Adding new functionality to cv.warpPolar in opencv.
Resolved edge information loss and omissions in cart2pol transformations, improving accuracy for image boundaries. Added the following macro definitions:
WARP_POLAR_EXP: Enables exponential sampling along the radial direction.
WARP_POLAR_SQRT: Similar to logPolar, supports square root sampling for smoother
scaling.
WARP_POLAR_SQUARE: Performs radial square sampling, compensating for shrinking
sectors to preserve edge details.
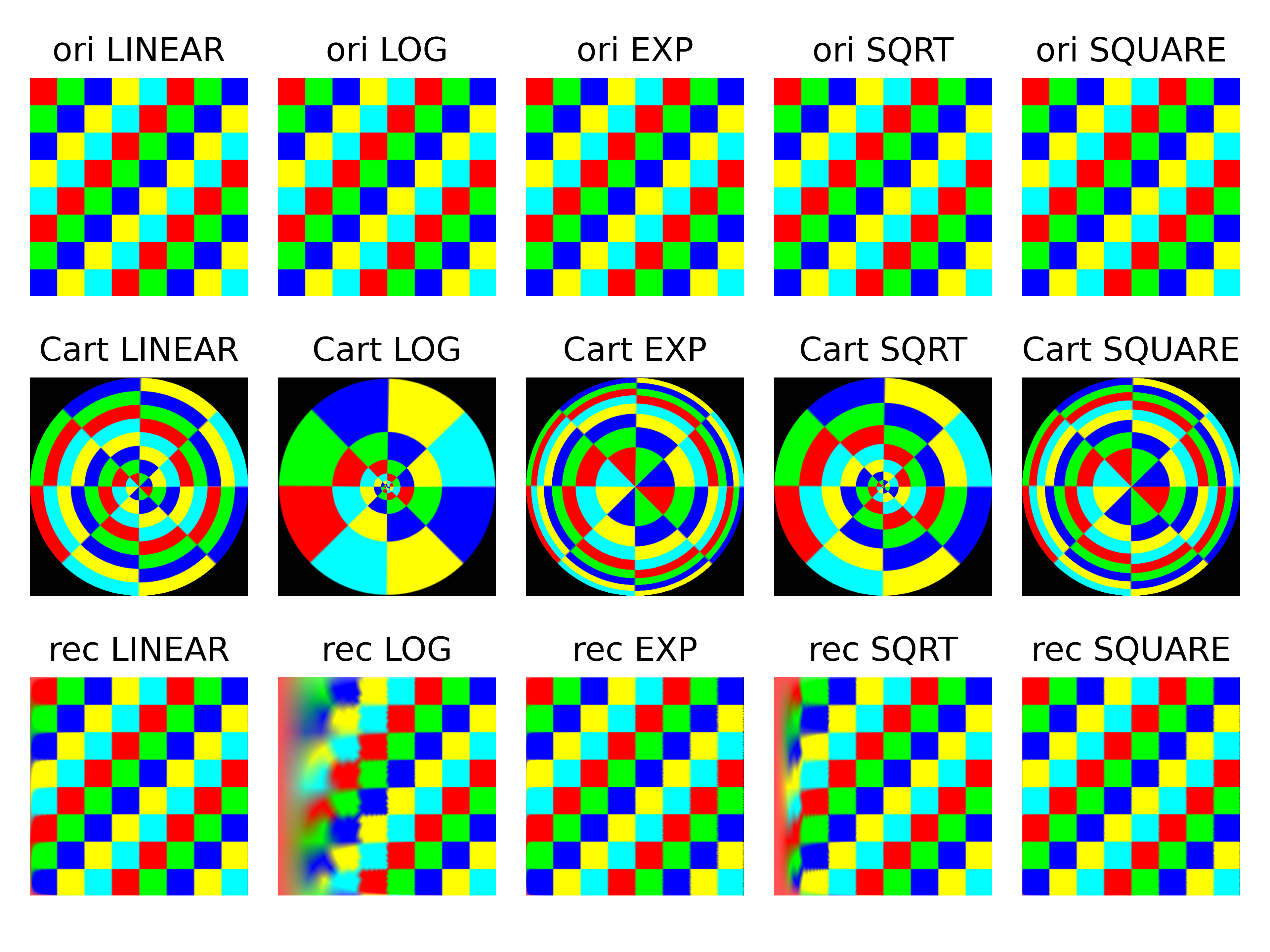
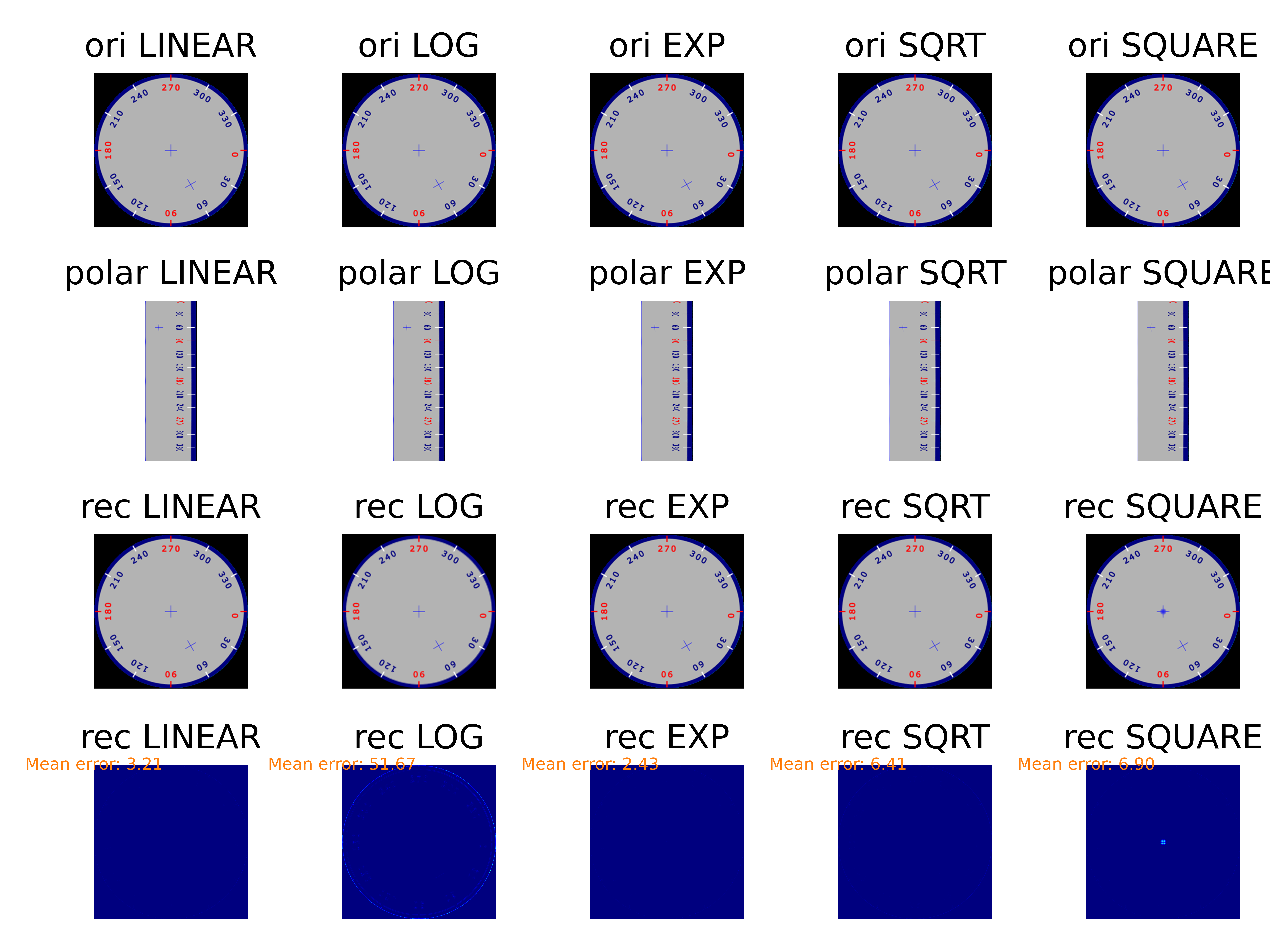
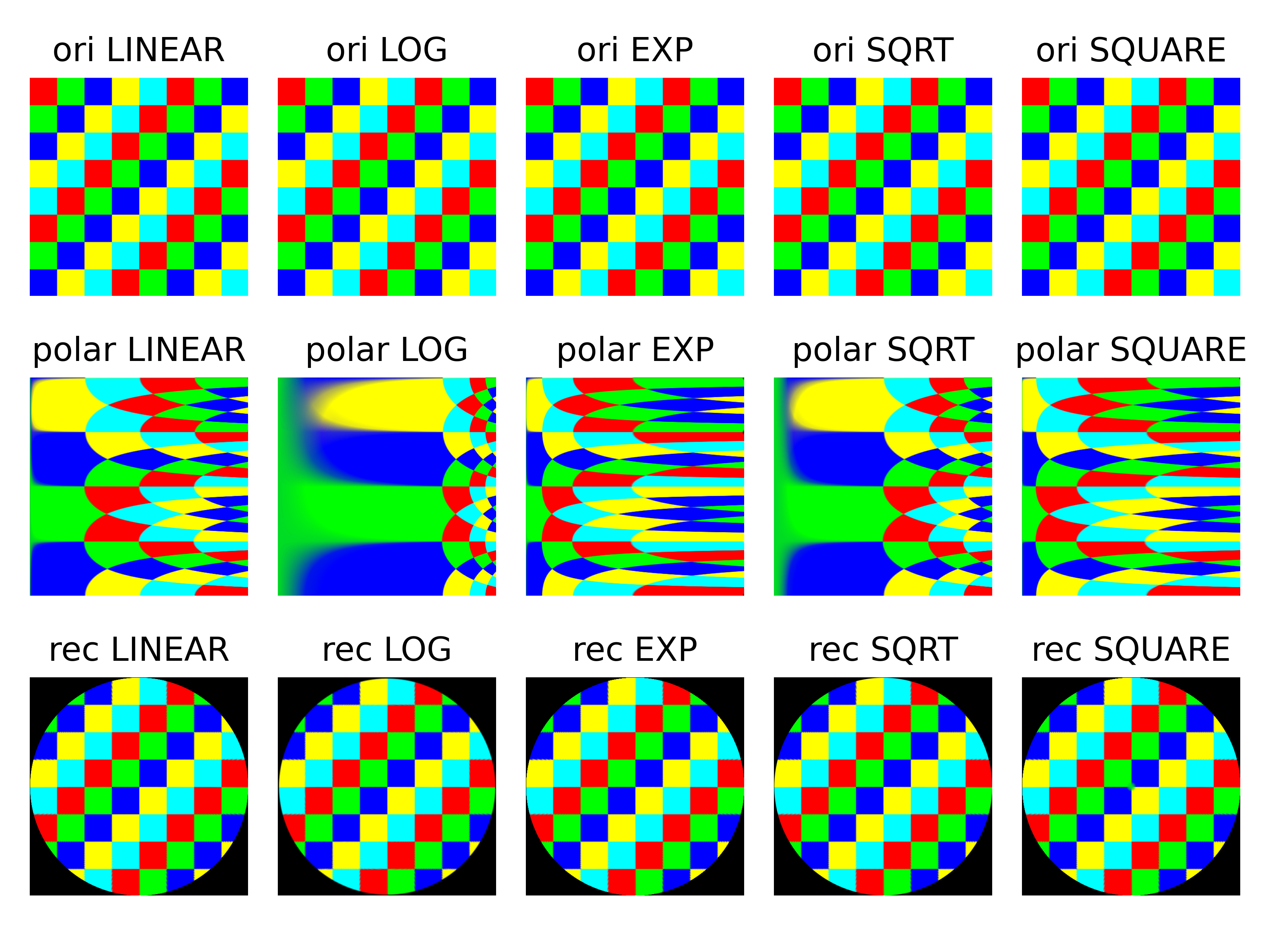
Run python main.py img.png will obtain the figures below.
- The first row is the original image in Cartesian space;
- the second row is the image transformed into polar coordinate space;
- and the third row is the image transformed back into Cartesian space.
The first two columns are generated using the original cv2.WARP_POLAR_LINEAR and cv2.WARP_POLAR_LOG.
The original method focuses too much on the centre of the image in the Cartesian coordinate system. For example, the cross in the image in Cartesian coordinates takes up too much area in polar coordinates, especially when using WARP_POLAR_LOG. This image is from the official opencv example.
