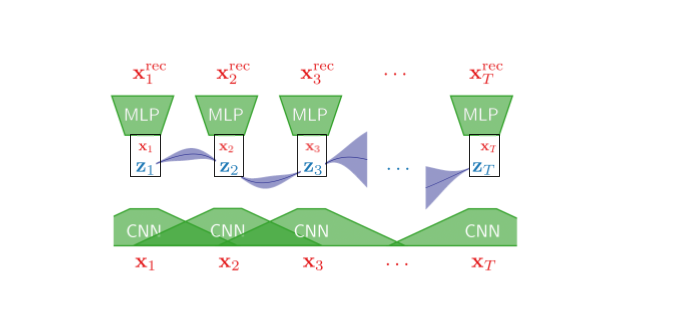
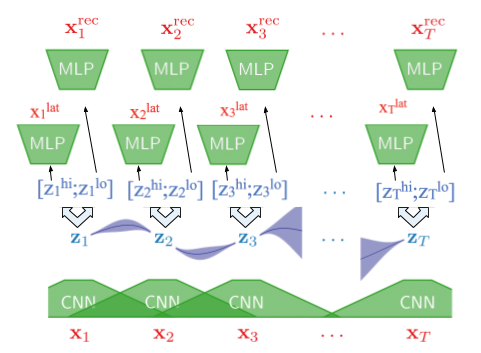
Our approach utilizes extends Variational Autoencoders with Gaussian Process (GP-VAE) prior for time series imputation paper by Fortuin et. al. This repository is a fork of the repository used for their paper.
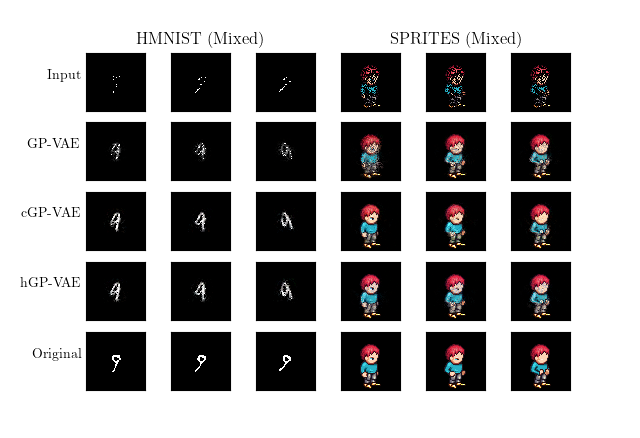
Our extensions include cGP-VAE (coerced GP-VAE) and hGP-VAE (hybrid GP-VAE).
- This extension model learns a latent representation of the corruption in the input.
- It then uses the learned representation with the original input to reconstruct the image.
- This extension model learns a latent representation of that combines the traditional Guassian multivariate distribution as well as the corruption representation.
- It then uses a multi-stage decoder to reconstruct the input image.
- Python >= 3.6
- TensorFlow = 1.15
- Some more packages: see
requirements.txt
-
Clone or download this repo.
cdyourself to it's root directory. -
Grab or build a working python enviromnent. Anaconda works fine.
-
Install dependencies, using
pip install -r requirements.txt -
Download data:
bash data/load_{hmnist, sprites}.sh. -
Convert and rescale hmnist data by running
python data/convert.pyandpython data/decompress.py. -
Run command
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=* python newexp.py --model_type {vae, hi-vae, gp-vae, cgp-vae, hgp-vae} --tr_src {hmnist, sprites, both} --val_src --exp_name <your_name> ...To see all available flags run:
python train.py --help
New Experiments use the rescaled HMNIST and Sprites data only. Goal is to optimize for general image/video reconstruction.
The following are commands to run our experiments. Exchange the model type argument to compare hgp-vae, cgp-vae, gp-vae:
- Train Sprites;Test HMNIST:
python newexp.py --model_type gp-vae --tr_src sprites --val_src hmnist --exp_name sprites_to_hmnist --testing --banded_covar --latent_dim 256 --encoder_sizes=32,256,256 --decoder_sizes=256,256,256 --window_size 3 --sigma 1 --length_scale 2 --beta 0.2 --num_epochs 10 --seed 0 - Train HMNIST;Test Sprites:
python newexp.py --model_type gp-vae --tr_src hmnist --val_src sprites --exp_name hmnist_to_sprites --testing --banded_covar --latent_dim 256 --encoder_sizes=32,256,256 --decoder_sizes=256,256,256 --window_size 3 --sigma 1 --length_scale 2 --beta 0.2 --num_epochs 10 --seed 0 - Train Mixed;Test Mixed:
python newexp.py --model_type gp-vae --tr_src both --val_src both --exp_name mixed --testing --banded_covar --latent_dim 256 --encoder_sizes=32,256,256 --decoder_sizes=256,256,256 --window_size 3 --sigma 1 --length_scale 2 --beta 0.2 --num_epochs 10 --seed 0
Remove the --testing flag if you want to simply use a validation split for the training data.
If you do remove the --testing flag, you must ensure that --val_src and --tr_src are the same.
Below is a qualitative comparison of our results from training using the homogenous data sets of either just HMNIST data or SPRITES data.
Below is a qualitative comparison of our results from training on the mixed dataset of both HMNIST and SPRITES data.