Arduino Library for Scanse Sweep LiDAR
Currently the library has only been tested with an Arduino Mega 2560, an Arduino Mega ADK, and an Arduino Micro.
| sweep firmware | compatibility |
|---|---|
| > v1.4 | untested |
| v1.4 | yes |
The library is designed to support the most recent Sweep firmware version. The communication protocol used by earlier firmware versions may not work properly with this library. A guide to updating the Sweep's firmware is available here.
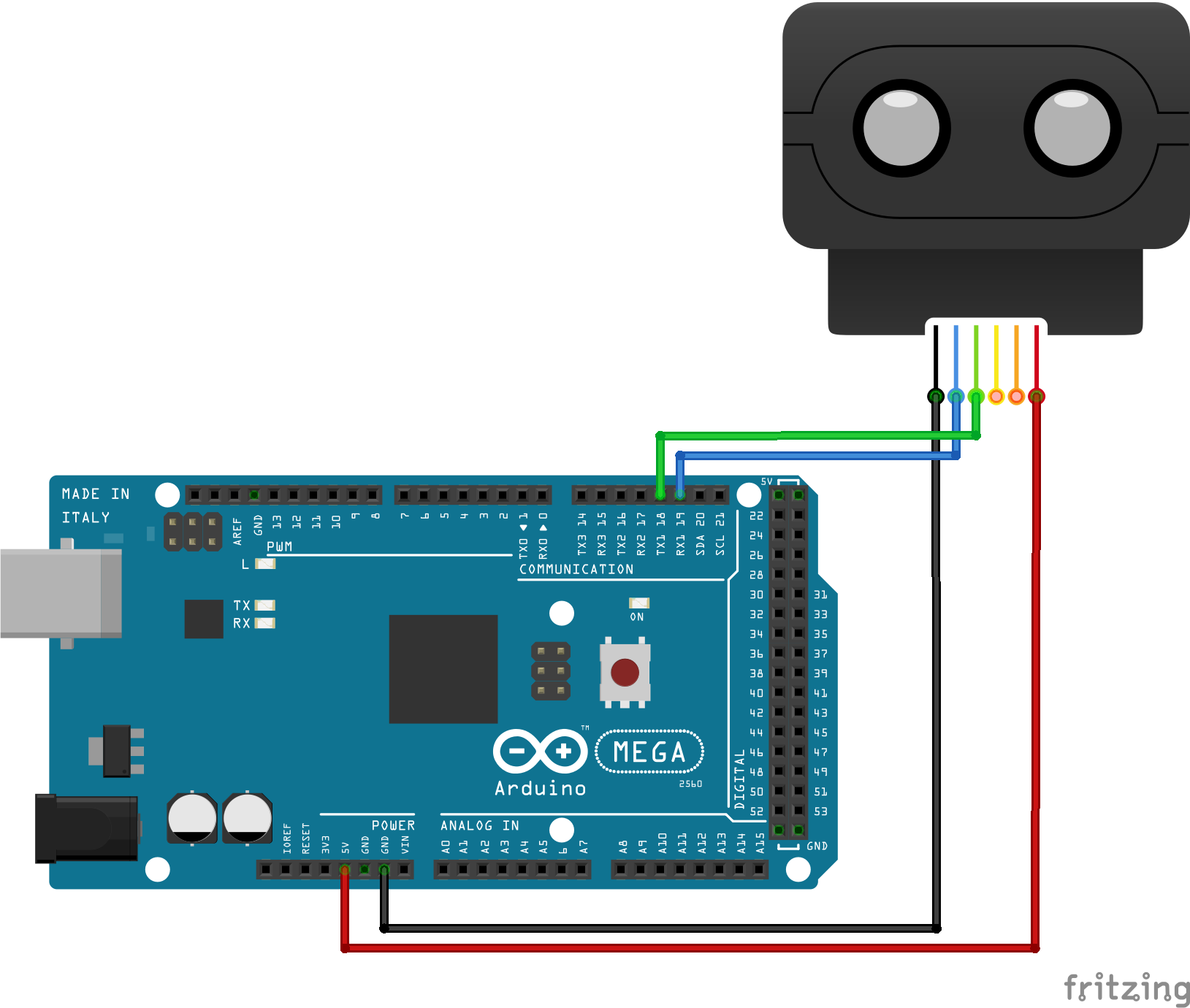
Copy the entire Sweep/ folder to your .../Arduino/libraries/ directory.
Checkout the provided Examples/ directory for 2 full examples.
For best results, you should provide dedicated external 5V power to the Sweep rather than using power from the Arduino. Just be sure to connect the ground from the power source and the arduino. If you are just experimenting, you can run the sweep off the 5V power from the Arduino with the Arduino receiving power over USB. However, it is possible that using a low power USB port (ex: laptop) to power the arduino + sweep will result in unexpected behavior.
Include the Sweep library in your sketch:
#include <Sweep.h>
...
Create a Sweep device with a Stream Object:
// Ex: assuming sweep is connected to Serial #1 (RX1 & TX1) on the Mega
Sweep device(Serial1);
...Adjust device settings:
// Set the motor speed to 5HZ (codes available from 1->10 HZ)
bool bSuccess = device.setMotorSpeed(MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_5_HZ);
...
