This repository contains the code examples and prerequisite materials for the hands-on Deep Learning Tutorial at the ISMRM Machine Learning Workshop 2018, as well as instructions for creating a new AWS EC2 GPU instance pre-configured with all the required Python dependencies, CUDA/cuDNN libraries and training data for following along the course.
If you wish to follow along on Amazon, proceed with the instructions here to create your own personal EC2 instance which you will use to train neural networks. The cost for a minimum single GPU p2.xlarge instance is approximately $0.90/hour. If you wish to follow along locally, feel free to clone this repository onto your own computer. A toy dataset is provided in dl_tutorial/data so that the code provided here can be executed. Alternatively, the Jupyter notebooks (*.ipynb) can be browsed directly on Github and can be found in the dl_tutorial/code directory of this repository.
- How to create a new AWS EC2 instance.
- How to access the AWS EC2 instance.
- How to run Jupyter notebook.
IMPORTANT NOTE: You should try to complete steps (1) and (2) above before the session as a new AWS user will by default need to complete a separate request for GPU-enable instances (requires up to 24 hours for approval).
The template Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provided as part of this tutorial contains the following preinstalled dependencies:
- Python 3.5
- NVIDIA driver version 390
- CUDA 9.0 toolbox
- cudNN 7.0 libraries
- Tensorflow 1.5
- Keras 2.1.4
- Utility packages: jupyter, pandas, scipy, scikit-learn, cv2, matplotlib, ipdb
New users to Amazon AWS have access to a free tier of services for the initial 12 months of subscription. Note that the GPU EC2 instance required for deep learning is not part of the free tier of services ($0.90/hour) however an Amazon AWS account is still required.
To sign up, begin by visiting: https://portal.aws.amazon.com/billing/signup#/start
