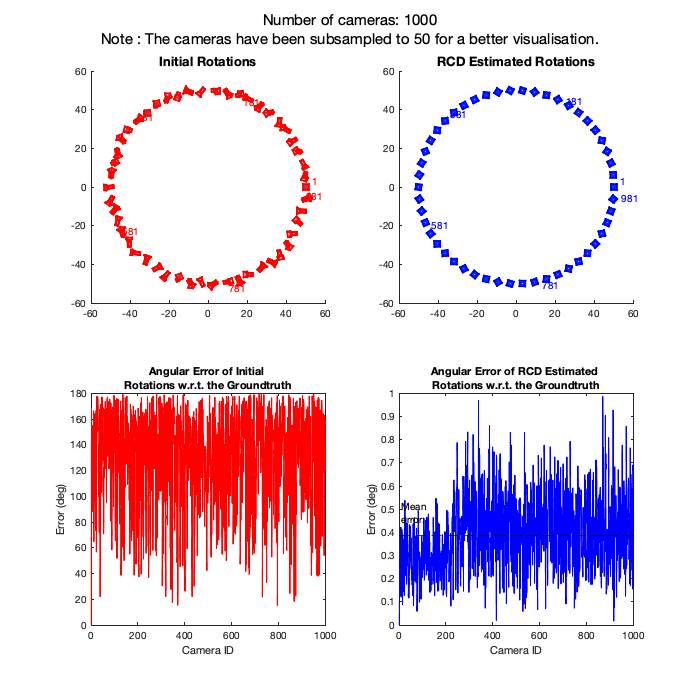
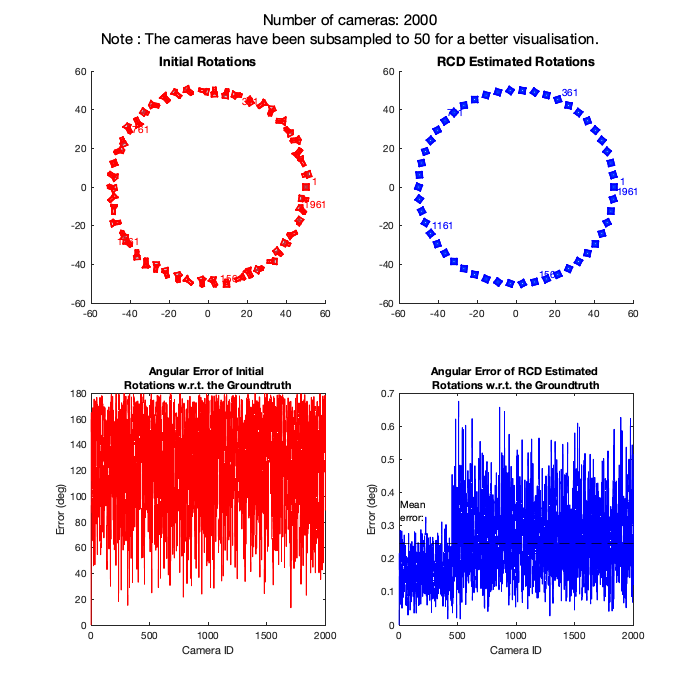
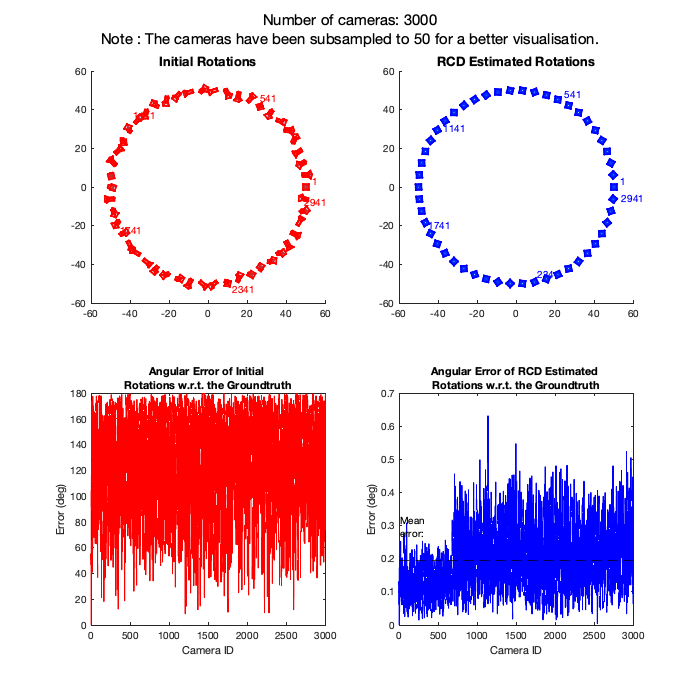
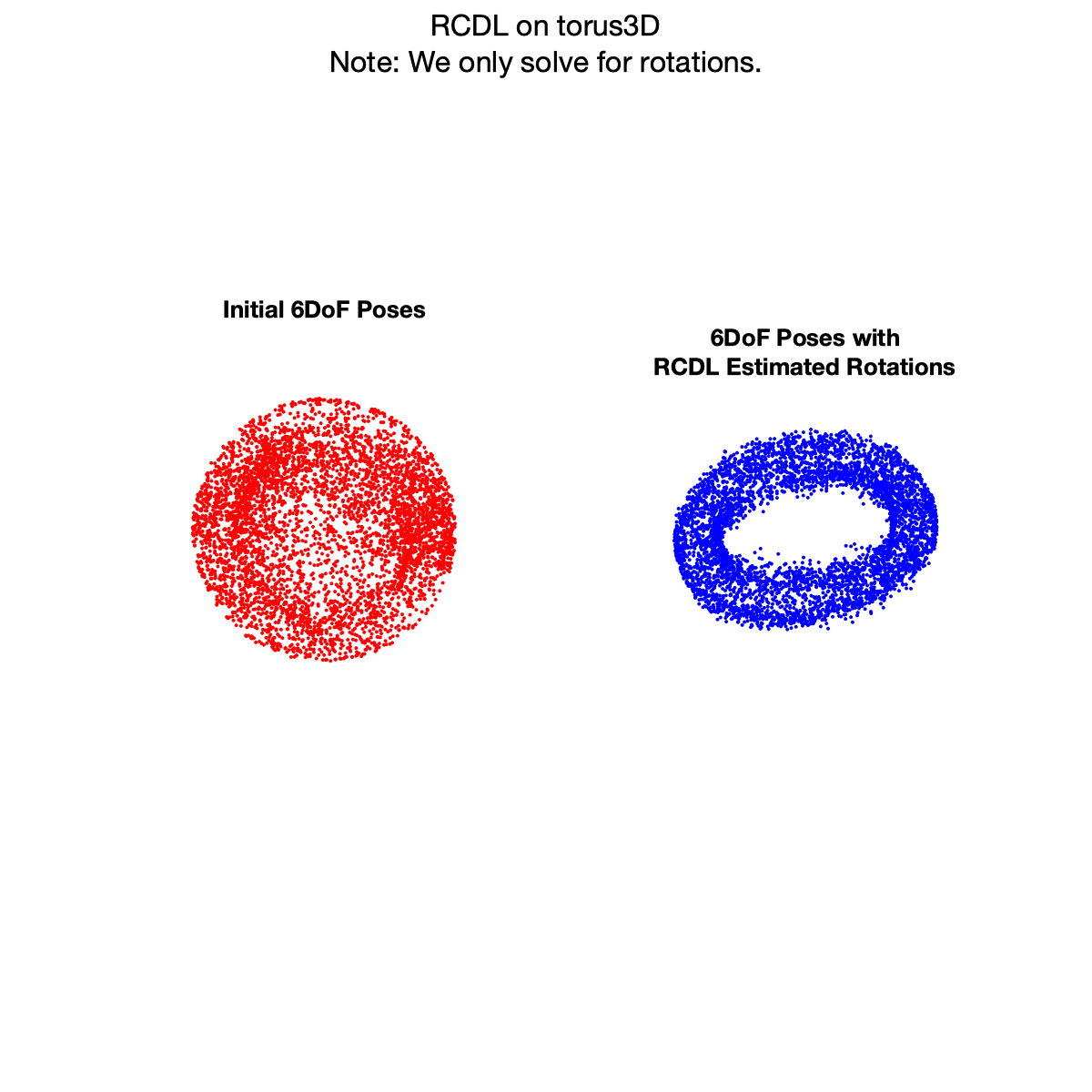
Rotation Coordinate Descent (RCD) is a fast rotation averaging algorithm that achieves global optimality under mild noise conditions on the noise level of the measurements.
@inproceedings{parra2021rotation,
title={Rotation Coordinate Descent for Fast Globally Optimal Rotation Averaging},
author={Parra, Alvaro and Chng, Shin-Fang and Chin, Tat-Jun and Eriksson, Anders and Reid, Ian},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={4298--4307},
year={2021}
}
This demo runs in MATLAB, with RCD and RCDL compiled in C++. We tested under version R2020a on systems with:
- macOS Catalina
- Ubuntu 18.04
Dependencies:
-
CMake 3.0 or later required cmake installation link
-
MacOS
brew install cmake -
Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install cmake
-
-
SuiteSparse required
-
MacOS
brew install suite-sparse -
Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install libsuitesparse-dev
-
We provide a script build.sh to build RCD and RCDL. Please make sure you have installed all required dependencies (see Section 1). Execute
chmod +x build.sh
./build.sh
which will create the executables RCD and RCDL in bin folder.
Run demo_rcd.m in MATLAB.
Here, we provide a demonstration on 3 different SfM camera graphs where number of nodes = 1000, 2000 and 3000 and graph density = 0.4. This demo is expected to finish in about 1 minute, which will generate the following outputs:
Run demo_rcdl.m in MATLAB.
Here, we provide a demonstration on 2 different SLAM camera graphs which are torus3D and grid3D. This demo is expected to finish in about 1 minute, which will generate the following outputs: