This repository provides the 2bRAD-M computational pipeline for microbiome analysis, which has been formally published on Genome Biology:
Species-resolved sequencing of low-biomass or degraded microbiomes using 2bRAD-M by Zheng Sun, Shi Huang, Pengfei Zhu, Lam Tzehau, Helen Zhao, Jia Lv, Rongchao Zhang, Lisha Zhou, Qianya Niu, Xiuping Wang, Meng Zhang, Gongchao Jing, Zhenmin Bao, Jiquan Liu, Shi Wang, Jian Xu. Genome Biology, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-021-02576-9
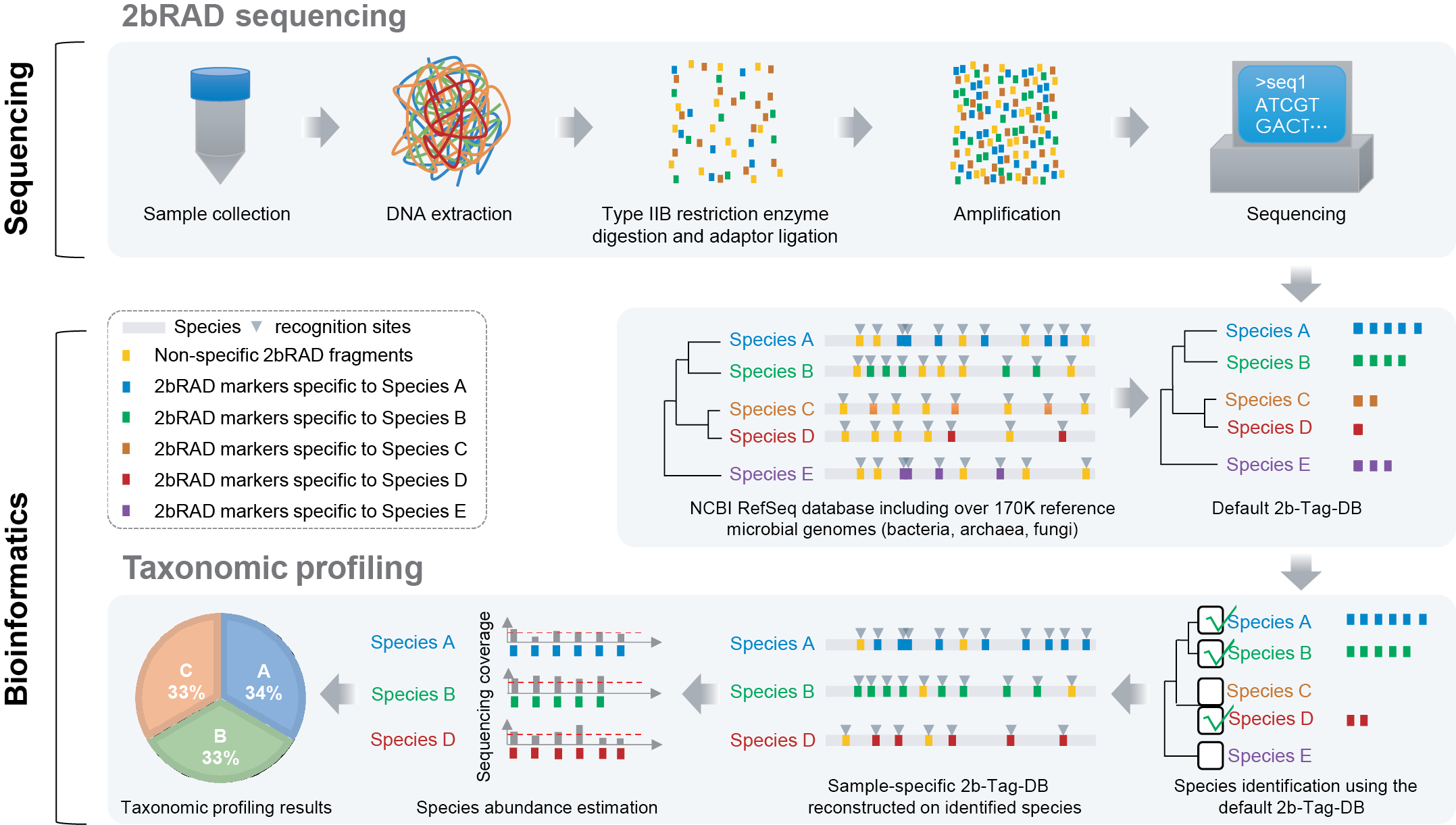
The principle of 2bRAD-M on microbiome analyses:
(1) reliable enzyme-digested sequence tags can be derived that are specific to high-resolution taxa (e.g., species or strain) yet universally applicable for a broad range or all of bacterial, archaeal and fungal genomes;
(2) these taxa-specific, iso-length sequence tags can be evenly amplified and sequenced;
(3) the tag sequences can be mapped to reference genomes to reconstruct faithfully the taxonomic composition.