Note that your chosen AWS account name cannot contain spaces or non-alphanumeric characters ({}[]()/\'"~,;:.<>). Follow the prompts on the remaining screens. A valid credit card will be required.
Use the following link to log into your new AWS account: https://console.aws.amazon.com/console/home
On the following page, enter the email address of your AWS account and click Next:
On the following page, enter the password of your AWS account and click Sign In:
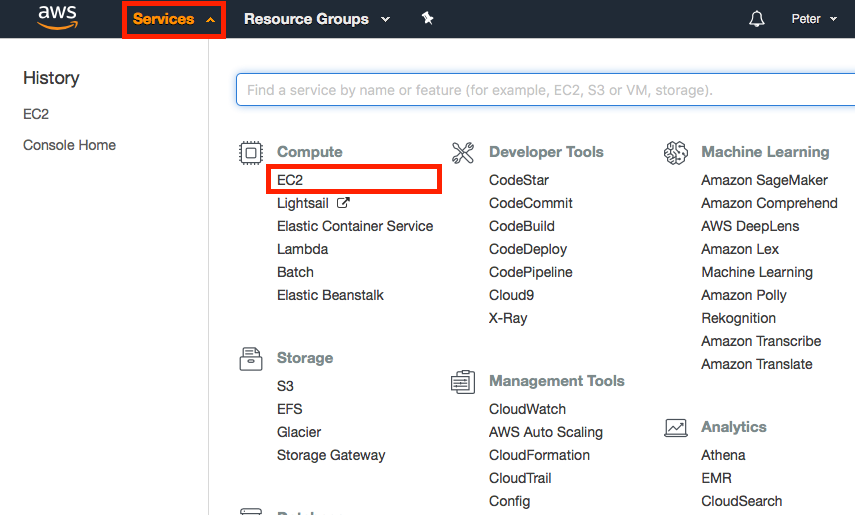
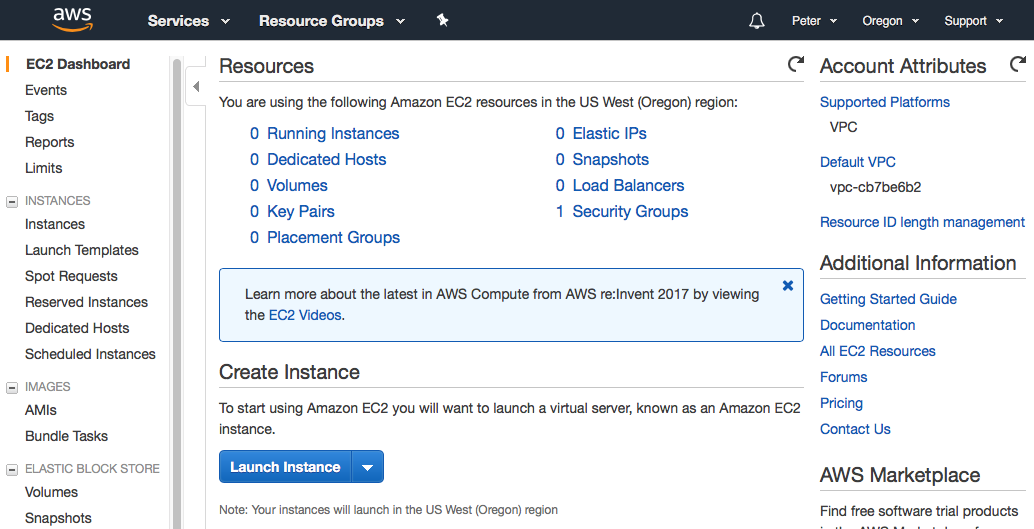
After logging in you will arrive at a launch page of various AWS services. We want to specifically manage EC2 instances. To navigate to the EC2 dashboard, click on the Services dropdown menu in the top left hand corner of the banner. You should now have a screen that looks like this:
Click on the EC2 link under the first Compute header within the first column. You have now arrived at the EC2 console (dashboard):
Here you can manage the servers in your AWS cloud, including creating, terminating, starting and stopping individual EC2 instances. For more general information about EC2 services and the console, see Amazon documentation here: https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/getting-started/
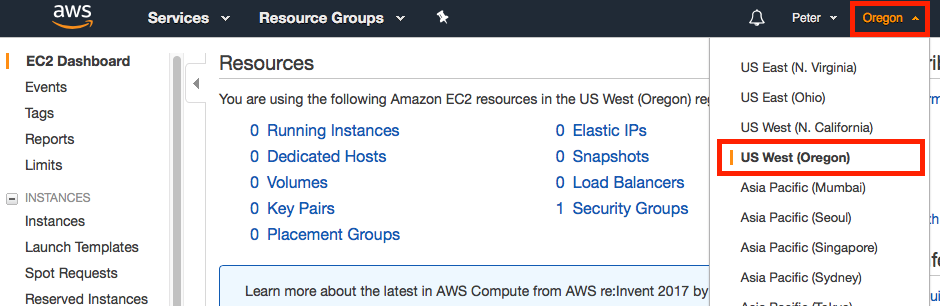
The EC2 instance we will create will be generated from a preconfigured Amazon Machine Image (AMI). To ensure that this AMI is visible to your AWS account, make sure you are in the US West (Oregon) region of service by changing the context in the top right hand corner of the banner as needed:
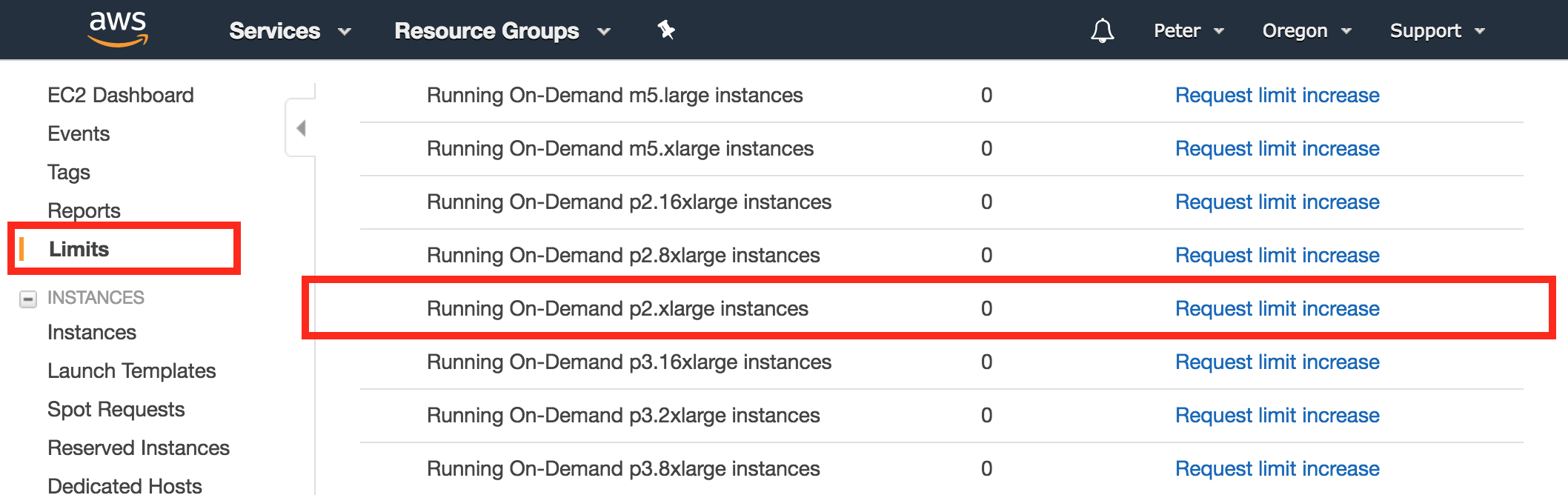
By default Amazon does not allow a user to create a new GPU-based instance to prevent accidental incurrence of charges. To request that AWS increase your GPU limit from 0 to 1, click on the Limits link on the EC2 console. Scroll down until you see the p2.xlarge selection and click on the corresponding link for Request limit increase.
