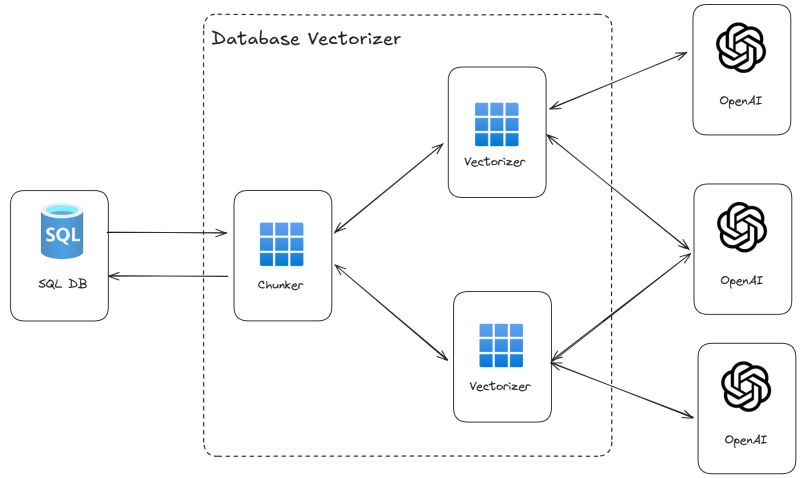
Quickly generate embeddings from data in Azure SQL. Point to the table that has text that must to turned into embeddings, configure the .env file and run the tool, to get text vectorized into embedding as fast as possible.
Embedding will be generated using the OpenAI API. The tool will connect to the Azure SQL Database, read the text from the specified table, send the text to the OpenAI API, and store the embeddings back in the same table. If the read text is too big to fit a single embedding API call, the tool will split the text into chunks and send each chunk to the API.
Chunking is done using the TextChunker.SplitPlainTextParagraphs method from the Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Text package. Maximum number of token per paragraph is set to 2048.
Embeddings will be stored into a dedicated table. If the table doesn't exist, the tool can create a new table to store the embeddings. The relationship between the original table and the table that stores the embeddings is done using the id / parent_id column and the relationship is a 1:N relationship, as each row in the original table will have one or more rows in the table that stores the embeddings due to the chunking process.
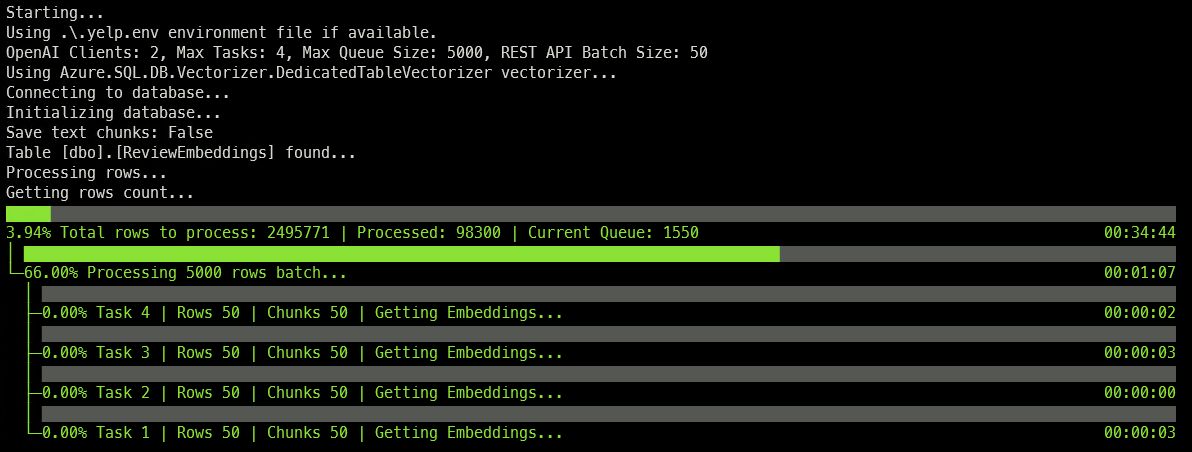
Rows from the database are processed in batch of 5000 rows. Those rows are read into a queue and then, by default, two threads per each OpenAI URL will pull data from the queue, chunk it if needed, and then send the embedding request to the OpenAI API. Each API call will batch togheter up to 50 text chunks to be vectorized.
Once the queue is empty, the process will start again until all rows in the source table are processed.
