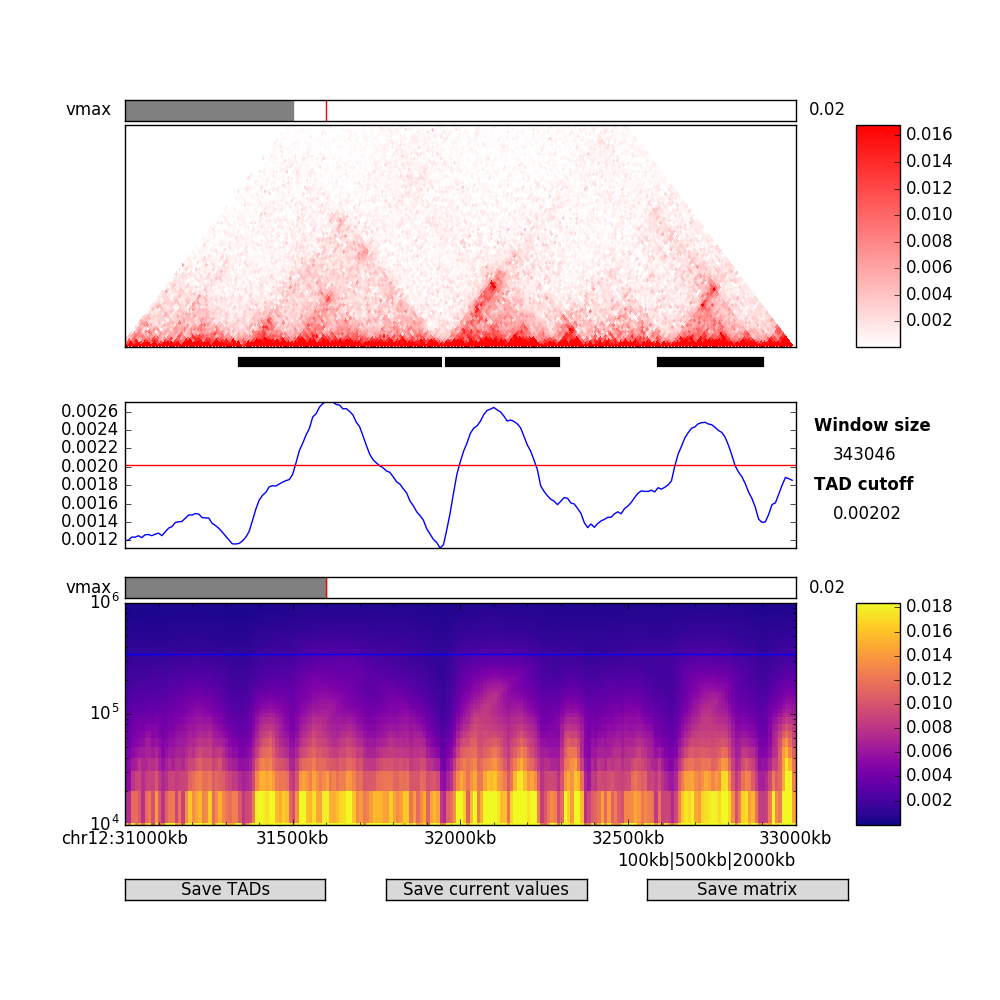
TADtool is an interactive tool for the identification of meaningful parameters in topologically-associating domains (TADs) algorithms for Hi-C data.
TADtool is supported on Linux and macOS. It might work on Windows, but is unsupported. Installation:
pip install tadtool
Run sample data from GitHub repo:
tadtool plot examples/chr12_20-35Mb.matrix.txt examples/chr12_20-35Mb_regions.bed chr12:31000000-33000000
This should open the interactive plotting window (see above). Start exploring by clicking in plots - the effects should be self-explanatory.
You can install TADtool from the command line using PyPI
pip install tadtoolor download the source from our GitHub repo and install manually
python setup.py installThis should install both the Python package and a command-line executable called tadtool.
Test the installation running
tadtool -hand you should see a brief help message.
TADtool has three basic commands: plot, which invokes the plotting window, tads, which can be used to
call TADs with predefined parameters, and subset, which can reduce a Hi-C matrix to a smaller region.
