Foldseek enables fast and sensitive comparisons of large structure sets.
Search your protein structures against the AlphaFoldDB and PDB in seconds using our Foldseek webserver: search.foldseek.com 🚀
# static Linux AVX2 build (check using: cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep avx2)
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldseek/foldseek-linux-avx2.tar.gz; tar xvzf foldseek-linux-avx2.tar.gz; export PATH=$(pwd)/foldseek/bin/:$PATH
# static Linux SSE4.1 build (check using: cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep sse4_1)
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldseek/foldseek-linux-sse41.tar.gz; tar xvzf foldseek-linux-sse41.tar.gz; export PATH=$(pwd)/foldseek/bin/:$PATH
# static macOS build (universal binary with SSE4.1/AVX2/M1 NEON)
wget https://mmseqs.com/foldseek/foldseek-osx-universal.tar.gz; tar xvzf foldseek-osx-universal.tar.gz; export PATH=$(pwd)/foldseek/bin/:$PATH
# conda installer
conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda foldseek
Other precompiled binaries for ARM64, PPC64LE amd SSE2 are available at https://mmseqs.com/foldseek.
easy-search can search single or multiple query structures formatted in PDB/mmCIF format (flat or .gz) against a target database (example/) of protein structures. It outputs a tab-separated file of the alignments (.m8) the fields are query,target,fident,alnlen,mismatch,gapopen,qstart,qend,tstart,tend,evalue,bits.
foldseek easy-search example/d1asha_ example/ aln.m8 tmpFolder
The output can be customized with the --format-output option e.g. --format-output "query,target,qaln,taln" returns the query and target accession and the pairwise alignments in tab separated format. You can choose many different output columns.
query Query sequence identifier
target Target sequence identifier
evalue E-value
gapopen Number of gap open events (note: this is NOT the number of gap characters)
pident Percentage of identical matches
fident Fraction of identical matches
nident Number of identical matches
qstart 1-indexed alignment start position in query sequence
qend 1-indexed alignment end position in query sequence
qlen Query sequence length
tstart 1-indexed alignment start position in target sequence
tend 1-indexed alignment end position in target sequence
tlen Target sequence length
alnlen Alignment length (number of aligned columns)
raw Raw alignment score
bits Bit score
cigar Alignment as string. Each position contains either M (match), D (deletion, gap in query), or I (Insertion, gap in target)
qseq Query sequence
tseq Target sequence
qaln Aligned query sequence with gaps
taln Aligned target sequence with gaps
qheader Header of Query sequence
theader Header of Target sequence
mismatch Number of mismatches
qcov Fraction of query sequence covered by alignment
tcov Fraction of target sequence covered by alignment
empty Dash column '-'
taxid Taxonomical identifier (needs mmseqs tax db)
taxname Taxon Name (needs mmseqs tax db)
taxlineage Taxonomical lineage (needs mmseqs tax db)
qset Query filename of FASTA/Q (useful if multiple files were passed to createdb)
qsetid Numeric identifier for query filename
tset Target filename of FASTA/Q (useful if multiple files were passed to createdb)
tsetid Numeric identifier for target filename
qca Calpha corrdinates of the query
tca Calpha corrdinates of the target
alntmscore TM-score of the alignment
u Rotation matrix (computed to by TM-score)
t Translation vector (computed to by TM-score)
The target database can be pre-processed by createdb. This make sense if searched multiple times.
foldseek createdb example/ targetDB
foldseek easy-search example/d1asha_ targetDB aln.m8 tmpFolder
# sensitivity
-s adjust the sensitivity to speed trade-off.
lower is faster, higher more sensitive (fast: 7.5, highest sensitivity (default): 9.5)
--max-seqs adjust the amount of prefilter that are handed to the alignment.
