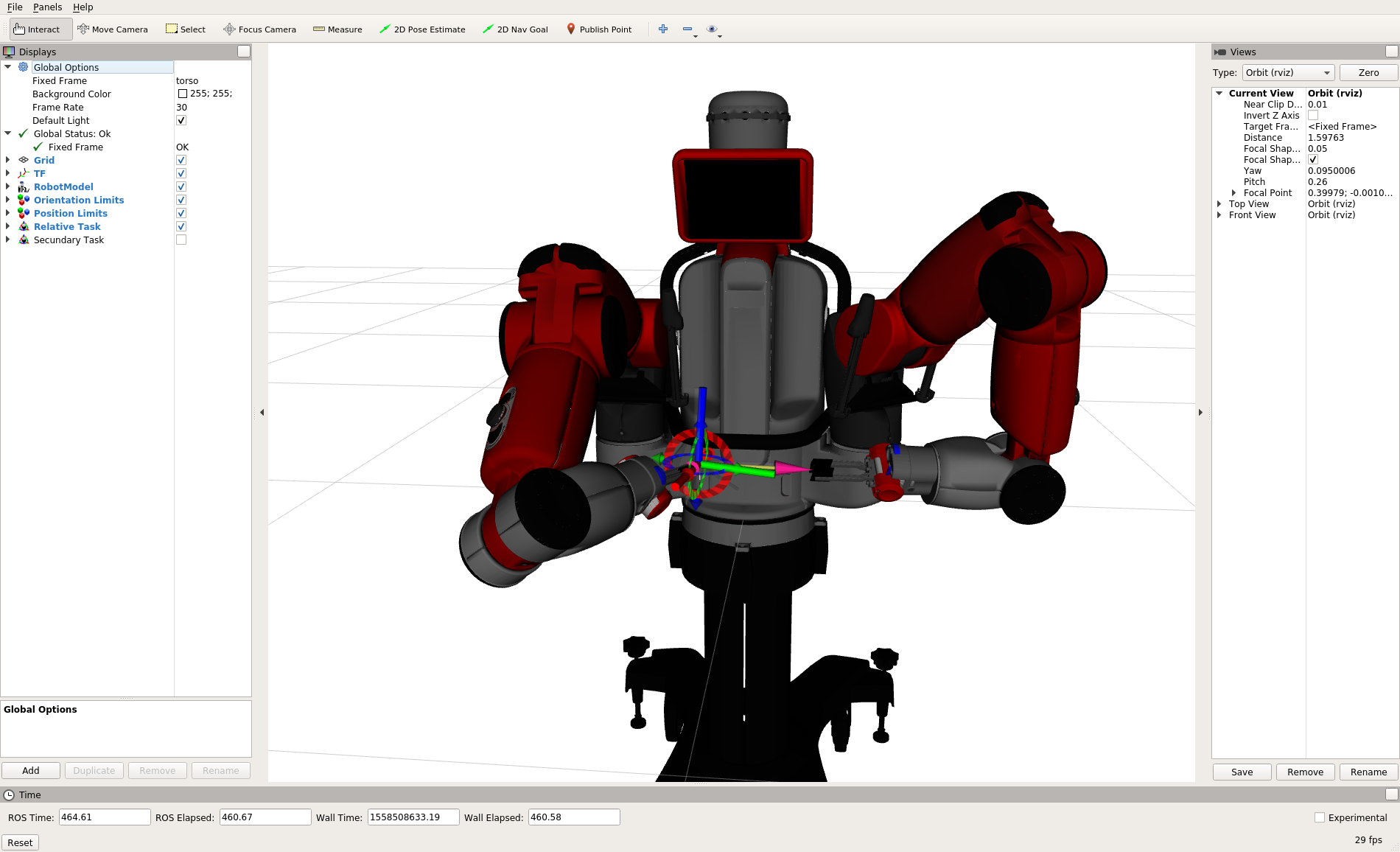
You can move the interactive markers to set the object frames for each manipulator. The relative motion task consists in aligning these two frames. To replicate the article's case studies and example, you can send a goal to the appropriate action server,
$ rosrun asymmetric_manipulation run_simulations.py
You can now choose which cases to run by setting the corresponding parameter to true.