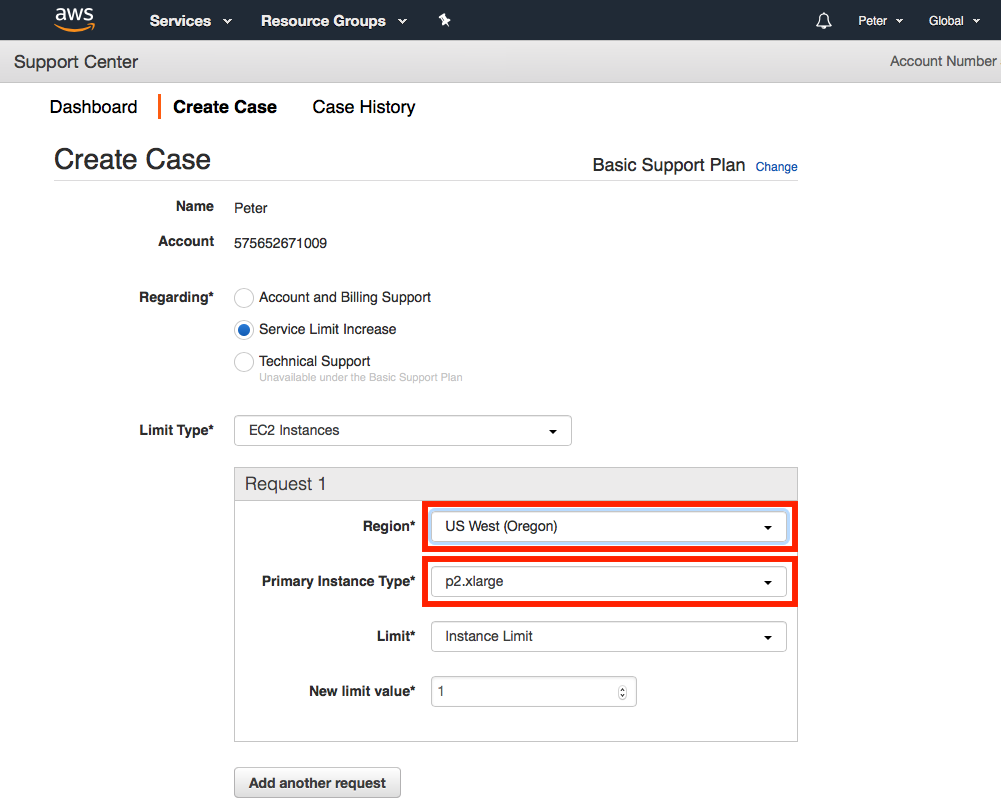
Complete the following request with the settings shown below. Ensure that the correct region and instance type are selected:
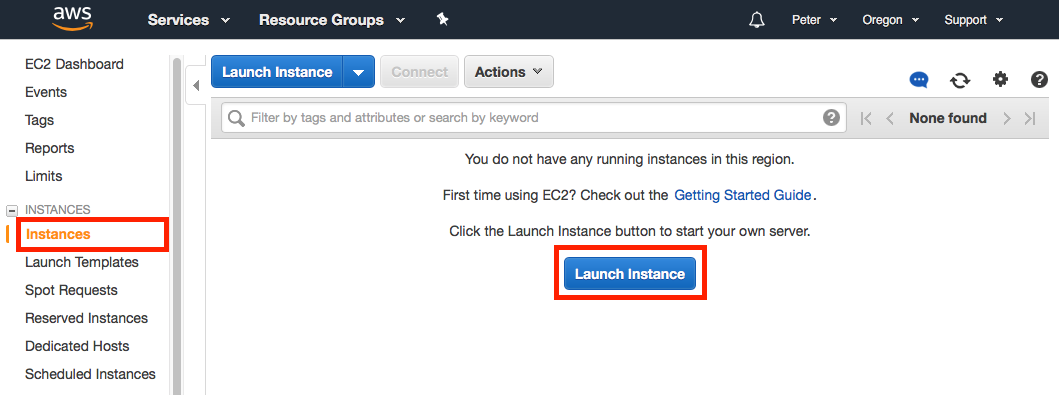
After recieving notification of successful limit increase, log into the EC2 console (see instructions above) to begin creating a new EC2 instance. Click the Instances link on the left hand toolbar and subsequently click on the blue Launch Instance button.
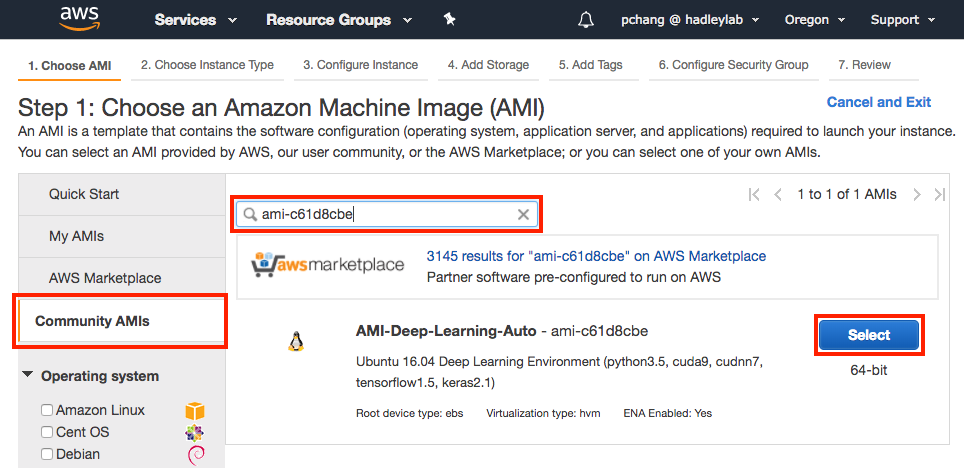
For the first step, choose Community AMIs on the left hand toolbar and type in ami-c61d8cbe into the Search community AMIs query field. Click on the blue Select button to choose this template image. This step configures the baseline software for the new EC2 instance. The remaining steps configure the baseline hardware and network protocol settings.
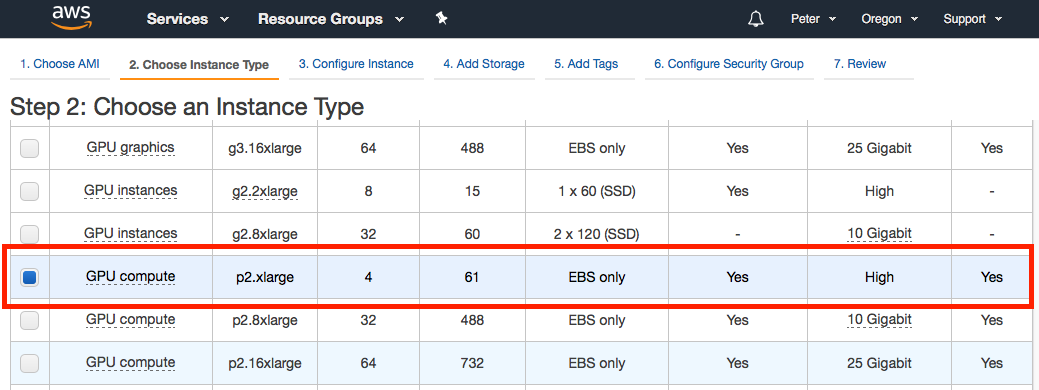
For the second step, we need to choose the EC2 instance type. Scroll down the page until you get to p2.xlarge in the Instance Type column. This is the baseline single GPU instance.