Another example
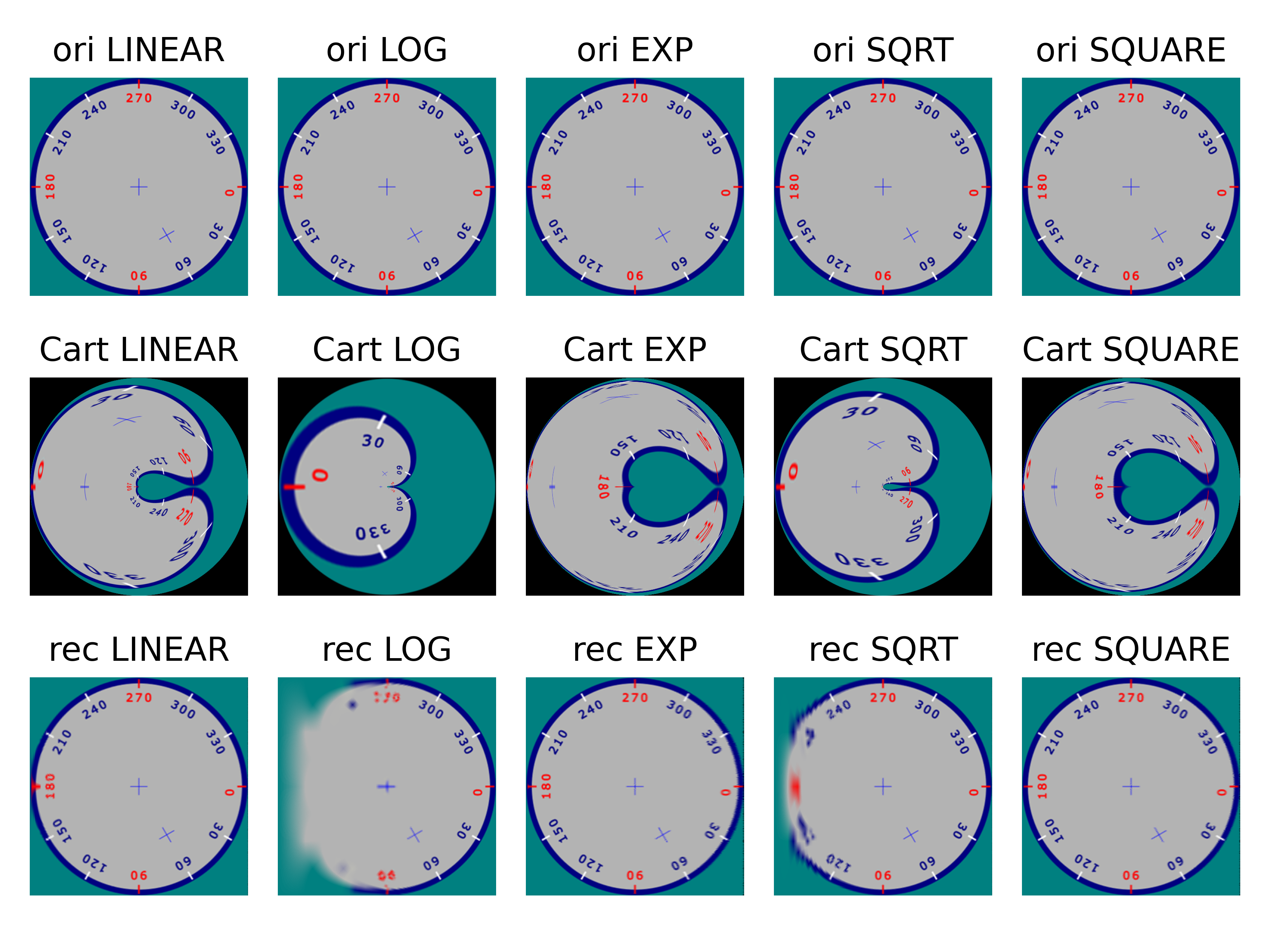
Run python main_inv.py img.png will obtain the figures below.
- The first row is the original image in polar space;
- the second row is the image transformed into Cartesian coordinate space;
- and the third row is the image transformed back into polar space.
The first two columns are generated using the original cv2.WARP_POLAR_LINEAR and cv2.WARP_POLAR_LOG. The original method focuses excessively on the centre of the image in Cartesian space.
Another example