You can also find more details for the 2bRAD-M workflow below.
-
The experimental workflow has two steps:
(1) BcgI (a commercially available Type IIB restriction enzymes) is used, as an example, to digest total genomic DNA extracted from microbiome samples. BcgI recognizes the sequence of CGA-N6-TGC in the genomic DNA and cleaves on both upstream (12-10 bp) and downstream (10-12 bp) of this signature, producing short and iso-length DNA (32bp without sticky ends) across all loci.
(2) These so-called “2bRAD fragments” are ligated to adaptors, amplified and then sequenced.
-
The computational workflow. The foundation here is a unique 2bRAD tag database (“2b-Tag-DB”), which contains taxa-specific 2bRAD tags identified from all the sequenced bacteria, fungi and archaea genomes. Mapping the 2bRAD reads against 2b-Tag-DB thus identifies the presence of species in a sample. Subsequently, to estimate relative abundance of the identified taxa, the mean read coverage of all 2bRAD tags specific to each taxon is derived. To improve utilization rate of reads and classification accuracy, a secondary, sample-specific 2b-Tag-DB was dynamically derived from only those candidate taxa identified in a particular sample, which produces more species-specific 2bRAD tags than the original 2b-Tag-DB and results in more accurate modeling of relative abundance of taxa.
All scripts in 2bRAD-M are written using Perl and recommended to run in a conda environment. This program should work properly in the Unix systems, or Mac OSX, as all required packages can be appropreiately download and installed.
Construction of a 2bRAD-M standard database (i.e., 2b-Tag-DB) requires approximately 10 GB of disk space.
Running the standard pipeline requires < 30Gb of RAM, which is also compatible with multithreading. For example, the BcgI-derived (default) database size is 9.32 GB, and you will need more than that in RAM if you want to build the default database. In a test early on, the peak memory can reach up to 29GB.
About 20 minutes are required for loading the 2b-Tag-DB. For a typical gut metagenome, ~40 minutes are required for species profiling.
-
Clone the latest version from GitHub (recommended):
git clone https://github.com/shihuang047/2bRAD-M/
cd 2bRAD-MThis makes it easy to update the software in the future using
git pullas bugs are fixed and features are added. -
Alternatively, directly download the whole GitHub repo without installing GitHub:
wget https://github.com/shihuang047/2bRAD-M/archive/master.zip
unzip master.zip
cd 2bRAD-M-master
-
Conda installation
Miniconda provides the conda environment and package manager, and is the recommended way to install 2bRAD-M. -
Create a conda environment for 2bRAD-M pipeline:
After installing Miniconda and opening a new terminal, make sure you’re running the latest version of conda:conda update condaOnce you have Miniconda installed, create a conda environment with the yml file
tools/2bRAD-M-20201225-conda.yml.conda env create -n 2bRAD-M-20201225 --file tools/2bRAD-M-20201225-conda.yml -
Activate the 2bRAD-M conda environment by running the following command:
source activate 2bRAD-M-20201225
The script tools/Download_2bRADTagDB_NCBI.pl in this repo can be used to:
- download the prebuilt 2b-Tag-DB from Figshare based on the NCBI Refseq (Oct., 2019) or GTDB
- download the example datasets for pipeline tutorial
You can specify $your_database_path locally ($your_database_path=./2B-RAD-M-ref_db_NCBI/ or $your_database_path=./2B-RAD-M-ref_db_GTDB/) and run the script as following:
perl tools/Download_2bRADTagDB_NCBI.pl $your_database_path or
perl tools/Download_2bRADTagDB_GTDB.pl $your_database_path
It usually can take around 30 mins to save all files in the $your_database_path, but it still depends on your internet connenction speed and stability.
