WORK IN PROGRESS
R scripts for annotation and exploration of protein phylogenetic trees and annotation of organism trees with phyletic patterns based on .
- Annotation of nodes by tip-associated information by traversing along to the last ancestor
- Manual annotation
- Annotation of organism tree with occurence phyletic pattern from gene tree with grouping and taxonomic information
- One code line plotting with annotations from columns
- branch color
- tip text
- bar plots
- internal and external labels
- highlights
- bootstrap information
- Flexible adjustment of taxonomic annotation
- Linking taxa by sharing same property in a column
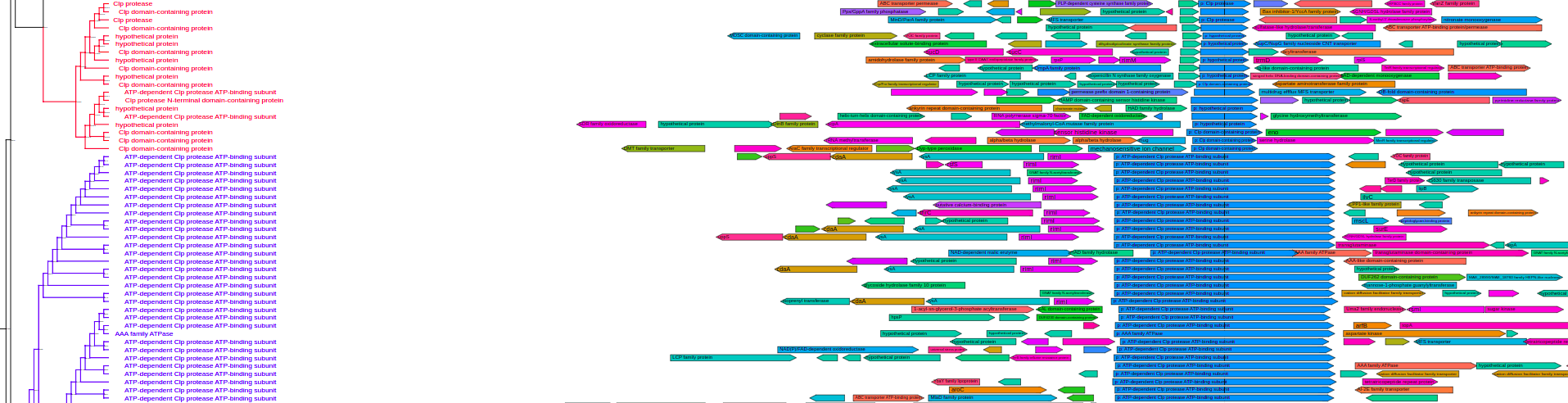
- Visualization of domain architecture and genome context data
- Visualization of trees with phyletic patterns at specified taxonomic prescision
- Make sure to install
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
library(readr)
library(data.table)
library(ggplot2)
library(treeio)
library(ggtree)
library(gggenes)
library(ape)
library(ggtreeExtra)
library(ggnewscale)To install ggtree run in the R console
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("ggtree")To install ggtreeExtra run
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("ggtreeExtra")For the rest try
install.packages(package)Currently, this tool is designed for working with data produced by tool. Perhaps in the future it will become more flexible.