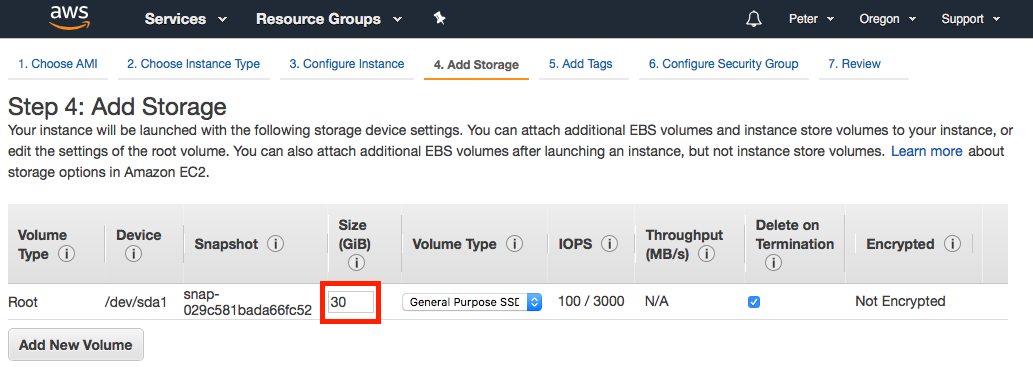
On the top set of links, click on Add Storage to configure the storage settings for the EC2 instance. Free tier users recieve up to 30 GiB of storage without charge, so we will configure this instance with 30 GiB of SSD storage.
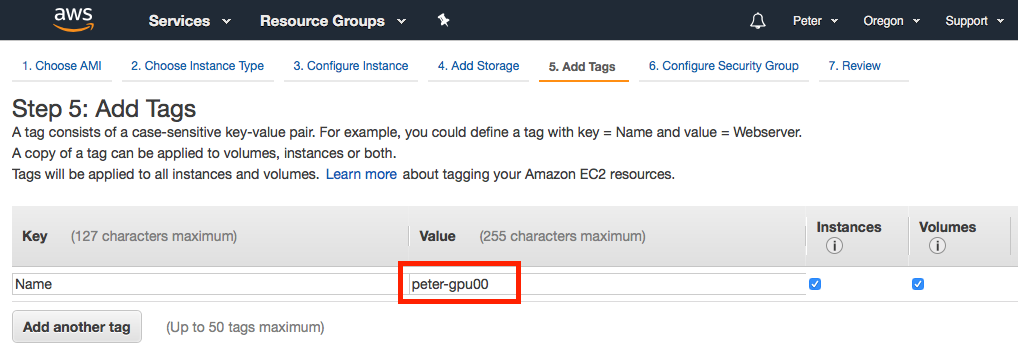
On the top set of links, click on Add Tags to name your new EC2 instance (for your own personal benefit in case you may have multiple EC2 instances to keep track of). In the middle of the screen click the link for click to add a Name tag and complete with an appropriate name:
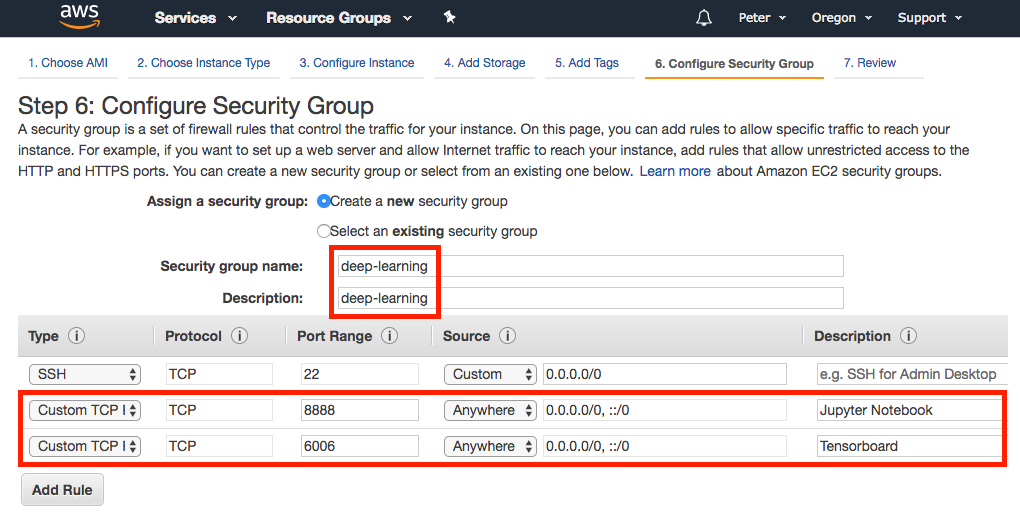
On the top set of links, click on Configure Security Group to set up port firewall settings. First we will create an arbitrary name for this profile of settings by changing Security group name and Description to deep-learning. By default port 22 (for SSH) is allowed. In addition we must open the default Jupyter notebook port 8888 to allow you to connect to the EC2 instance and edit code through a web browser. To do so, click Add Rule and fill in the following settings:
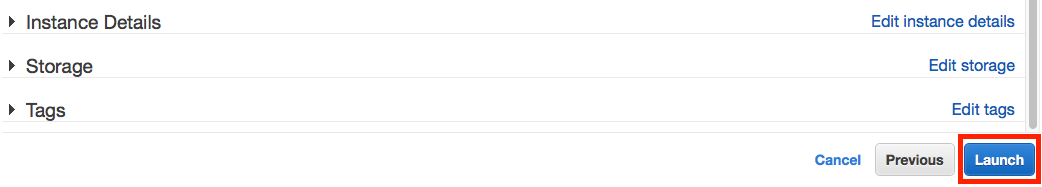
On the top set of links, click on Review to see a summary of the EC2 settings. Click on the bottom right hand Launch button.
