This repo contains the source code of our paper:
MS-RRFSegNet: Multi-Scale Regional Relation Feature Segmentation Network for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scene Point Clouds
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (Early Access)
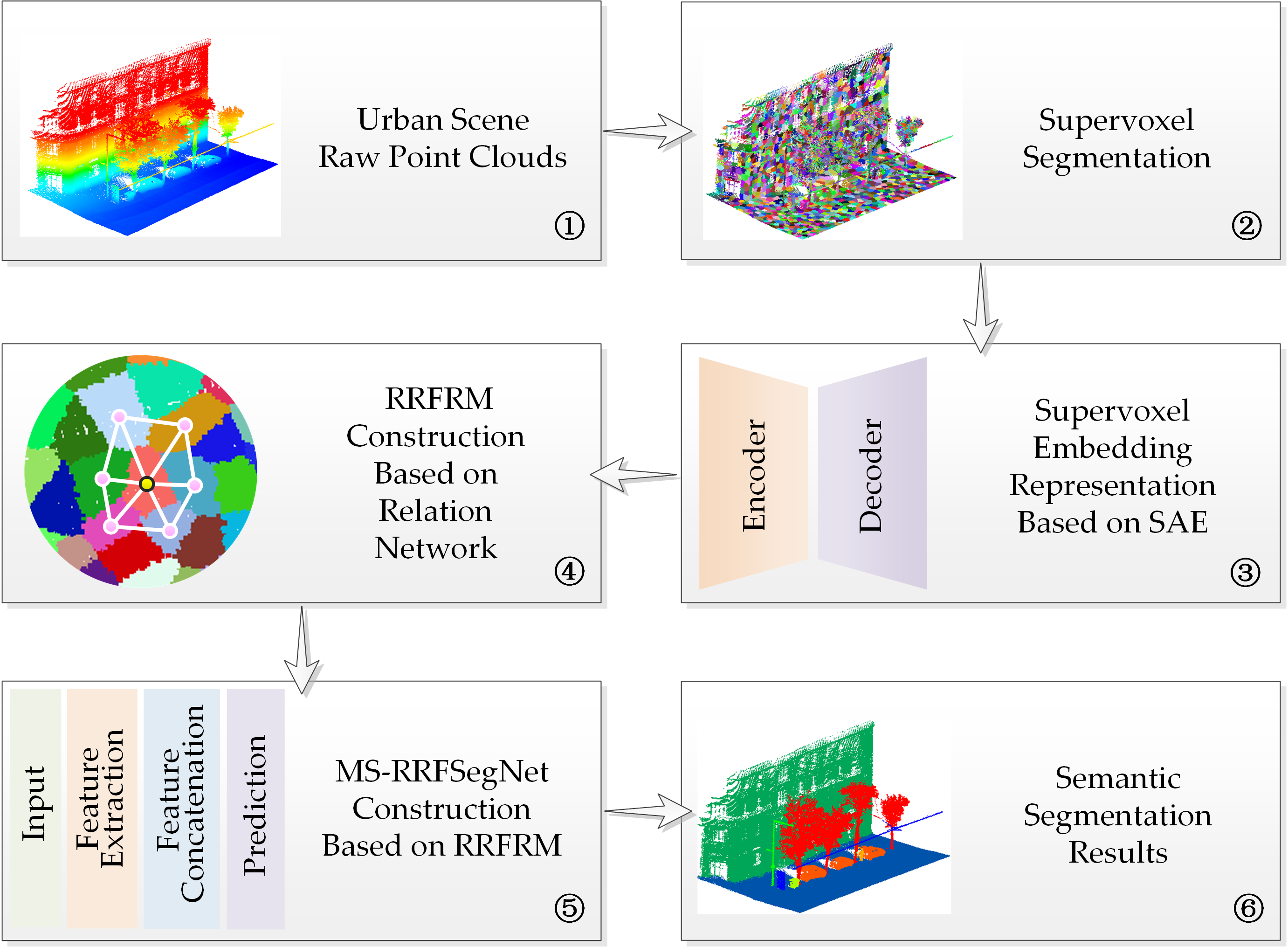
In this paper, we propose a novel method for urban scene point cloud semantic segmentation using deep learning. Firstly, we use homogeneous supervoxels to reorganize raw point clouds to effectively reduce the computational complexity and improve the non-uniform distribution. Then, we use supervoxels as basic processing units, which can further expand receptive fields to obtain more descriptive contexts. Next, a sparse auto-encoder (SAE) is presented for feature embedding representations of the supervoxels. Subsequently, we propose a regional relation feature reasoning module (RRFRM) inspired by relation reasoning network and design a multi-scale regional relation feature segmentation network (MS-RRFSegNet) based on the RRFRM to semantically label supervoxels. Finally, the supervoxel-level inferences are transformed into point-level fine-grained predictions.