- Load functions from tree_annotation.R and plot_tree.R
source('[path to tree_annotation.R]')
source('[path to plot_tree.R]')- Set working directory to directory with your data:
setwd('[path to your data]')- Load data
# protein tree
tree <- read.iqtree(file="tree.contree")
# annotation dataframe
annotation <- read.csv("filtered_clustered.csv")
# load the annotation data of filtered but not clustered hits (for the bacterial tree with phyletic pattern)
filtered_data <- read.csv("filtered_hits.csv")[, c('ID', 'assembly', 'taxid')]
# load the cluster data. which protein inherits properties from which representative
cluster_data <- read.csv("cluster_dict.csv")
# load the domain data.list of domains: which molecule they belong, domain name, start & end coordinates
domain_data <- read.csv("domains.csv")
# load genome context data
context_data <- read_context_data("genome_context.csv") # working directory should contain "genome_context.csv" file
# LOAD SPECIES TREES AND ANNOTATIONS
org_tree_full <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_full.nwk")
org_tree_genus <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_genus.nwk")
org_tree_family <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_family.nwk")
org_tree_order <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_order.nwk")
org_tree_class <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_class.nwk")
org_tree_phylum <- read.tree(file="org_trees/org_tree_phylum.nwk")
org_tree_data <- read_delim("org_trees/org_tree_full_data.csv", delim=';')- Tweak your data if you need For example, replace "Candidatus" to "C." in org_tree_data
library('stringr')
org_tree_data$name <- str_replace(org_tree_data$name, "Candidatus", "C.")- Annotate the tree with data
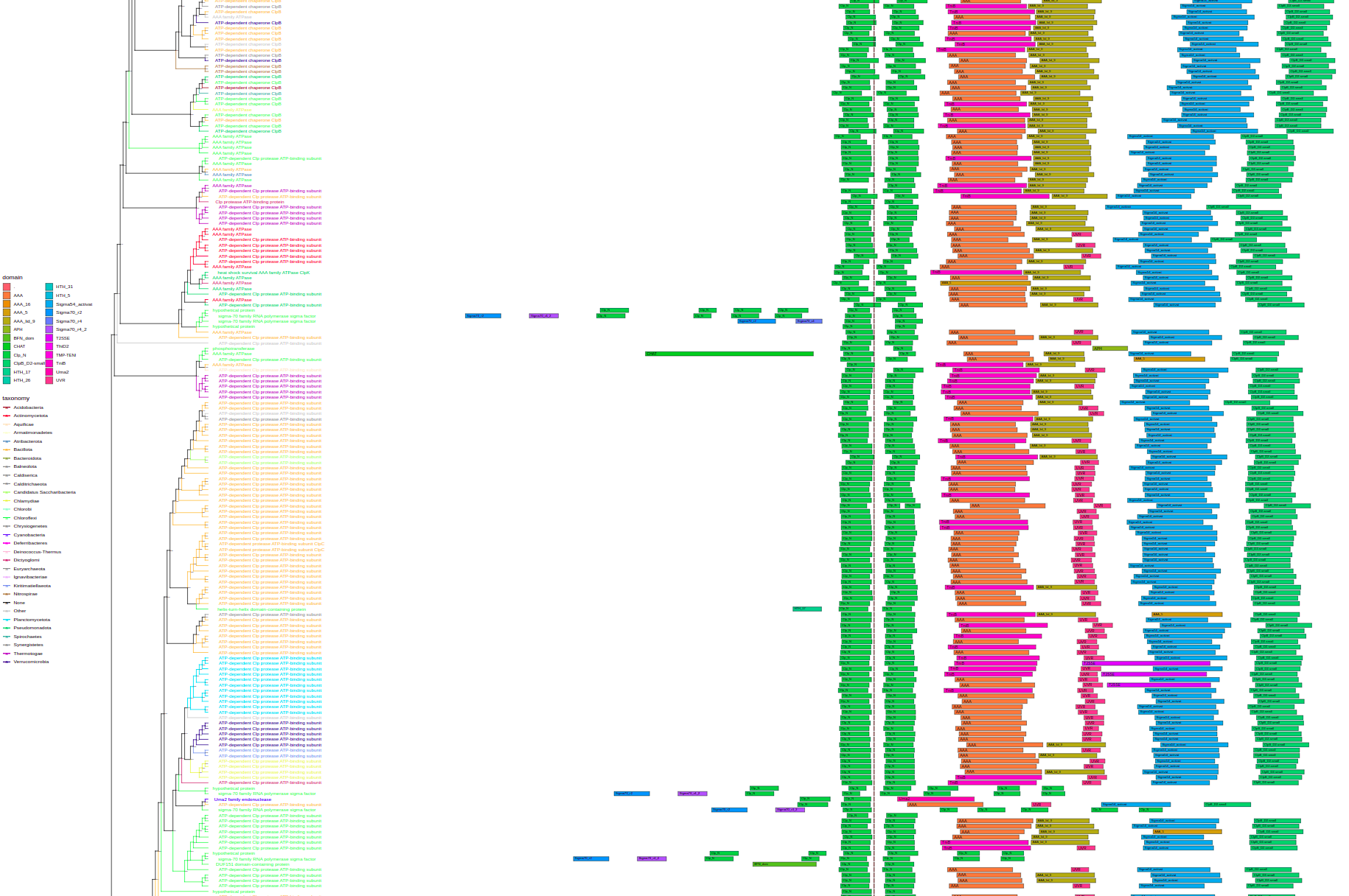
tree <- annotate_tree(tree, annotation)For the most basic tree run
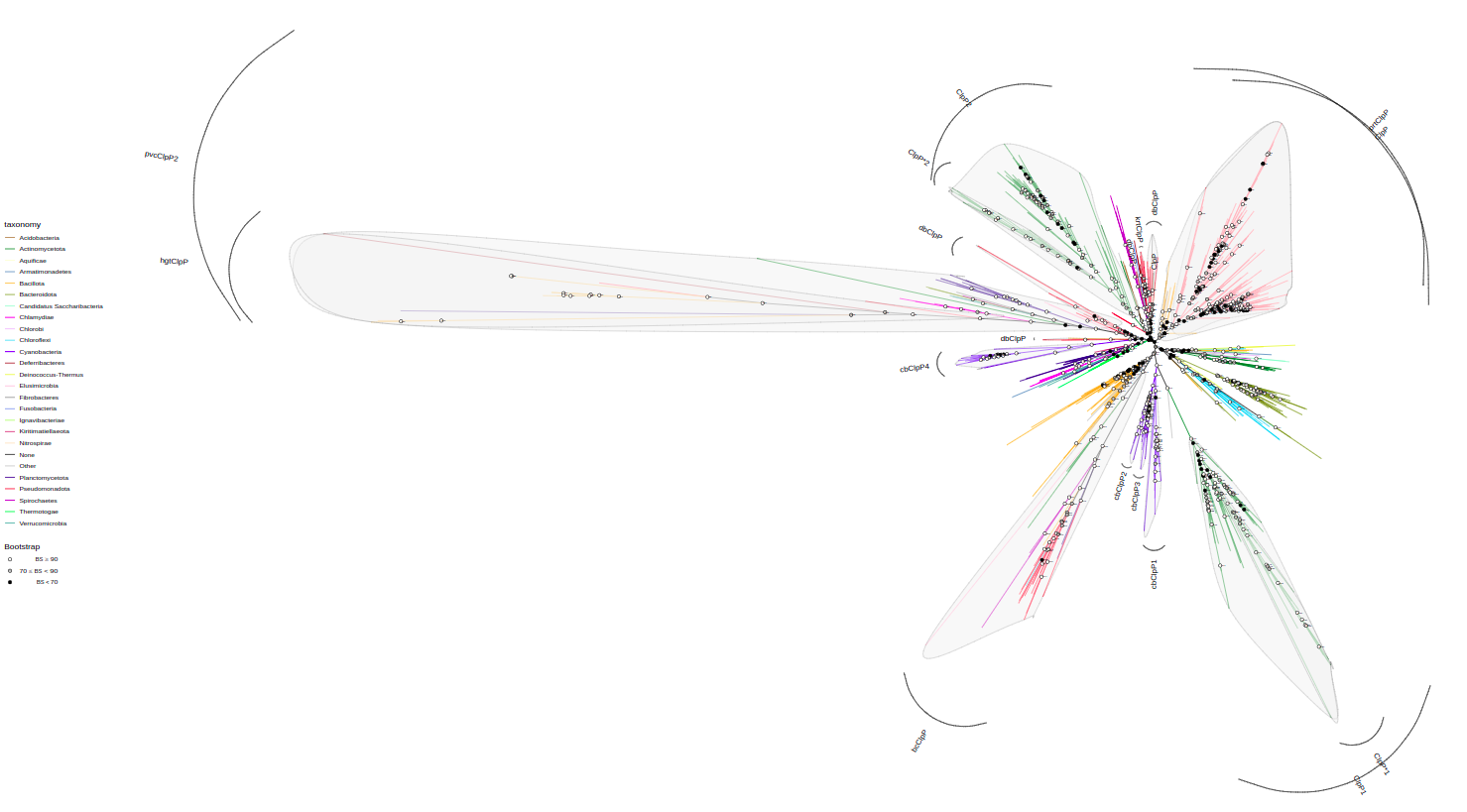
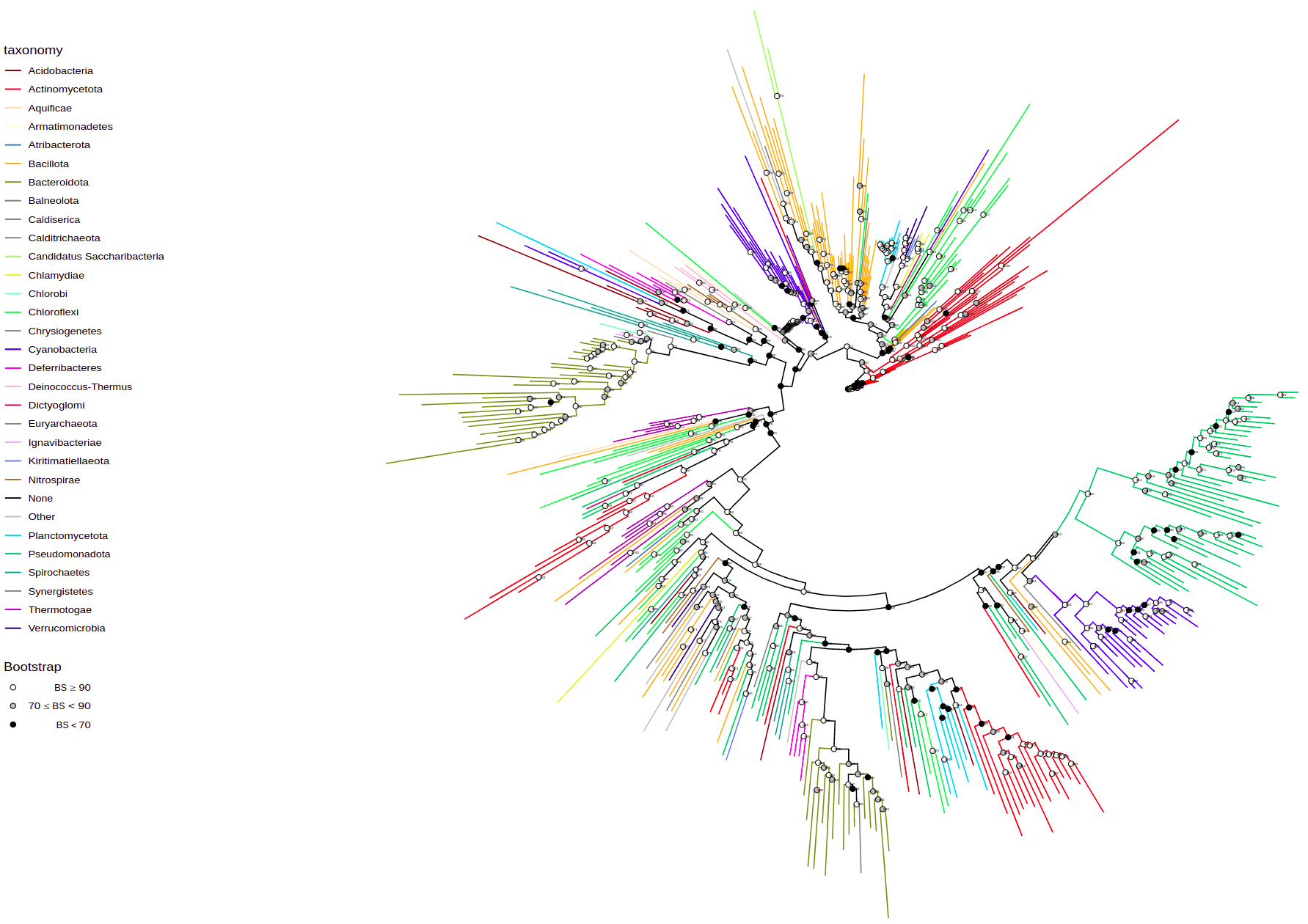
plot_tree(tree, filename="tree-base.svg", width=50, height=50)By default it has circular layout, colored by taxonomy (phyla), and shows bootstrap values. These parameters are tweakable and additional annotations can be added.