The 2bRAD-M analysis pipeline comprises a combination of 2bRAD-M scripts and optimized parameters for analyzing the 2bRAD or shotgun metagenomics sequencing data, which can output the most comprehensive output on each sample. The pipeline includes:
(1) The digital restriction digestion It is required when input DNA sequences are longer than 31bp or 33bp (e.g., 150bp) or derived from the common shotgun sequencing protocols. If input DNA sequences were produced by the 2bRAD sequencing protocol this step will be skipped.
(2) Qualitative analysis Identify the microbes and preliminarily estimate their abundances based on the 2bRAD (such as. BcgI derived) species-specific markers of a prebuilt 2b-Tag-DB based on the NCBI Refseq (Oct., 2019).
(3) Quantitative analysis Estimate the microbial abundances more precisely based on the 2bRAD species-specific markers in a sample-specific 2b-Tag-DB. Firstly, we fetch condidate genomes that were identified in a particular biolgical sample in step (2) from NCBI Refseq to construct a sample-targeted 2b-Tag-DB. Next, we remapped the sequencing reads to this more concise 2b-Tag-DB to estimate the abundance of all detected taxa and used G score to filter potential false positive discovery of microbial features.
(4) Merging results from multiple samples The sample-wise results will be automatically merged into a feature table.
The main script for implementing those analyses is bin/2bRADM_Pipline.pl in this repo. You can check out the usage by printing the help information via perl bin/2bRADM_Pipline.pl -h.
DESCRIPTION
We here provided a streamlined 2bRAD pipeline for analyzing microbial compositions from the 2bRAD/shotgun metagenomics data based on the species-specific 2bRAD markers.
USAGE
perl bin/2bRADM_Pipline.pl
PARAMETERS
-t <int> The acceptable types of an input sequencing data file. The file path should be also listed in the sample list file (para -l).
[1] generic genome data in a fasta format
[2] shotgun metagenomic data in a fastq format(either SE or PE platform is accepted)
[3] 2bRAD data from a SE sequencing platform in a fastq format
[4] 2bRAD data from a PE sequencing platform in a fastq format
-l <file> The filepath of the sample list. Each line includes an input sample ID and the file path of corresponding DNA sequence data where each field should be separated by <tab>. A line in this file that begins with # will be ignored. Only four formats of a sample list file are accepted and should match with parameter -t:
[1] sample<tab>sample.fa(.gz)
[2] sample<tab>shotgun.1.fq(.gz)(<tab>shotgun.2.fq.gz)
[3] sample<tab>2bsingle.fq(.gz or 2bsingle.1.fq.gz)
[4] sample1<tab>sample2<tab>sample3<tab>sample4<tab>sample5<tab>R1.fq(.gz)<tab>R2.fq(.gz)
-d <dir> The working path of 2B-Tag-DB.
-o <dir> The output directory (if it doesn't exist, will be created automatically as 'outdir').
OPTIONS of Qualitative Analysis
-p <str> If qualitative analysis applies or not [default: yes] (yes or no)
-s1 <str> The enzymatic site(s) for the qualitative analysis. One or more sites can be specified(comma separated) [default: 5]
It represents which enzymatic recognition site(s) will be used for digital restriction digestion, and contructing 2b-Tag-DB for the following qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis.