Our proposed method has been evaluated on two open benchmarks -- Paris-Lille-3D and Semantic3D.
- Python 3.6
- Tensorflow 1.15
./auto_encoder/*- Supervoxl embedding representation code../ms_rrfsegnet/*- RRFRM and MS-RRFSegNet code.- Note that the details of supervoxl segmentation can be found in the Supervoxel-for-3D-point-clouds.
We also provide three training supervoxel samples and one testing supervoxel sample (
./data/*) for testing the code. Training data format: [x, y, z, r, g, b, supervoxel_id, training_label]. Testing data format: [x, y, z, r, g, b, supervoxel_id].
- Download dataset, and then generate samples according to the related description in our paper.
- Over segment samples into supervoxels like the examples in
./data/*. - Run
./auto_encoder/train_SAE.pyto train a SAE model for supervoxel embedding representation (SER). - Run
./auto_encoder/ser.pyto convert all samples into SER. - Run
./ms_rrfsegnet/ms_associated_region.pyto build supervoxel-based graph G and generate the supervoxel index of multi-scale associated regions. - Run
./ms_rrfsegnet/train_ms_rrfsegnet.pyto train MS-RRFSegNet for supervoxel-level semantically labeling. - Run
./ms_rrfsegnet/test_spl2pl.pyto test the trained MS-RRFSegNet and transform supervoxel-level predictions into dense point-level results.
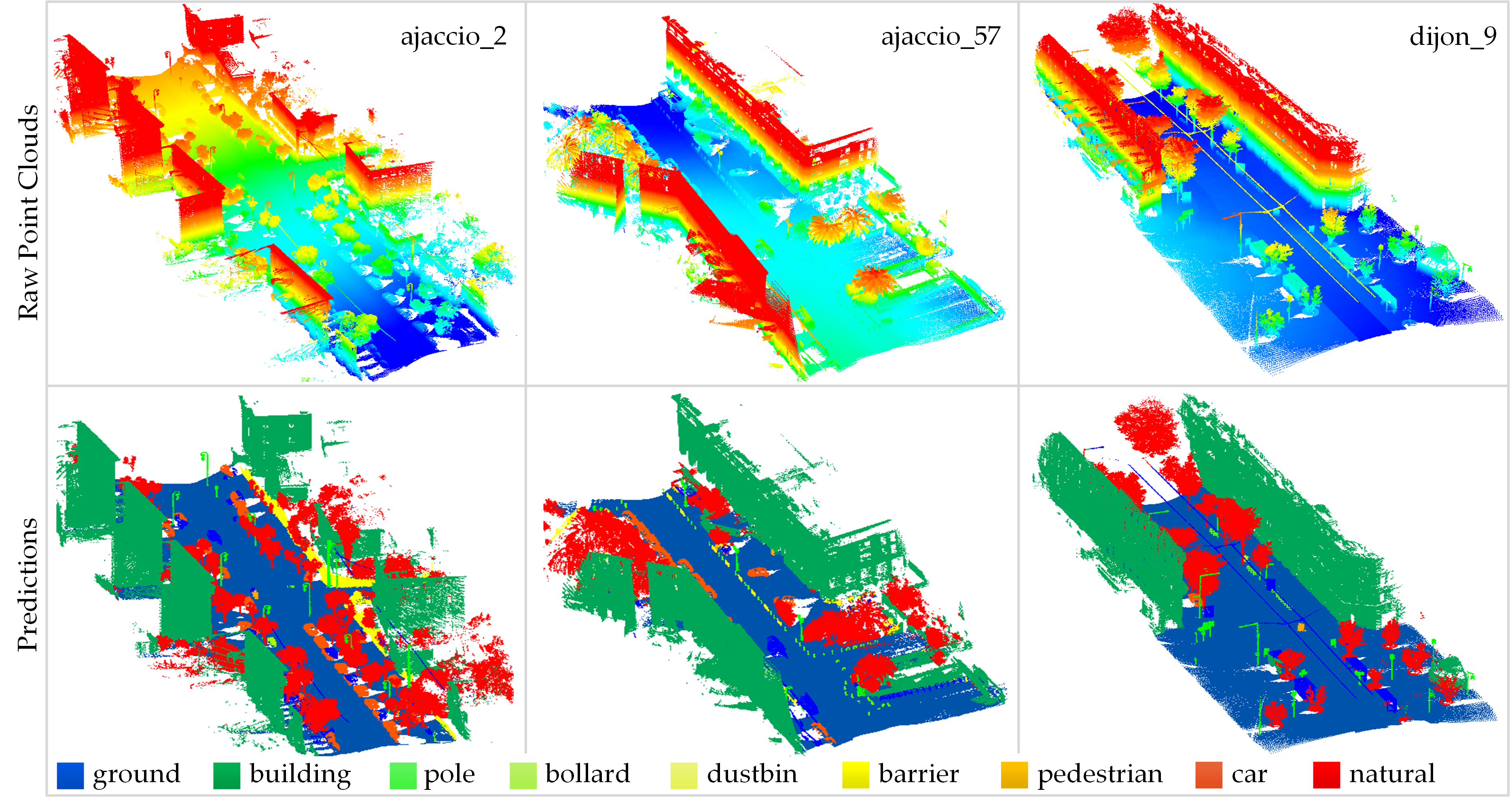
- Semantic segmentation results of Paris-Lille-3D official testing set.