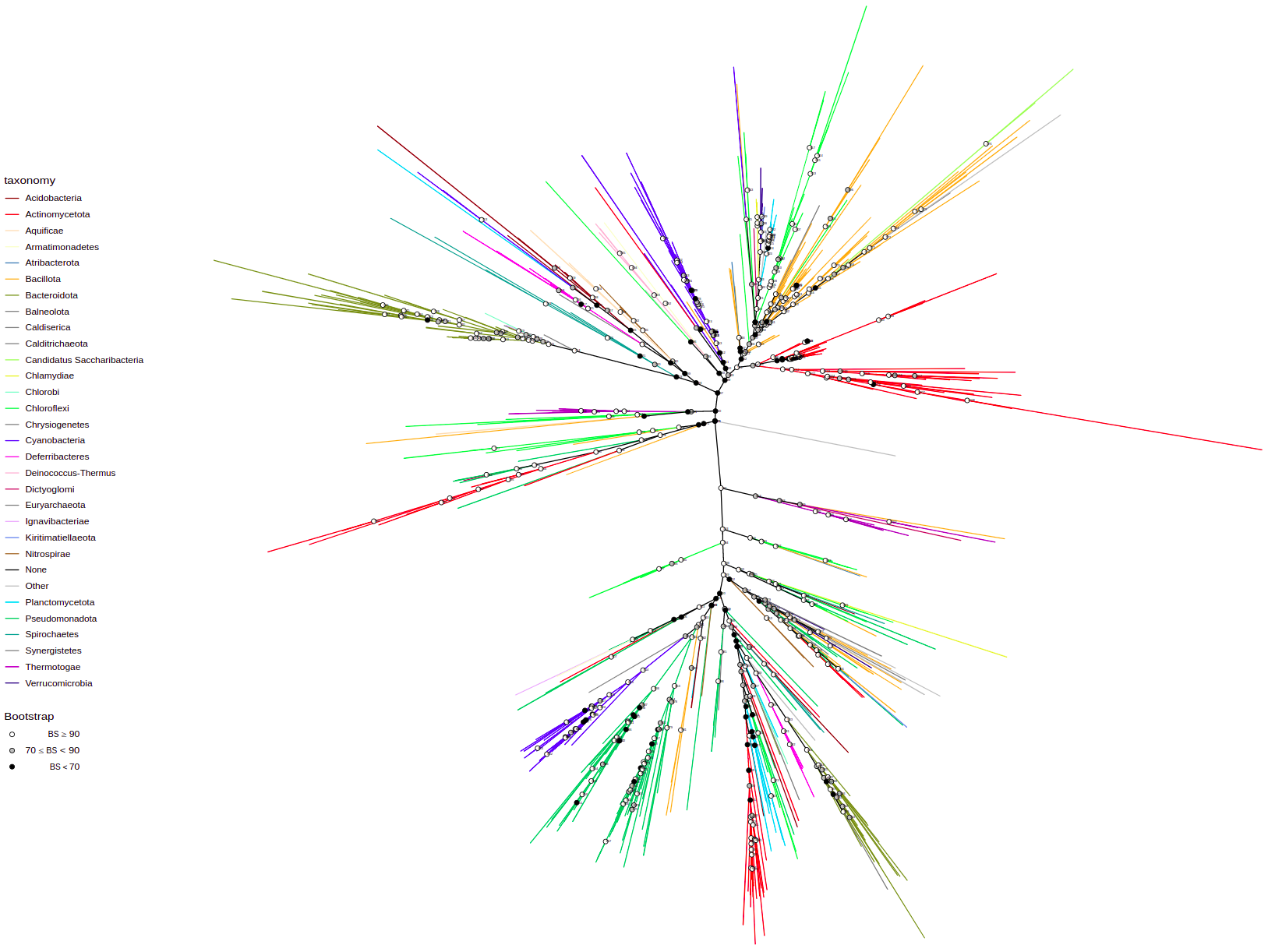
You can change tree layout using layout parameter. Available options: "circular", "rectangular", "equal_angle", "inward_circular".