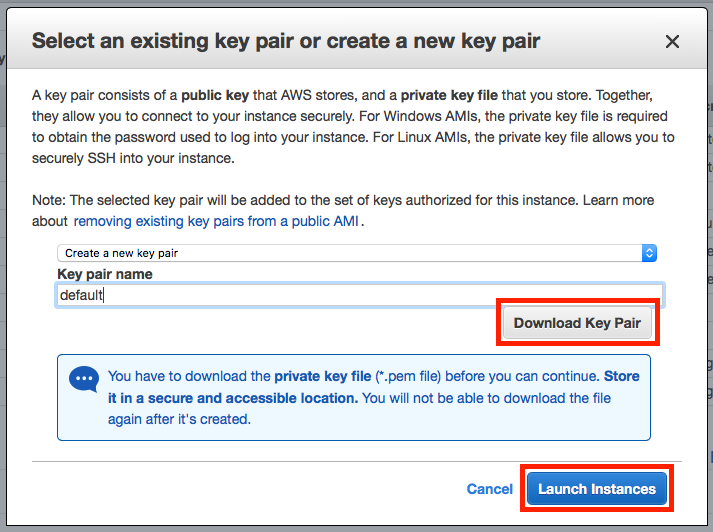
The final step is to create an SSH key pair to remotely connect to your EC2 instance. To do so type in a key pair name (default) and click Download Key Pair. It is important to remember the name and location of this downloaded key. If you lose this key you will be unable to access the EC2 instance. A recommended strategy to store AWS key pairs is to place it in a hidden folder easily accessible from your home folder (~/.aws). After downloading and saving the SSH key, click Launch Instance to complete the EC2 creation process.
Before continuing, open a terminal and navigate to the location of your saved key. If you did not create a ~/.aws folder to place your key and would like to do so now, use the following commands:
mkdir ~/.aws
mv name_of_your_key.pem ~/.aws/default.pem
Note that some OS's may automatically append a *.txt to the end of your *.pem file when downloading. If so the mv command above wil rename your file appropriately. At this time, also go ahead and change the permissions on the SSH key to not be publically viewable (otherwise SSH client will not accept the key):
chmod 400 ~/.aws/default.pem
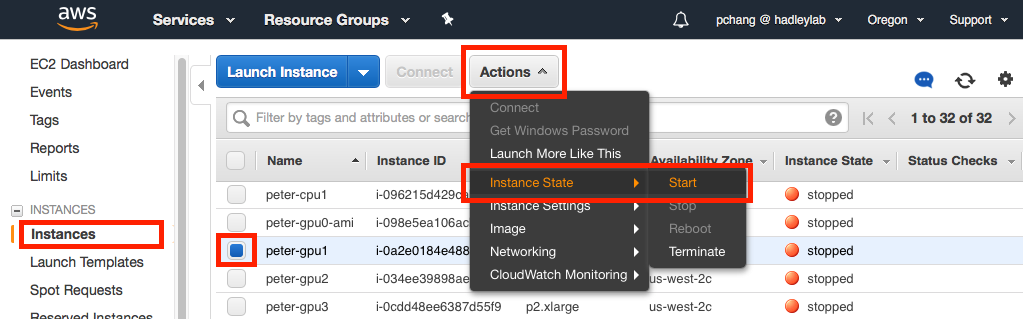
Upon completing the EC2 instance creation steps described above, the new EC2 instance will be automatically be started. On each subsequent future session, you will have to start (e.g. boot) your EC2 instance before you can connect and use it. To do so, select the Instances link on the left hand toolbar, select the instance you want to boot (blue check box to the left of the instance name), select Actions > Instance State > Start. Your EC2 instance will be ready to connect in about 30-60 seconds.
