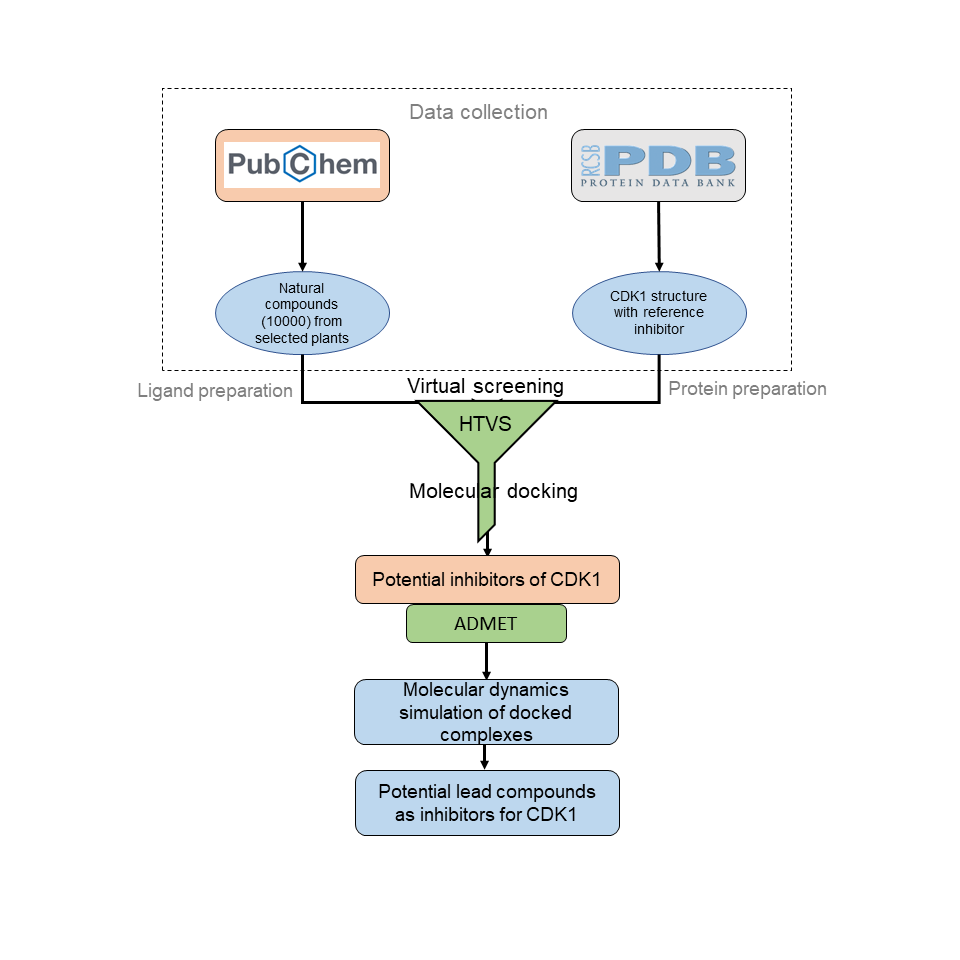
- Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer, next to lung and breast cancers, with an estimated mortality of approximately 900,000 annually. The actual mechanism of the cause of CRC is unknown, but it is linked to numerous sedentary lifestyles, food habits, family history, etc. The currently available chemotherapy drugs for treating CRC are limited by several factors, like adverse reactions, drug resistance, and re-occurrence.
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) enzyme has been implicated in the oncogenesis of CRC. CDK1 is a serine/threonine kinase that belongs to a family of cyclic cell regulatory proteins involved in maintaining cell cycle efficiency. The overexpression of CDK1 leads to uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor development associated with several cancers, including CRC. Thus, the project is aimed to identify potential natural compounds as inhibitors for CDK1 and assess their viability using in silico approaches.
- To screen natural compounds against CDK1 and identify potential inhibitors using molecular docking
- To study the stability of the docked complexes using molecular dynamics simulation
- The findings from the study suggest that the identified natural compounds could act as potential inhibitors against CDK1 for developing new therapeutics for colorectal cancer.
- Uchechukwu Chibuzo Ogbodo
- Halimat Chisom Atanda
- Ojochenemi Enejoh
- Pauline Gachanja
- Shamim Osata
- Kenneth Okolo
- Pranavathiyani G
- We thank African Society for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (ASBCB) and The National Institutes of Health Office of Data Science Strategy for organizing the ASBCB Omics Codeathon providing the required support and resources.
Licensed under MIT License - Copyright (c) 2022 omicscodeathon (Refer LICENSE file for more details)