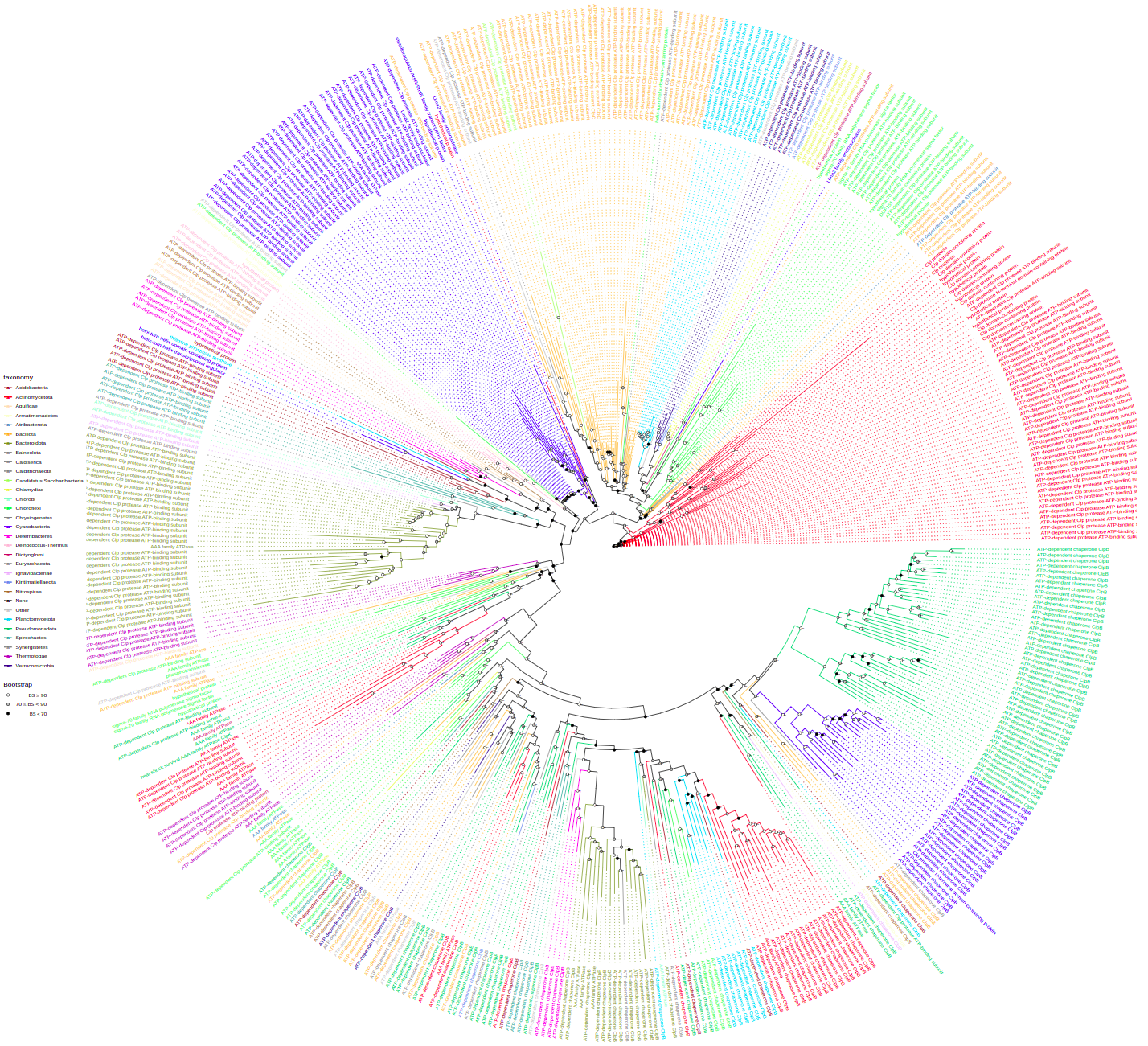
plot_tree(tree, layout="equal_angle", filename="equal_angle.svg", width=50, height=50)You can label tree tips by tips parameter by different data associated with the tree, e.g. "gene", "product", "species", and so on.