Here is the help output from tadtool plot -h:
usage: tadtool plot [-h] [-w WINDOW_SIZES [WINDOW_SIZES ...]] [-a ALGORITHM]
[-m MAX_DIST] [-d DATA]
matrix regions plotting_region
Main interactive TADtool plotting window
positional arguments:
matrix Square Hi-C Matrix as tab-delimited or .npy file
(created with numpy.save) or sparse matrix format
(each line:
<row region index> <column region index> <matrix value>)
regions BED file (no header) with regions corresponding to
the number of rows in the provided matrix.
plotting_region Region of the Hi-C matrix to display in plot. Format:
<chromosome>:<start>-<end>, e.g.
chr12:31000000-33000000
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-w WINDOW_SIZES [WINDOW_SIZES ...], --window-sizes WINDOW_SIZES [WINDOW_SIZES ...]
Window sizes in base pairs used for TAD calculation.
You can pass (1) a filename with whitespace-delimited
window sizes, (2) three integers denoting start, stop,
and step size to generate a range of window sizes, or
(3) more than three integers to define window sizes
directly. If left at default, window sizes will be
logarithmically spaced between 10**4 and 10**6, or
10**6.5 for the insulation and directionality index,
respectively.
-a ALGORITHM, --algorithm ALGORITHM
TAD-calling algorithm. Options: insulation,
ninsulation, directionality. Default: insulation.
-m MAX_DIST, --max-distance MAX_DIST
Maximum distance in base-pairs away from the diagonal
to be shown in Hi-C plot. Default: 3000000
-d DATA, --data DATA Matrix with index data. Rows correspond to window
sizes, columns to Hi-C matrix bins. If provided,
suppresses inbuilt index calculation.
plot takes three mandatory (positional) arguments:
- A Hi-C matrix file, which can be
- square matrix format: a tab-delimited text file that has the same number of columns as lines.
Will be read internally by
numpy.loadtxt - sparse matrix format: a tab delimited file where each line has three columns: <row index> <column index> <value>
- a numpy
.npyfile: created from a numpy matrix in Python with thenumpy.savemethod
- square matrix format: a tab-delimited text file that has the same number of columns as lines.
Will be read internally by
NOTE: It is possible to load large matrices at high resolution, but bear in mind that a large matrix will consume more memory and may slow down TAD calculations. We recommend using intra-chromosomal matrices of a single chromosome for the best experience. Alternatively, it is possible to use several smaller sub-matrices to identify suitable TAD-calling parameters in the interactive tool, and to call TADs on the whole matrix (or individual chromosome matrices) using the non-interactive
tadscommand (see below).
-
A BED file with region information for the Hi-C matrix, i.e. a tab-delimited file where each row contains chromosome name, start, and end coordinates (exclusive) of the region. This file must not contain any headers. If a fourth column is present, it is assumed to be a unique identifier (index/name) for that region, which is then used to refer to that region in sparse matrix format (see above).
-
A region selector string to inform TADtool about the region it is supposed to plot. The string must be of the format
<chromosome>:<start>-<end>, where<end>is inclusive. Examples:chr5:34000000-37000000,chrIX:300000-1000000
When called with only these three arguments
tadtool plot /path/to/matrix.txt /path/to/regions.bed chr1:1000000-3000000
TADtool will calculate the insulation index for a range of automatically selected window sizes.
Optional arguments give you more control about the data that is generated:
-
-wlets you define a custom range of window sizes, either as a file (txtornpy), a range, or specific values. -
-alets you select the directionality index instead of the insulation index or, by usingninsulation, the insulation index can be normalised to a chromosomal or region average. -
-mlets you specify a distance away from the Hi-C matrix diagonal that should be omitted from the plot. -
-dlets you bypass the TAD-calling calculation completely by providing a file with precomputed index data.
After starting TADtool with the plot option as instructed above, the interactive plotting window will open.
The window consists of four parts: the Hi-C plot with bars indicating the currently called TADs, a line plot with the insulation or directionality index at the current window size, a heatmap with the insulation or directionality index for all specified window sizes, and a row of buttons to save the currently displayed data.
You can use the toolbar at the very bottom of the window to zoom and pan each plot (they will be synchronized) or to save the figure window in its current state.