// Set the sample rate to 500HZ (codes available for 500, 750 and 1000 HZ)
bool bSuccess = device.setSampleRate(SAMPLE_RATE_CODE_500_HZ);Retrieve current device settings:
// Read the current motor speed
int32_t currentMotorSpeed = device.getMotorSpeed();
if (currentMotorSpeed < 0)
// Failed to get current motor speed
...
// Read the current sample rate
int32_t currentSampleRate = device.getSampleRate();
if (currentSampleRate < 0)
// Failed to get current sample rate
...Data collection:
// Start scanning
bool bSuccess = device.startScanning();
...
// read 10 individual sensor readings
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// Create a scan packet to populate with the sensor reading
bool success = false;
ScanPacket reading = device.getReading(success);
if(success) {
bool bFirstOfNewScan = reading.isSync();
float angle = reading.getAngleDegrees();
uint16_t range = reading.getDistanceCentimeters();
uint8_t confidence = reading.getSignalStrength();
...
// stop scanning
bool bSuccess = device.stopScanning();Sweep(Stream &serial)Constructs a sweep device on the provided Stream object.
bool isScanning()Returns true if the device is currently scanning.
bool startScanning()Blocks until the sweep device is ready, then signals the device to start scanning. Initiates an indefinite stream of individual sensor readings until stopScanning() is called.
During an active data stream, any attempt to communicate with the device other than stopScanning() will fail.
To avoid blocking, you can use the getMotorReady() command to query the current state of the device , and do work in the meantime if it isn't ready.
bool stopScanning()Signals the sweep device to stop scanning. Will block for ~500ms to flush leftover data stream from the buffer and validate a second response from the sensor.
ScanPacket getReading(bool &success)Reads a single sensor reading from the serial buffer. Must be called frequently enough to keep up with the data stream.
class ScanPacketClass representing a single sensor reading (ranging). ie: a full 360deg scan would be composed of many such readings.
bool getMotorReady()Returns true if the device is ready. A device is ready when the motor speed has stabilized to the current setting and the calibration routine is complete. If a device was just powered on, or the motor speed was just changed, it can take up to 9 seconds for the device to get ready. For visual confirmation, the blue LED on the face of the sweep will blink until the device is ready.
bool waitUntilMotorReady()Blocks until the device is ready. Returns true if the device is ready, and false if the check timed out (max 10 seconds).
int32_t getMotorSpeed()Returns the current motor speed setting in HZ
bool setMotorSpeed(const uint8_t motorSpeedCode[2])
// Available Codes
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_0_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_1_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_2_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_3_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_4_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_5_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_6_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_7_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_8_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_9_HZ
MOTOR_SPEED_CODE_10_HZBlocks until the device is ready, then adjusts the motor speed setting to the provided code. Recommend users pass one of the const codes defined by library.
To avoid blocking, you can use the getMotorReady() command to query the current state of the device , and do work in the meantime if it isn't ready.
int32_t getSampleRate()Returns the current sample rate setting in HZ.
bool setSampleRate(const uint8_t sampleRateCode[2])
// Available Codes
SAMPLE_RATE_CODE_500_HZ
SAMPLE_RATE_CODE_750_HZ
SAMPLE_RATE_CODE_1000_HZAdjusts the sample rate setting to the provided code. Recommend users pass one of the const codes defined by library.
void reset()Resets the device. Attempting to communicate with the device while it is resetting will cause issues. While the device is booting the LED on the device will blink green. The device is capable of communication when the LED turns from green to blue, although the motor may still be adjusting until the blue LED stops blinking as well.
ScanPacket(const bool bIsSync, const uint16_t rawAngle, const uint16_t distance, const uint8_t signalStrength)Constructs a ScanPacket object with the given parameters. The construction of the ScanPacket object for a reading is handled by the Sweep class's getReading() method; you should not need to use this constructor.
bool isSync() constReturns true if this reading was the first reading of a new scan; otherwise, returns false.
float getAngleDegrees() constReturns the angle of this reading as a float, in degrees.
uint16_t getAngleRaw() constReturns the angle of this reading as the raw 16-bit fixed point value. The scaling factor of this value is 16; this means that the angle in degrees is obtained by dividing the raw value by 16.
uint16_t getDistanceCentimeters() constReturns the distance of this reading, in centimeters.
uint8_t getSignalStrength() constReturns the signal strength of this reading as an integer value between 0 and 255. Signal strength can be thought of as a confidence metric. A low value indicates low strength, and a high value indicates high strength.
Note: The signal strenth value is affected by light conditions, material properties etc. For more information, see the article on the Theory of Operation.
float getNormalizedSignalStrength() constReturns the signal strength of this reading as a float value normalized between 0 and 1. ie: ints [0:255] map to floats [0.0f:1.0f].
Note: this method only normalizes a raw byte value. It does NOT normalize the signal strength of this reading in the context of the min and max signal strengths from all readings in a scan, as the reading class has no knowledge of a scan.