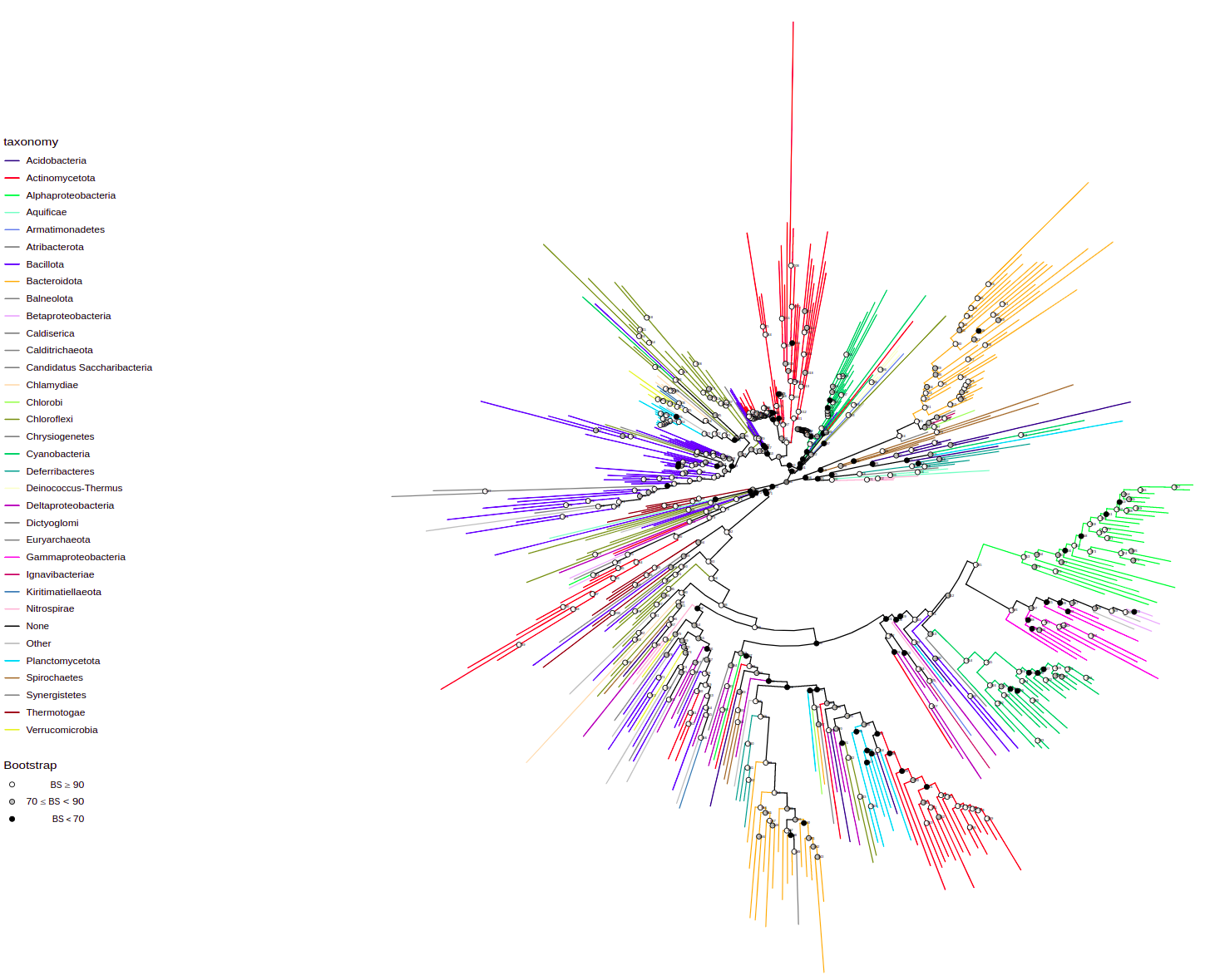
plot_tree(tree, tips="product", filename="tree-base-product.svg", width=75, height=75)To annotate some taxa on a lower taxonomic level use tax_expand parameter that contains taxon or vector of taxa that should be annotated at higher pescision. Here, we