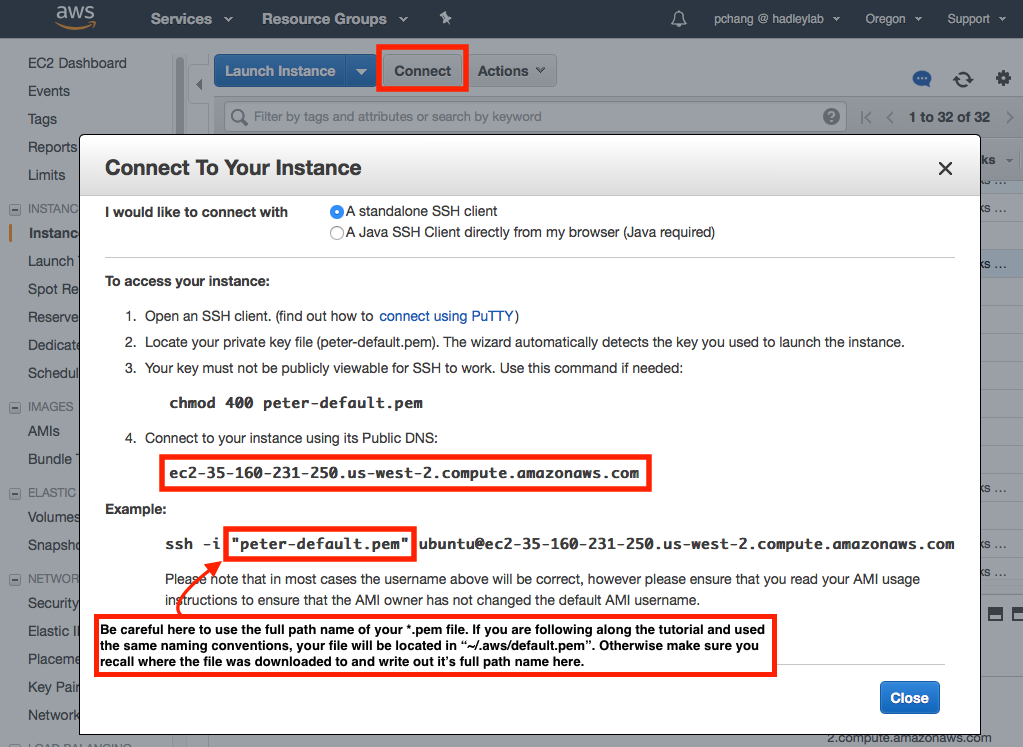
There are two options to start a remote connection to your EC2 instance. Instructions can be found by selecting a particular EC2 instance (blue check box to the left of the instance name) and clicking the Connect button.
The recommended option is to connect through a standalone SSH client (from your local machine) of your choice. For Mac OS X users, the default SSH client located in the Terminal appliation (Applications > Utilities) is recommended. After opening a terminal session, type in the following command:
ssh -i "/path/to/your/pem/file" ubuntu@[ec2-public-dns]
Note the you should replace [ec2-public-dns] with your EC2 instances public DNS. In the above screenshot this would be c2-35-160-231-250.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com. Assuming that your SSH key is located at ~/.aws/default.pem (if you followed the instructions per EC2 creation above) then the full command would be:
ssh -i "~/.aws/default.pem" ubuntu@c2-35-160-231-250.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com
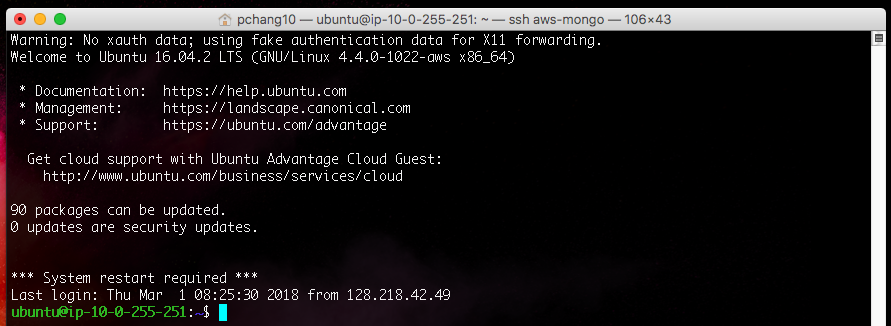
You should now be successfully logged into your remote SSH session.
AWS charges a fixed cost per hour of EC2 instance usage, prorated to the second. To keep your charges low, it is advised to stop (e.g. turn off) your EC2 instance whenever your are finished. To do so, select the Instances link on the left hand toolbar, select the instance you want to stop, select Actions > Instance State > Stop.
During the tutorial session, all code written by the participants will be completed using the Jupyter notebook, an iPython kernel / server that will be running from your own personal AWS instance and accessed through a web-browser. Through this web-based interface one will be able to write, edit and run code in an easy way without needing to use the Linux command line. For more advanced users, this entire Github repository is available for access from the command line at ~/dl_tutorial. See below for more information.
A preconfigured Jupyter server has been set up on the EC2 instance broadcasting on port 8888. To launch this server simply run the following bash script after connecting to your EC2 instance (located in your home folder):
./start_jupyter.sh
This bash script will:
- update to the latest version of this repository from Github
- activate the
dl_awsconda environment - launch a Jupyter server listening of port 8888
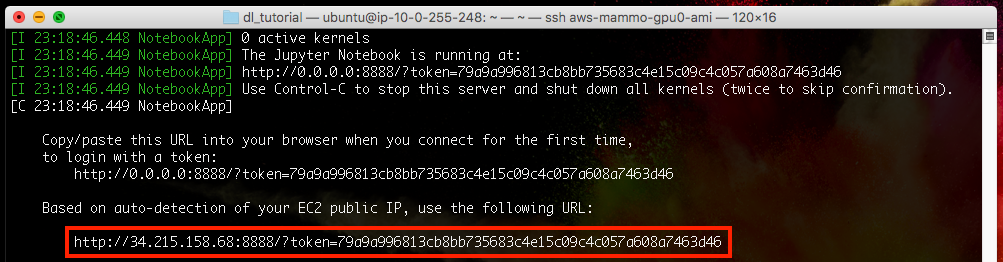
Upon execution, two URLs are shown:
The first URL is prefixed with 0.0.0.0, the default template provided by the Jupyter notebook server, and the second URL is created by an auto-IP detection script, filling the address with your public IP address. If this does not appear, see Finding your public IP address section below to locate this manually.
