TerraVision is a CLI tool that converts Terraform code into Professional Cloud Architecture Diagrams and solves the problem of keeping the most important document in cloud projects, the architecture document, up to date. With high velocity releases the norm now, machine generated architecture diagrams are more accurate than relying on the freestyle diagram drawn by the cloud architect that doesn't match reality anymore. Terravision securely runs 100% Client Side without any dependency on Terraform or access to your Cloud environment, to dynamically parse your conditionally created resources and variables and generate an automatic visual of your architecture. Terravision is designed to be a 'Docs as Code' (DaC) tool that can be included in your CI/CD pipeline to update architecture diagrams after your build/test/release pipeline phases and supplement other document generators like readthedocs.io alongside it. It currently Supports AWS and soon Google and Azure cloud.
Turn this...
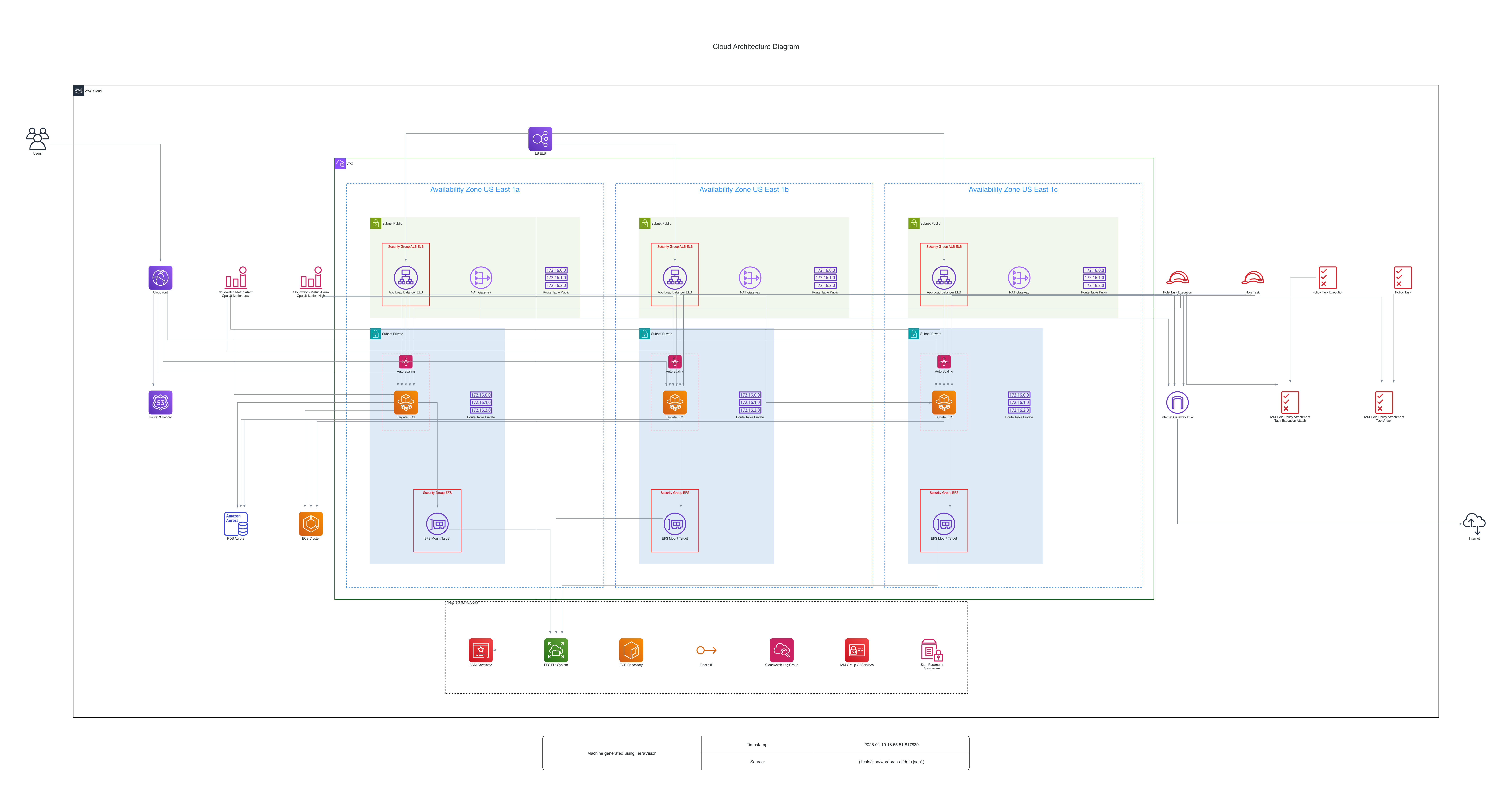
into this...
