This is a customized version of Lazy-Theta-with-optimization-any-angle-pathfinding. Given a map and a set of starts and goals, this algorithm can return an optimal path. This repo has very easy-to-build-and-use C++ implementation and Python wrapper.
This repo has been tested with:
- GCC 10.2.0, CMake 3.16.3, Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS
- GCC 9.3.0, CMake 3.16.3, Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS
- Clang 12.0.0, CMake 3.18.3, macOS 10.15.7
- Clang 12.0.0, CMake 3.19.3, macOS 11.1
For Python:
- pybind11 If you only install
pybind11bypip, it's possible that CMake can't find it. But you can install it byaptorbrew. - numpy.
- matplotlib.
$ sudo apt install python3-pybind11 # For macOS: brew install pybind11
$ pip3 install numpy matplotlib
$ git clone https://github.com/zehuilu/Lazy-Theta-with-optimization-any-angle-pathfinding.git
$ cd <MAIN_DIRECTORY>
$ mkdir build
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
For C++, the main file is src/main_single_path.cpp.
$ cd <MAIN_DIRECTORY>
$ build/main_single_path
For Python, the main file is test/test_LazyThetaStarPython.py.
$ cd <MAIN_DIRECTORY>
$ python3 test/test_LazyThetaStarPython.py
Or test/test_solver_and_plot.py.
$ cd <MAIN_DIRECTORY>
$ python3 test/test_solver_and_plot.py
Python
To call the Lazy Theta Star solver in Python, a simple example is shown below. More details are in test/test_solver_and_plot.py and test/test_LazyThetaStarPython.py.
import LazyThetaStarPython
map_width = 20
map_height = 20
# world_map is a 1D list (row-major), 0 means no obstacles, 255 means blocked by obstacles
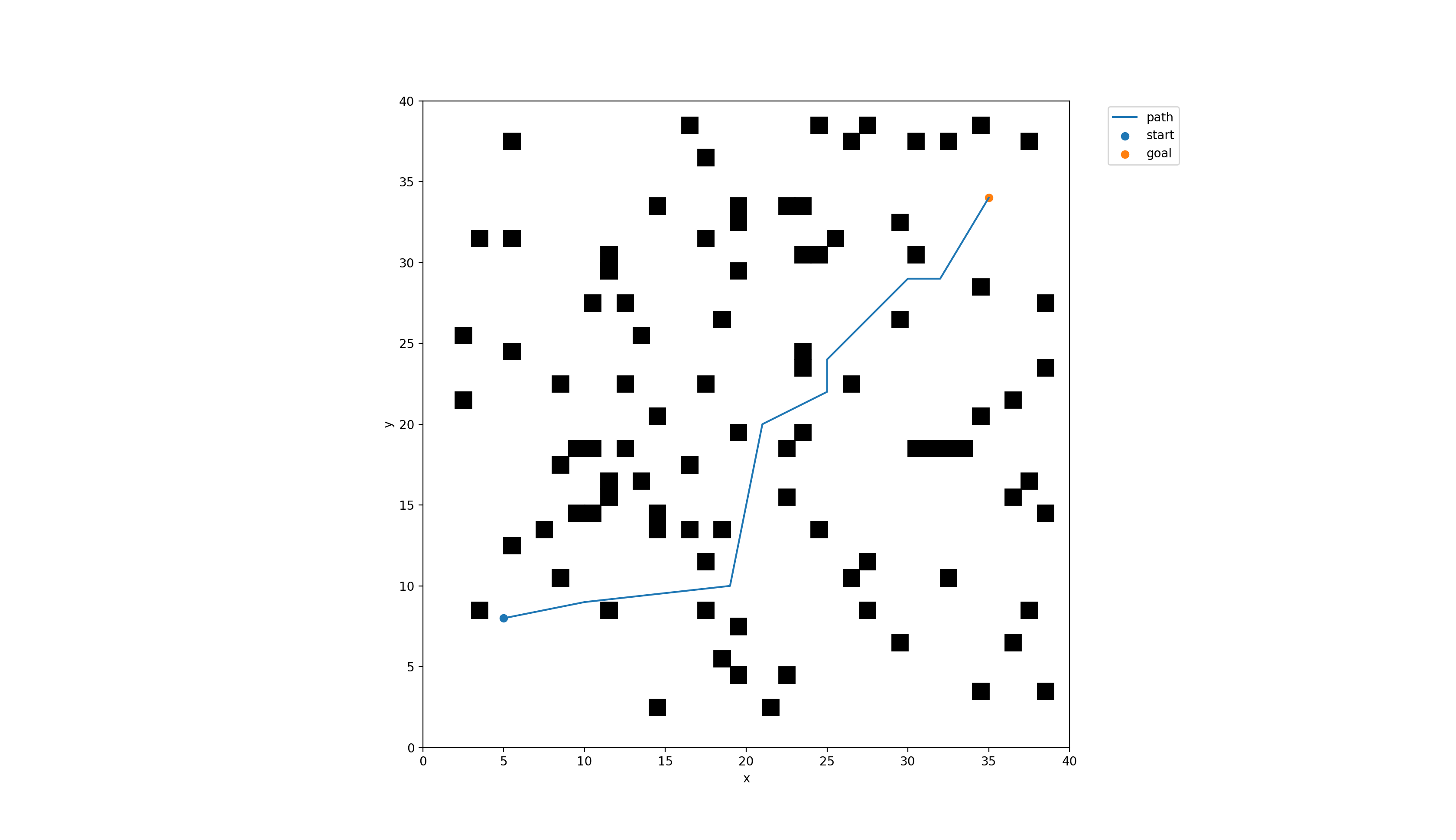
start = [5, 8] # coordinates for start
goal = [35, 34] # coordinates for goal
# solve it
path_single, distance_single = LazyThetaStarPython.FindPath(start, goal, world_map, map_width, map_height)Run test/test_solver_and_plot.py, the result is shown below. Time used is 0.55 ms.
C++
To call the Lazy Theta Star solver in C++, a simple example is shown below. More details are in src/main_single_path.cpp.
// ignore all the headers, see more details in src/main_single_path.cpp
int mapSizeX = 70; // width
int mapSizeY = 20; // length
int start[2] = {1, 1};
int end[2] = {68, 18};
// Map_1D is a std::vector<int>, 0 means no obstacles, 255 means blocked by obstacles
// solve it
// this is a tuple: std::tuple<std::vector<int>, float>
auto [path, distance] = find_path(start, end, Map_1D, mapSizeX, mapSizeY);Run src/main_single_path.cpp, the result is shown on the console. Time used is 0.697 ms.
######################################################################
#S # # #
# # # #
# # # #
# # # 3 4#
# # # ################## #
# # # # #
# # # #5 #
# # # # ####
# # # # #
# # # # #
# # # # #
# # # # #
# # # # #
# 1 # # #
# # #6 #
# 2 # #
# # #
# # E#
######################################################################
# = walls
S = start
E = end
number = path nodes