To connect to this Jupyter server, open a web-browser (e.g. Google Chrome) enter the URL into the address bar.
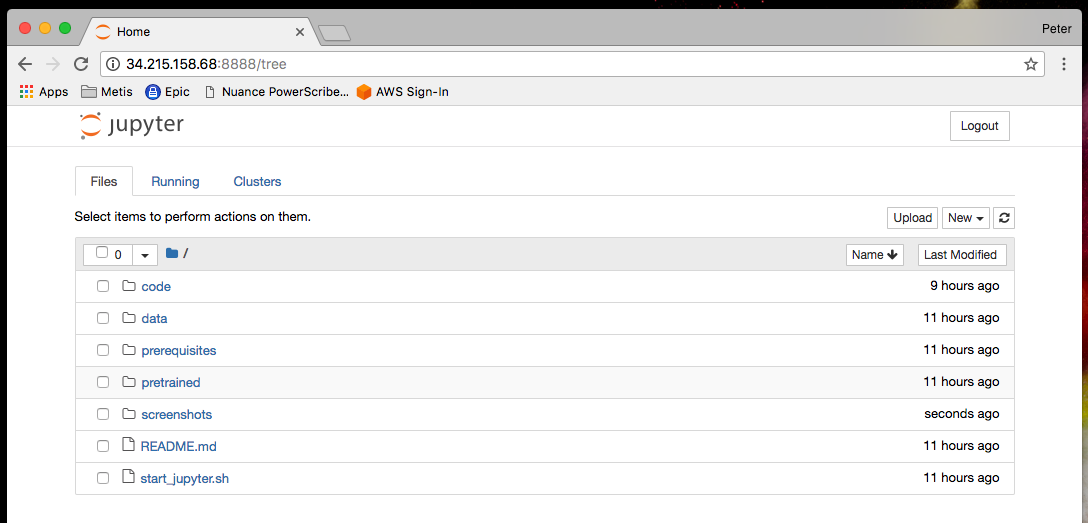
Press [enter] to navigate to the web page. You now have access to a web-based iPython kernel though the Jupyter notebook. You also have access to the files on your AWS EC2 instance. By default you will login into a clone of this Github code repository pre-configured into your EC2 instance:
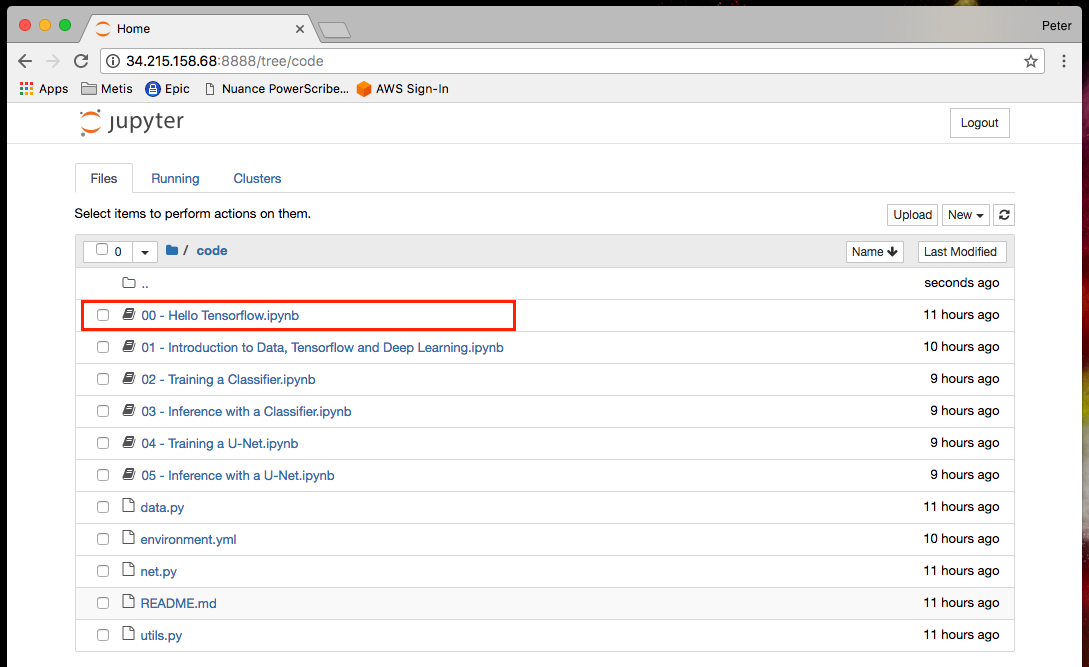
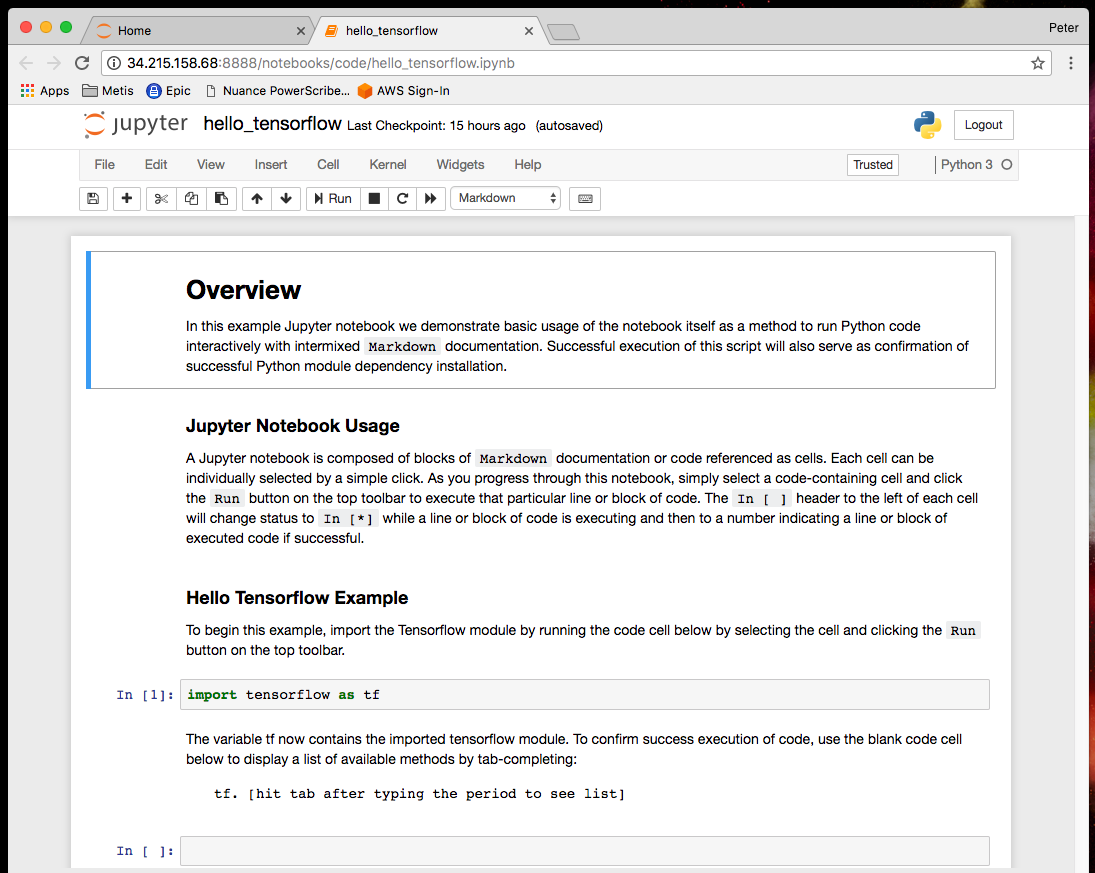
Click on the Code folder to open and access the series of Jupyter notebook lectures (*.ipnyb) and template code provided for you as part of this tutorial. If you are unfamiliar with Jupyter you can launch the 00 - Hello Tensorflow.ipynb notebook to walk through a basic working example by simply clicking on it:
You should now have access to our first example Jupyter notebook. Feel free to walk through this template, execute the code (which will be run on your EC2 instance) and edit as you see fit.