[1]CspCI [5]BcgI [9]BplI [13]CjePI [17]AllEnzyme
[2]AloI [6]CjeI [10]FalI [14]Hin4I
[3]BsaXI [7]PpiI [11]Bsp24I [15]AlfI
[4]BaeI [8]PsrI [12]HaeIV [16]BslFI
-t1 <str> The taxonomic rank for 2bRAD markers in the qualitative database, which should be one of the following: kingdom,phylum,class,order,family,genus,species,strain. [default: species]
OPTIONS of Quantitative Analysis
-q <str> If quantitative analysis applies or not [default: yes] (yes or no)
-gsc <int> G score threshold for identifying the condidate microbes present in a sample in qualitative analysis, which also determines the membership of sample-specific 2B-Tag-DB in the quantitative analysis step. [default: 5, it means >5]
-gcf <int> The threshold of the 2bRAD tag number for the presence of a microbial genome (i.e., GCF) in the qualitative analysis, which also determines the membership of sample-specific 2B-Tag-DB in the quantitative analysis step. [default: 1, it means >1]
-s2 <str> The enzyme site for the quantitative analysis. (refer to -s1) [default: 5, must be included in para -s1]
-t2 <str> The taxonomic rank for 2bRAD markers in the quantitative analysis, which should be one of the following: kingdom,phylum,class,order,family,genus,species,strain. [default: species]
OPTIONS of CPU
-c1 <int> The number of CPUs used for parallelizing the digital digestion step for multiple samples. [default: 10]
-c2 <int> The number of CPUs used for parallelizing abundance profiling for multiple samples based on a single enzyme and combining results from multiple enzymes have been set via -s1. [default: 8] (each CPU needs about 15~65G of memory)
OPTIONS of Quality Control
-qc <str> If quality control applies or not. [default: yes] (yes or no)
-qcn <float> The maximum ratio of base "N". [default: 0.08]
-qcq <int> The minimum quality score to keep. [default: 30]
-qcp <int> The minimum percentage of bases that must have [-qcq] quality. [default: 80]
-qcb <int> ASCII+33 or ASCII+64 quality scores as Phred scores [default: 33]
OPTIONS of Merging profiles
-ms <str> The mock-community sample name(s) (separated by commas). The specified samples will be removed from the merged output table.
-ncs <str> The sample name(s) (separated by commas) of negative control that can be used for filtering potential contaminations.
-h|help Print this help information.
- Analyze a in silico mock community (synthetic data:
simulate_50.BcgI.fq.gz) To test the generalizability of our 2bRAD markers for microbial profiling, we designed a mock microbiome structure containing 50 microbial species from a wide range of habitats such as oral, gut and soil environments. Given a specified abundance profile, we simulated the sequencing data based on all related genomes using wigsim. The sequence data filesimulate_50.BcgI.fq.gzand its corresponding list filelist_simulationwill be automatically downloaded to$your_database_pathviatools/Download_2bRADTagDB.plas described above. Once all these downloaded, you can try to run the following command that will output the estimated microbial profile.
perl bin/2bRADM_Pipline.pl \
-t 3 \
-l $your_database_path/list_simulation \
-d $your_database_path/ \
-o outdir \
-gsc 60 \
-qc no
- Analyze a mock microbial community: MSA1002 (sequencing data:
MSA1002_R1.fq.gz) MSA1002 comprises the genomic material from 20 microbial strains that are evenly mixed. We sequenced this DNA sample using our 2bRAD protocol for optimizing and testing the bioinformatic pipeline. The sequencing data fileMSA1002_R1.fq.gzand its corresponding list filelist_mockwill be automatically downloaded to$your_database_pathviatools/Download_2bRADTagDB.plas described above. Once all these downloaded, you can try to run the following command that will output the estimated microbial profile.