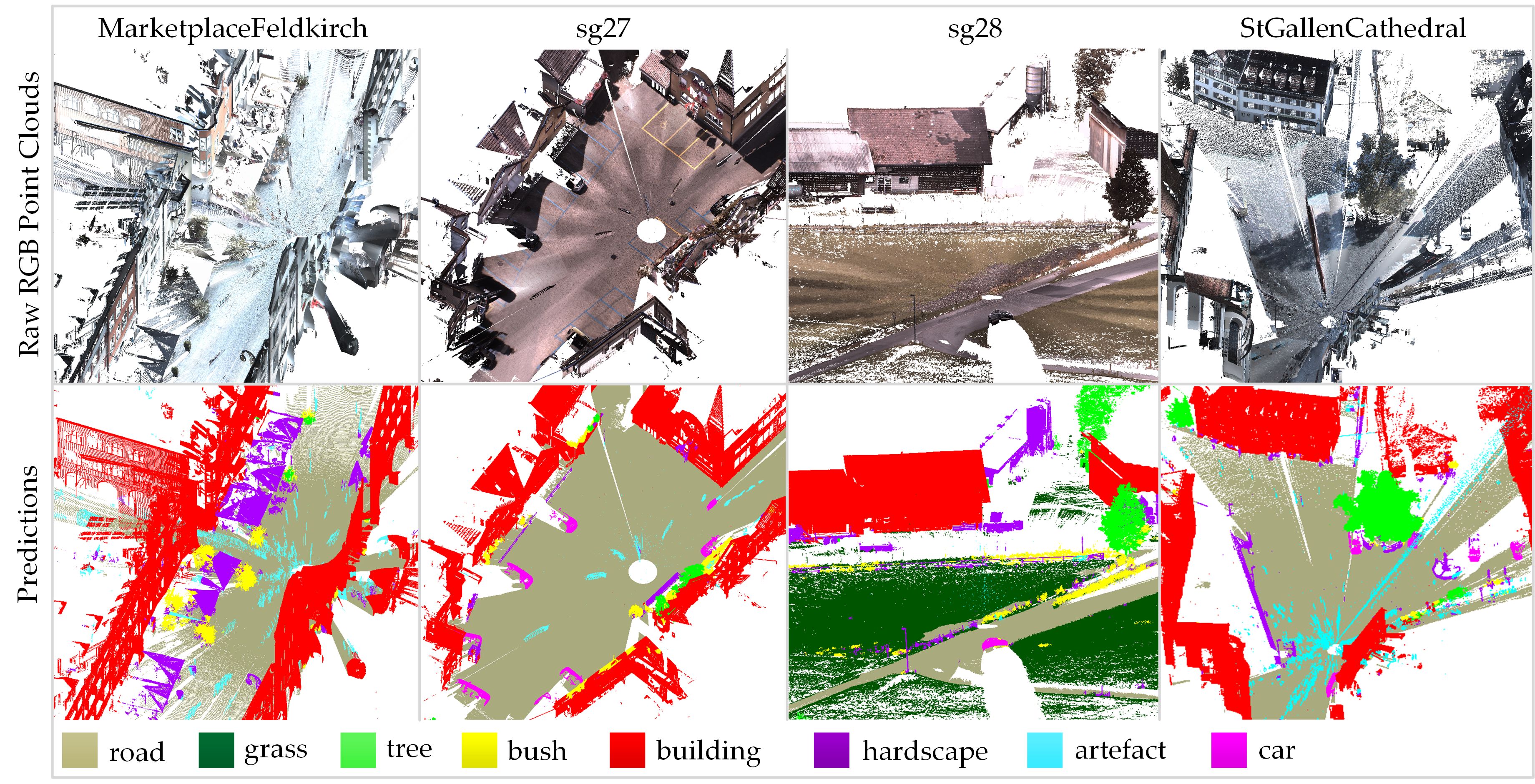
- Semantic segmentation results of Semantic3D official testing set (reduced-8 version).
If you find this project useful for your research, please kindly cite our paper:
Our paper is coming soon...
We would like to acknowledge the provision of reference code by Charles R. Qi and Yue Wang, respectively.
If you have any questions, please contact Haifeng Luo.