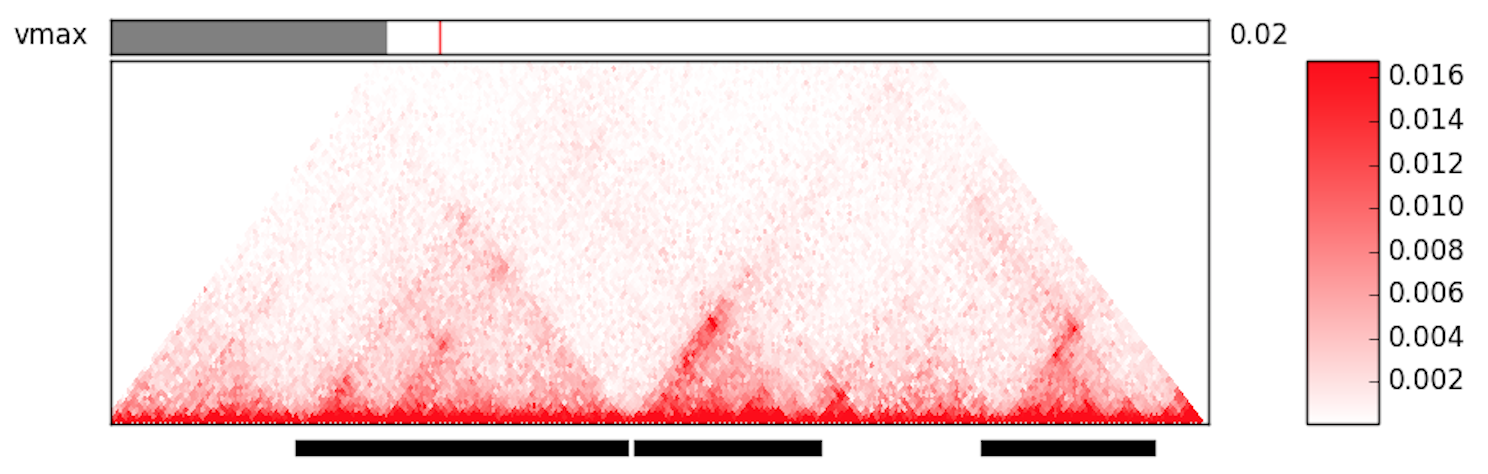
This triangular plot shows a Hi-C map in the selected region from the command line. Use the slider on the top to adjust the color intensity as appropriate. On the bottom you will find bars that indicate the currently called TADs as calculated with the selected parameters.
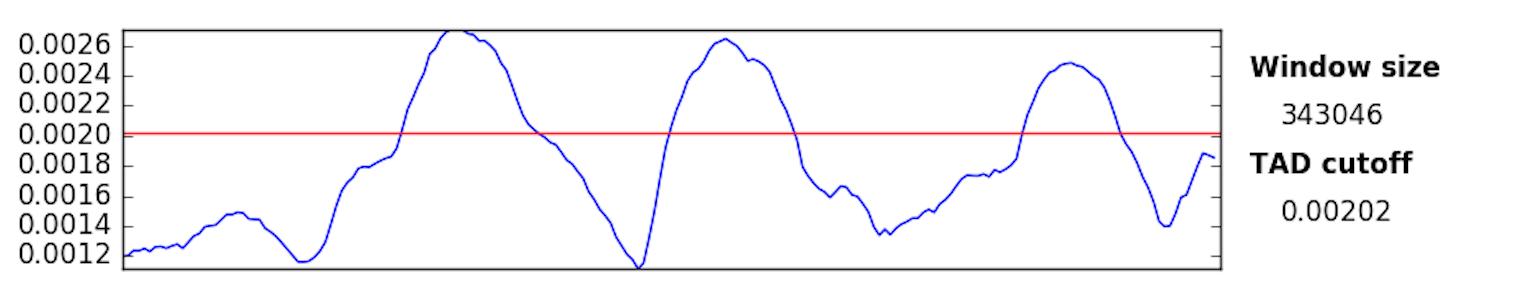
This plot shows the insulation or directionality index for each region in the Hi-C matrix at the currently selected window size. The red line(s) indicate the cutoff that is used to call TADs in this plot. Clicking within the plotting area moves the cutoff and simultaneously recalculates the TADs with the new cutoff. By default, for non-symmetric indexes (insulation index), the cutoff is set directly between the maximum and minimum of the y axis. For symmetric indexes (ninsulation, directionality), the cutoff is set to +/- half the maximum of the y axis.