Note
Vector Functions are in Early Adopter Preview. Get access to the preview via https://aka.ms/azuresql-vector-eap-announcement
More details and samples on vector support in Azure SQL can be found here:
- Azure SQL DB and OpenAI
- Chatbot in pure T-SQL
- Session Recommender (RAG Pattern)
- Azure SQL & Langchain (RAG Pattern, End-To-End chatbot)
Just run
dotnet runor
dotnet run -- .my-env-fileif you want to use a different .env file.
All configuration options are read from environment variables. Create a .env file starting from the .env.sample and specifiy values as per the following instructions:
The URL and the API Key used to connect to Azure OpenAI or OpenAI. For example:
OPENAI_URL="https://open-ai-test.openai.azure.com/"
OPENAI_KEY="a12...bdf"to improve performance and scale out horizontally you can specify more URLs and more API keys by separateing them with a comma. The first URL will be used with the first API_KEY, the second URL with the second API_KEY and so on. Calls to OpenAI will be spread round-robin across all the configured URLs.
OPENAI_URL="https://open-ai-test-1.openai.azure.com/,https://open-ai-test-2.openai.azure.com/"
OPENAI_KEY="a12...bdf, d02...4ee"The name of the deployment that has the model that will be used to generate the embeddings. For example:
OPENAI_EMBEDDING_DEPLOYMENT_NAME="my-text-embedding-3-small"All OpenAI url defined in the OPENAI_URL must have the same deployment name.
The number of dimensions of the embeddings. For example:
EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS=1536The connection string to the Azure SQL Database. For example:
MSSQL_CONNECTION_STRING="Server=my-server.database.windows.net;Database=sampledb;Authentication=Active Directory Default;"The name of the table that contains the text that must be turned into embeddings. For example:
TABLE_NAME="dbo.wikipedia_articles"The name of the column that contains the unique identifier for each row in the table. For example:
ID_COLUMN_NAME="id"The id column must be an integer.
The name of the column that contains the text that must be turned into embeddings. For example:
CONTENT_COLUMN_NAME="title"The name of the table that will store the embeddings. For example:
DEDICATED_EMBEDDINGS_TABLE="dbo.wikipedia_articles_embeddings"The name of the column that will contain the embeddings. For example:
EMBEDDING_COLUMN_NAME="title_vector_text3"If set to True, the tool will create a new table to store the embeddings. For example:
AUTO_CREATE_DEDICATED_EMBEDDINGS_TABLE=TrueIf the table doesn't exist, the tool will create a new table to store the embeddings.
create table <DEDICATED_EMBEDDINGS_TABLE>
(
id int identity(1,1) primary key nonclustered,
parent_id int not null,
<EMBEDDING_COLUMN_NAME> vector(<EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS>) not null
);
If set to True, the tool will save the text chunks that were sent to the OpenAI API. For example:
SAVE_TEXT_CHUNKS=TrueTech chunks will be saved in a column named chunk_text in the same table that stores the embeddings.
create table <DEDICATED_EMBEDDINGS_TABLE>
(
id int identity(1,1) primary key nonclustered,
parent_id int not null,
chunk_text nvarchar(max) null,
<EMBEDDING_COLUMN_NAME> vector(<EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS>) not null
);
Download the wikipedia embeddings from here, unzip it and upload it (using Azure Storage Explorer for example) to an Azure Blob Storage container.
In the example the unzipped csv file vector_database_wikipedia_articles_embedded.csv is assumed to be uploaded to a blob container name playground and in a folder named wikipedia.
Once the file is uploaded, get the SAS token to allow Azure SQL database to access it. (From Azure storage Explorer, right click on the playground container and than select Get Shared Access Signature. Set the expiration date to some time in future and then click on "Create". Copy the generated query string somewhere, for example into the Notepad, as it will be needed later)
Use a client tool like Azure Data Studio to connect to an Azure SQL database and then use the ./sql/00-setup-blob-accees and ./sql/01-import-wikipedia.sql to create the wikipedia_articles where the uploaded CSV file will be imported.
Make sure to replace the <account> and <sas-token> placeholders with the value correct for your environment:
<account>is the name of the storage account where the CSV file has been uploaded<sas-token>is the Share Access Signature obtained before
Run each section (each section starts with a comment) separately. At the end of the process (will take up to a couple of minutes) you will have all the CSV data imported in the wikipedia_articles table.
Create a .wikipedia.env file starting from the .wikipedia.env.sample and set the values as per instructions provided in the Configuration section.
Then run
dotnet run -- .wikipedia.envAnd the tool will start to vectorize the text in the wikipedia_articles table and store the embeddings in the wikipedia_articles_embeddings table.