This software is still in alpha testing and code is shared on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. Use at your own risk.
- Cost
- Save Visio/Drawing software licenses - Terravision is free and open source
- Doesn't require any cost incurring cloud resources to be spun up, it works instantly from your local machine
- Regularly updating diagrams aligning, connecting dots and laying out icons is not the best use of your architect staff costs
- Accelerate and Automate
- Use TF variable files as inputs to create multiple variant diagrams from the same TF code
- Automate creation of architecture diagrams by running terravision as part of CI/CD pipelines
- YAML based Diagrams as code allows you to Annotate generated diagrams with additional custom labels and resources e.g. unmanaged resources or external systems not captured in TF code
- Consistency across organisation
- Auto downloads your organisational / external modules to ensure the latest view of downstream Terraform modules
- Consistent design of architecture diagrams using industry standard icons and AWS/GCP/Azure approved style across teams
- Accurate Visibility
- Real time state of diagram shows current infrastructure that matches exactly what is deployed in production today
- Helps in third party architecture reviews, auditing, monitoring, reporting and debugging of the stack in a visual way
- Custom Diagram code and output images can be put into source/version control for better maintainability and discoverability
- Security
- Don't need to give access to your AWS account or CLI to draw diagram
- Doesn't create intrusive cloud resources e.g. scanning instances or metadata tables which enterprises would need to approve
- All source code stays in your local environment, diagrams are generated on your machines without calling out to external APIs
- graphviz https://graphviz.org/download/
- git https://git-scm.com/downloads
- terraform https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/downloads
- Install all external dependencies as listed above
- Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/patrickchugh/terravision.git - Get the working directory (full path) by doing
cd terravisionand doingpwd. - Add the terravision folder to your
PATHvalue e.g.export PATH=$PATH:/Users/<PATH TO TERRAVISION>so you can run it from anywhere.<PATH TO TERRAVISION>would be the output from line 3. - Install python requirements
cd terravision && pip install -r requirements.txt - Ensure your terravision python script is executable with
chmod +x terravision - Run
terravisionand specify your Terraform source files in the format:
$ terravision draw --source ~/src/my-terraform-codeFor Terraform stacks with workspaces, you can use the --workspace parameter:
$ terraform draw --source ~/src/my-terraform-code --workspace developmentFor Terraform source code in a Git repo you can also use the form:
$ terravision draw --source https://github.com/your-repo/terraform-examples.gitUse the // character for subfolders within Git repos if the code you want is under a folder hierarchy.
$ terravision draw --source https://github.com/your-repo/terraform-examples.git//mysubfolder/secondfolder/No automatically generated diagram is going to have all the detail you need, at best it will get you 80-90% of the way there. To add custom annotations such as a main diagram title, additional labels on arrows or additional resources created outside your Terraform, include a terravision.yml file in the source code folder and it will be automatically loaded. Alternatively, specify a path to the annotations file as a parameter to terravision.
terravision --source https://github.com/your-repo/terraform-examples.git --annotate /Users/me/MyDocuments/annotations.ymlThe .yml file is a standard YAML configuration file that is similar to the example below with one or more headings called title, connect, disconnect, add, remove or update. The node names follow the same conventions as Terraform resource names https://registry.terraform.io/providers/hashicorp/aws/latest/docs and support wildcards. You can add a custom label to any TF resource by modifying the attributes of the resource and adding the label attribute (doesn't exist in Terraform). For lines/connections, you can modify the resource attributes by adding terravision specific edge_labels to add text to the connection line to a specific resource node. See the example below:
format: 0.1
# Main Diagram heading
title: Serverless Wordpress Site
# Draw new connection lines that are not apparent from the Terraforms
connect:
aws_rds_cluster.this:
- aws_ssm_parameter.db_master_user : Retrieve credentials from SSM
# Remove connections between nodes that are currently shown
disconnect:
# Wildcards mean these disconnections apply to any cloudwatch type resource called logs
aws_cloudwatch*.logs:
- aws_ecs_service.this
- aws_ecs_cluster.this
# Delete the following nodes
remove:
- aws_iam_role.task_execution_role
# Add the following nodes
add:
aws_subnet.another_one :
# Specify Terraform attributes for a resource like this
cidr_block: "123.123.1.1"
# Modify attributes of existing node
update:
aws_ecs_service.this:
# Add custom labels to the connection lines that already exist between ECS->RDS
edge_labels:
- aws_rds_cluster.this: Database Queries
# Wildcards save you listing multiple resources of the same type. This edge label is added to all CF->ACM connections.
aws_cloudfront* :
edge_labels:
- aws_acm_certificate.this: SSL Cert
# Add a custom label to a resource node. Overrides default label
aws_ecs_service.this :
label: "My Custom Label"
Type terravision --help for full command list or for help with a specific command