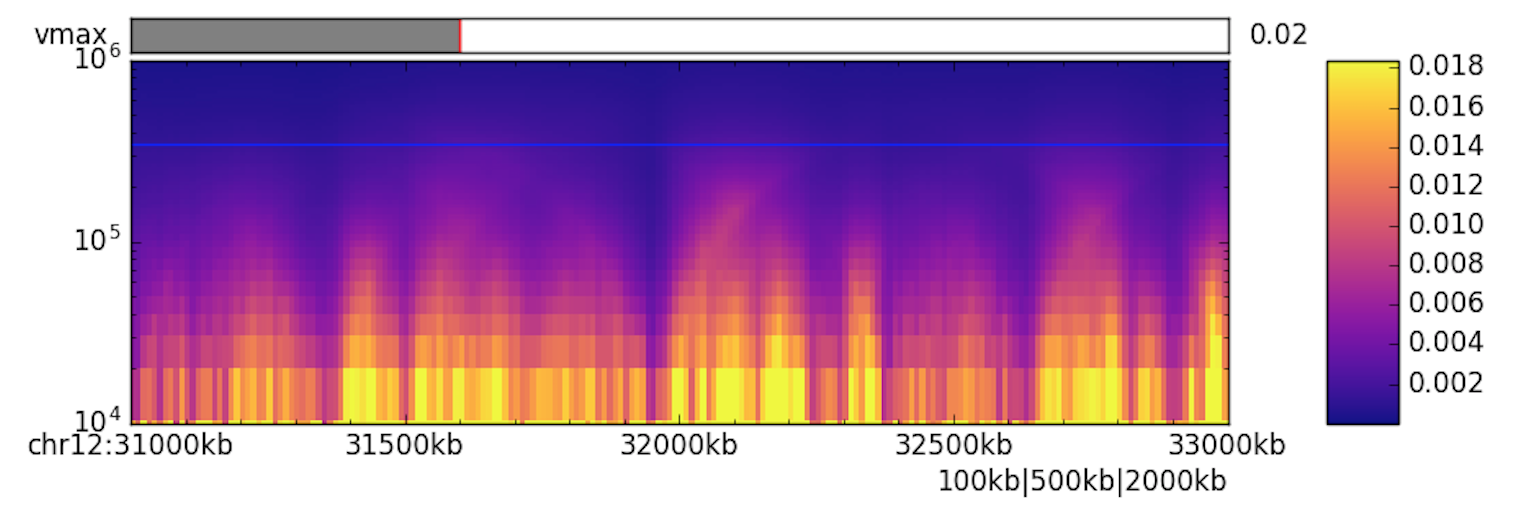
The heatmap shows all insulation/directionality indexes for each specified window size simultaneously in a condensed form. Every row corresponds to one window size. A red bar indicates the currently chosen window size. Clicking within the plotting area changes the current window size and updates the index plot and TAD indicators. By default, the window size is set to the middle of all calculated window sizes.
At the bottom of the plotting window you will find three buttons that allow you to export TADs, index data, and the index matrix, respectively. Exported values are calculated for the whole supplied matrix, not just the visible region.
This command allows the calculation of TADs directly using one of the provided algorithms. This may be useful for
quick TAD calculations when parameters are already known, or to fine-tune parameters estimated from the main
TADtool plot. Here is the help output from tadtool tads -h:
usage: tadtool tads [-h] [-a ALGORITHM]
matrix regions window_size cutoff [output]
Call TADs with pre-defined parameters
positional arguments:
matrix Square Hi-C Matrix as tab-delimited or .npy file
(created with numpy.save) or sparse matrix format
(each line:
<row region index> <column region index> <matrix value>)
regions BED file (no header) with regions corresponding to
the number of rows in the provided matrix.
window_size Window size in base pairs
cutoff Cutoff for TAD-calling algorithm at given window size.
output Optional output file to save TADs.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-a ALGORITHM, --algorithm ALGORITHM
TAD-calling algorithm. Options: insulation,
ninsulation, directionality. Default: insulation.
-n NORMALISATION_WINDOW, --normalisation-window NORMALISATION_WINDOW
Normalisation window in number of regions. Only
affects ninsulation algorithm. If not specified,
window will be the whole chromosome.
As plot, tads needs a Hi-C matrix and a regions BED file as input. In addition, it requires a window size
in base pairs and a cutoff (floating point). Optionally, the user can specify an output file to save TAD regions,
otherwise TADs will be written to the command line. For further parameters, see plot.
This is a convenience command that can extract submatrices from Hi-C matrices. Uses this if your matrix is so big
that it slows down the plotting window or TAD calling. Here is the help output: tadtool subset -h:
usage: tadtool subset [-h]
matrix regions sub_region output_matrix output_regions
Reduce a matrix to a smaller region.
positional arguments:
matrix Square Hi-C Matrix as tab-delimited or .npy file (created
with numpy.save) or sparse matrix format (each line: <row
region index> <column region index> <matrix value>)
regions BED file (no header) with regions corresponding to the
number of rows in the provided matrix.
sub_region Region of the Hi-C matrix to display in plot. Format:
<chromosome>:<start>-<end>, e.g. chr12:31000000-33000000
output_matrix Output matrix file.
output_regions Output regions file.