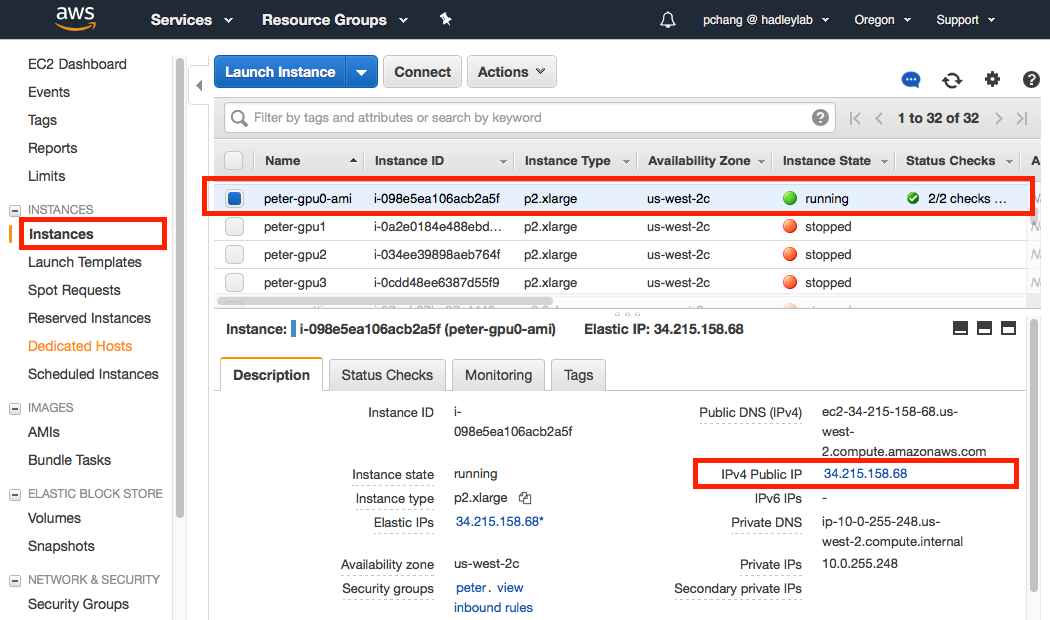
If the auto-IP detection feature does not work on your EC2 instance, you will need to manually find your IP address in the AWS dashboard. The public IP address of your instance can be found in the Instances menu of the EC2 dashboard:
For more advanced users wishing to follow along directly through the EC2 command line instead of the Jupyter notebook, these are instructions for basic access. In the EC2 instance, all required dependencies have been installed in a separate Conda virtual enivornment named dl_aws. To activate simply run:
source activate dl_aws
From here simply access code and materials from this cloned Github repository at ~/dl_tutorial. You may use your favorite editor. Note that vim has been preconfigured with syntax highlighting, Vundle and several useful plugins for Python development (see ~/.vimrc for further details). Code may be executed with either python or the ipython kernel.