perl bin/2bRADM_Pipline.pl \
-t 3 \
-l $your_database_path/list_mock \
-d $your_database_path/ \
-o outdir
2bRAD-M offers a standard format of sample-wide results. You can find this standard profiling result of a single sample at $outdir/quantitative/$sample_id.combine.xls. Taking the MSA1002 analysis as example, the output is located at outdir/quantitative/MSA1002.combine.xls. 2bRAD-M standard sample report format is tab-delimited with one line per taxon. The fields of the output, from left-to-right, are as follows:
1 to 7- The taxonomic ranks for a microbial taxon identified: 1 - "Kingdom"; 2 - "Phylum"; 3 - "Class"; 4 - "Order"; 5 - "Family"; 6 - "Genus"; 7 - "Species"
8 - "Theoretical_Tag_Num": Average number of all 2bRAD marker tags of genomes under this taxon in theory
9 - "Sequenced_Tag_Num": Number of 2bRAD marker tags detected in the sequencing data under this taxon
10 - "Percent": The percent of sequenced 2bRAD marker tags under this taxon
11 - "Sequenced_Reads_Num": Total number of sequenced reads
12 - "Sequenced_Reads_Num/Theoretical_Tag_Num": The ratio of "Sequenced_Reads_Num" and "Theoretical_Tag_Num", which further used for calculating "relative abundance" of this taxon within a sample via a normalization by the column-wise sum
13 - "Sequenced_Reads_Num/Sequenced_Tag_Num": The ratio of "Sequenced_Reads_Num" and "Sequenced_Tag_Num"
14 - "Sequenced_Tag_Num(depth>1)": Number of sequenced tags that have >1 sequencing coverage
15 - "G_Score": the geometric mean of "Sequenced_Reads_Num" and "Sequenced_Tag_Num", which is used for controlling false positive discovery
2bRAD-M also offer a standard format of the study-wise result. If you provided multiple sample IDs and corresponding fasta/fastq file names in the list file, this pipeline can automatically merge the abundance profiling results from multiple samples into one feature table, which is located at $outdir/quantitative/Abundance_Stat.all.xls. If you setup the negative-control samples for filtering potential contaminations in biological samples, you can find the filtered abundance profiles in the $outdir/quantitative/Abundance_Stat.filtered.xls. Otherwise, these two files should be identical. The standard study report format is also tab-delimited with one line per taxon. The fields of the output, from left-to-right, are as follows:
1 to 7 - The taxonomic ranks for a microbial taxon identified: 1 - "Kingdom"; 2 - "Phylum"; 3 - "Class"; 4 - "Order"; 5 - "Family"; 6 - "Genus"; 7 - "Species"
8 to N - The column name indicates a sample ID in this study, where you can find the relative abundances of taxa within this sample. N = (the number of samples) + 7
- Extract 2b tags This script conducts digital type-2B-restriction disgestion of DNA data generated by a wide range of sequencing protocols by one of 16 restriction enzymes. For a given type 2b restriction enzyme, it can return a Fasta file including resulting 2b-RAD tags, and a statistical summary including raw number of input sequences, restriction enzyme used, number of restriction fragments produced, percentage of restriction fragments over the whole (meta)genome data.
- Build your own customized 2b-Tag-DB This script constructs the taxa-specific 2b-RAD reference genome database from a whole-genome reference database.
- Species profiling for a single sample based on 2bRAD markers of a single enzyme This script computes the relative abundance of taxa identified from each of 2b-RAD samples using a precalcuated taxa-specific 2b-RAD reference database by one or multiple type 2b restriction enzymes.
- Species profiling for a single sample based on 2bRAD markers of multiple enzymes This script computes the relative abundance of taxa identified from each of 2b-RAD samples using a precalcuated taxa-specific 2b-RAD reference database by a single type 2b restriction enzyme.
- Merge species profiles for multiple samples This script can merge the abundance profiles from mulitple samples and filter potential contaminations in each biological sample using negative control samples.
- Wang S, Meyer E, McKay JK, Matz MV. 2b-RAD: a simple and flexible method for genome-wide genotyping. Nat Methods. 2012 May 20;9(8):808-10. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2023. PMID: 22609625.
- Wang S, Liu P, Lv J, Li Y, Cheng T, Zhang L, Xia Y, Sun H, Hu X, Bao Z. Serial sequencing of isolength RAD tags for cost-efficient genome-wide profiling of genetic and epigenetic variations. Nat Protoc. 2016 Nov;11(11):2189-2200. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.133. Epub 2016 Oct 6. PMID: 27711051.
This work was funded by Grant 31800088 from National Natural Science Foundation and 2019M652501 from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, and Taishan Scholar Fund of Shandong Province of China.