Increasing it can lead to more hits (default: 300)
# other
--alignment-type 0: 3Di Gotoh-Smith-Waterman (local, not recommended),
1: TMalign (global),
2: 3Di+AA Gotoh-Smith-Waterman (local, default)
-c list matches above this fraction of aligned (covered) residues (see --cov-mode) (default: 0.0)
--cov-mode 0: coverage of query and target, 1: coverage of target, 2: coverage of query
The databases command downloads pre-generated databases like PDB or AlphaFoldDB.
# pdb
foldseek databases PDB100 pdb tmp
# alphafold db
foldseek databases Alphafold/Proteome afdb tmp
We currently support the following databases:
Name Type Taxonomy Url
- Alphafold/UniProt Aminoacid yes https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/
- Alphafold/UniProt-NO-CA Aminoacid yes https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/
- Alphafold/UniProt50 Aminoacid yes https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/
- Alphafold/Proteome Aminoacid yes https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/
- Alphafold/Swiss-Prot Aminoacid yes https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/
- PDB Aminoacid yes https://www.rcsb.org
easy-searchfast protein structure searchcreatedbcreate a database from protein structures (PDB,mmCIF, mmJSON)databasesdownload pre-assembled databases
Foldseek supports to realign hits using TMalign as well as rescoring alignments using TMscore.
foldseek easy-search example/d1asha_ example/ aln tmp --alignment-type 1
In case of the alignment type (--alignment-type 1) tmalign we sort the results by the TMscore normalized by query length. We write the TMscore into the e-value(=TMscore) as well as into the score(=TMscore*100) field.
Easiest way to get the alignment TMscore normalized by min(alnLen,qLen,targetLen) as well as a rotation matrix is through the following command:
foldseek easy-search example/ example/ aln tmp --format-output query,target,alntmscore,u,t
Alternative, it is possible to compute TMscores for the kind of alignment output (e.g. 3Di/AA) using the following commands:
foldseek createdb example/ targetDB
foldseek createdb example/ queryDB
foldseek search queryDB targetDB aln tmpFolder -a
foldseek aln2tmscore queryDB targetDB aln aln_tmscore
foldseek createtsv queryDB targetDB aln_tmscore aln_tmscore.tsv
Output format aln_tmscore.tsv: query and target identifier, TMscore, translation(3) and rotation vector=(3x3)
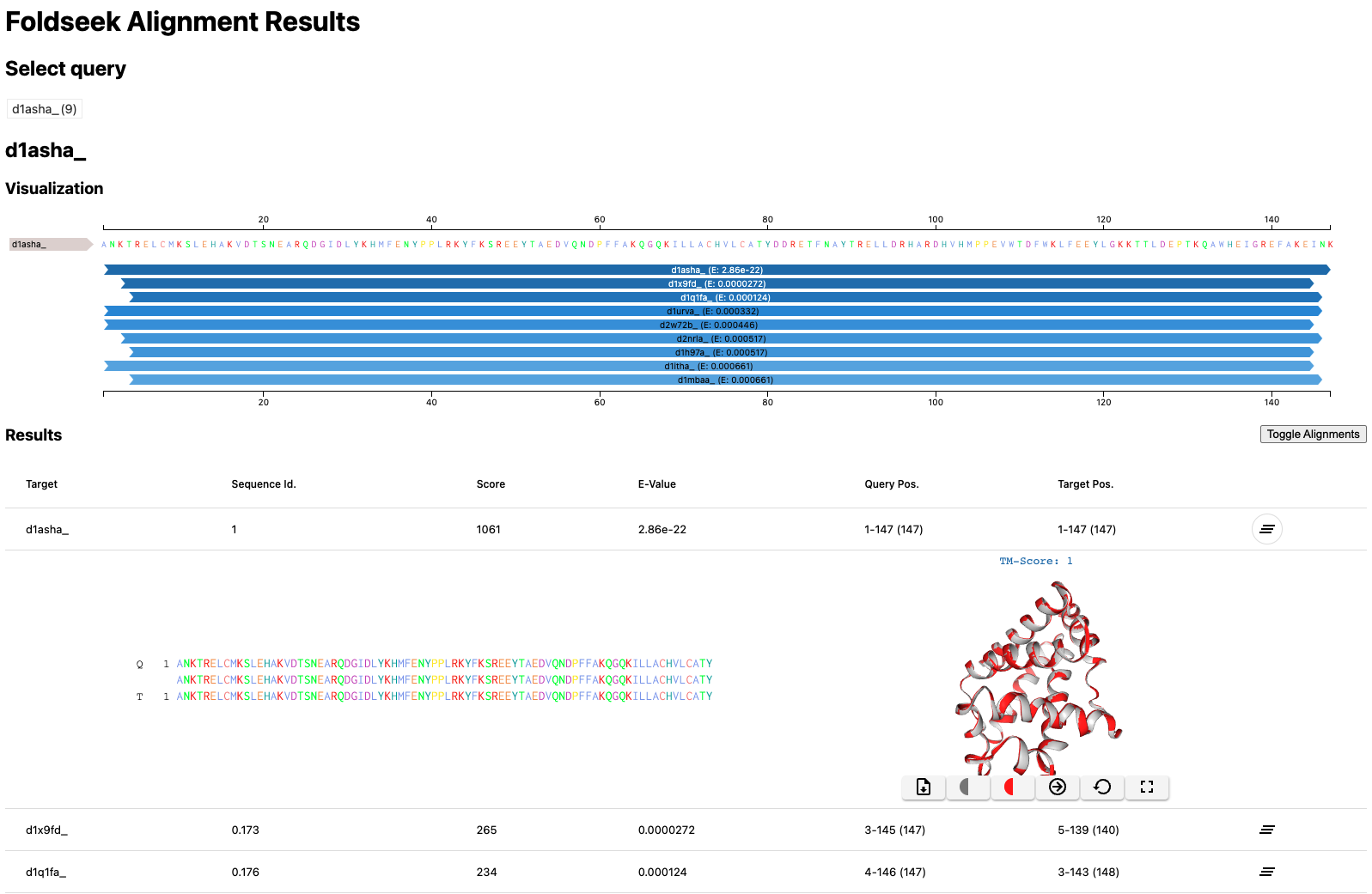
Foldseek can locally generate a search result HTML similiar to the webserver by specifying the format mode --format-mode 3
foldseek easy-search example/d1asha_ example/ result.html tmp --format-mode 3
The following command aligns the input structures all-against-all and keeps only alignments with 80% of the sequence covered by the alignment (-c 0.8) (read more about alignment coverage here). It then clusters the results using greedy set cover algorithm. The clustering mode can be adjusted using --cluster-mode, read more here. The clustering output format is described here.
foldseek createdb example/ db
foldseek search db db aln tmpFolder -c 0.8
foldseek clust db aln clu
foldseek createtsv db db clu clu.tsv
Foldseek can generate a3m based multiple sequence alignments using the following commands.
a3m can be converted to fasta format using reformat.pl (reformat.pl in.a3m out.fas).
foldseek createdb example/ targetDB
foldseek createdb example/ queryDB
foldseek search queryDB targetDB aln tmpFolder -a
foldseek result2msa queryDB targetDB aln msa --msa-format-mode 6
foldseek unpackdb msa msa_output --unpack-suffix a3m --unpack-name-mode 0
Compiling foldseek from source has the advantage of system-specific optimizations, which should improve its performance. To compile it git, g++ (4.9 or higher) and cmake (3.0 or higher) are required. Afterwards, the foldseek binary will be located in the build/bin directory.
git clone https://github.com/steineggerlab/foldseek.git
cd foldseek
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=. ..
make -j
make install
export PATH=$(pwd)/foldseek/bin/:$PATH
❗ If you want to compile foldseek on macOS, please install and use gcc from Homebrew. The default macOS clang compiler does not support OpenMP (by default) and foldseek will not be able to run multi-threaded. Adjust the cmake call above to:
CC="$(brew --prefix)/bin/gcc-11" CXX="$(brew --prefix)/bin/g++-11" cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=. ..