annotate Pseudomonadota (these are Proteobacteria) at the level of class
plot_tree(tree, tax_expand="Pseudomonadota",
filename="tree-expanded.svg", width=50, height=50)Also you can specify the taxon, you want to start the annotation from by tax_start parameter
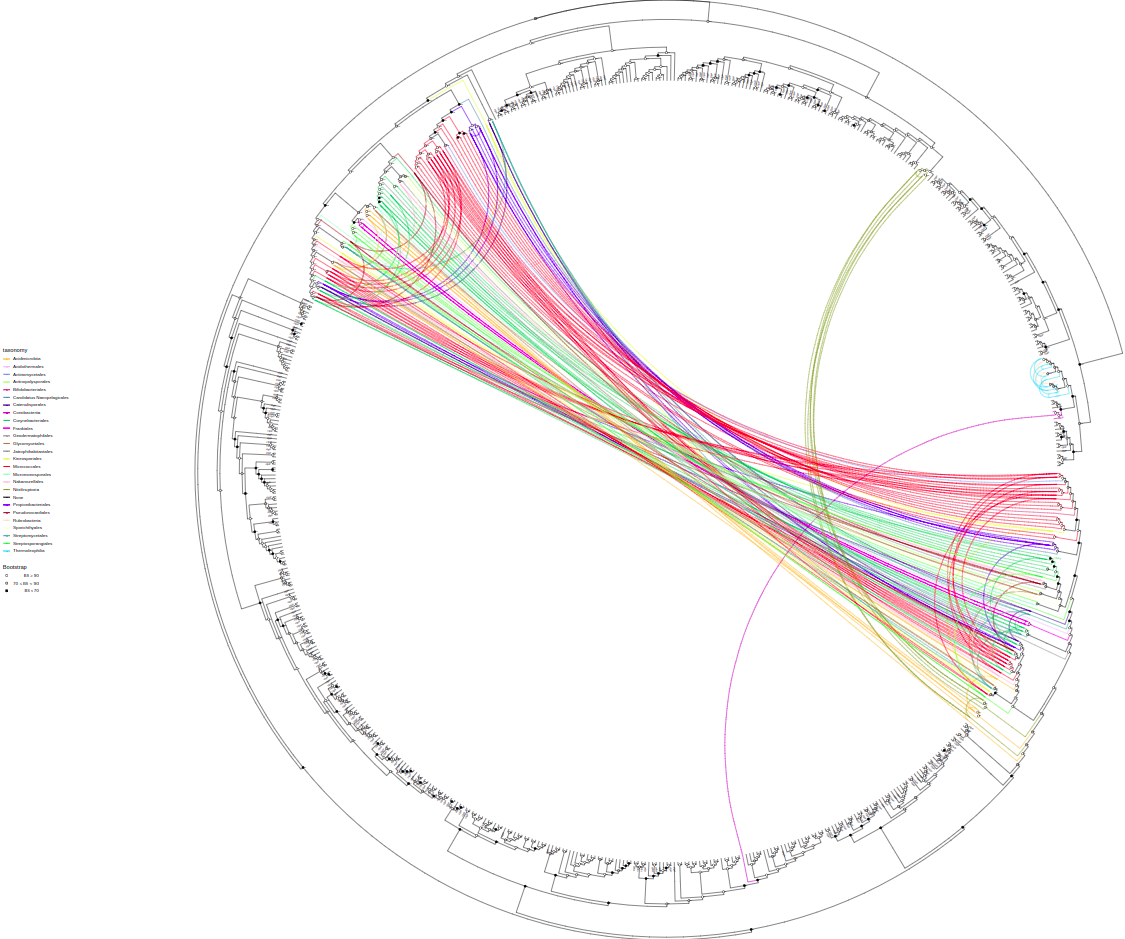
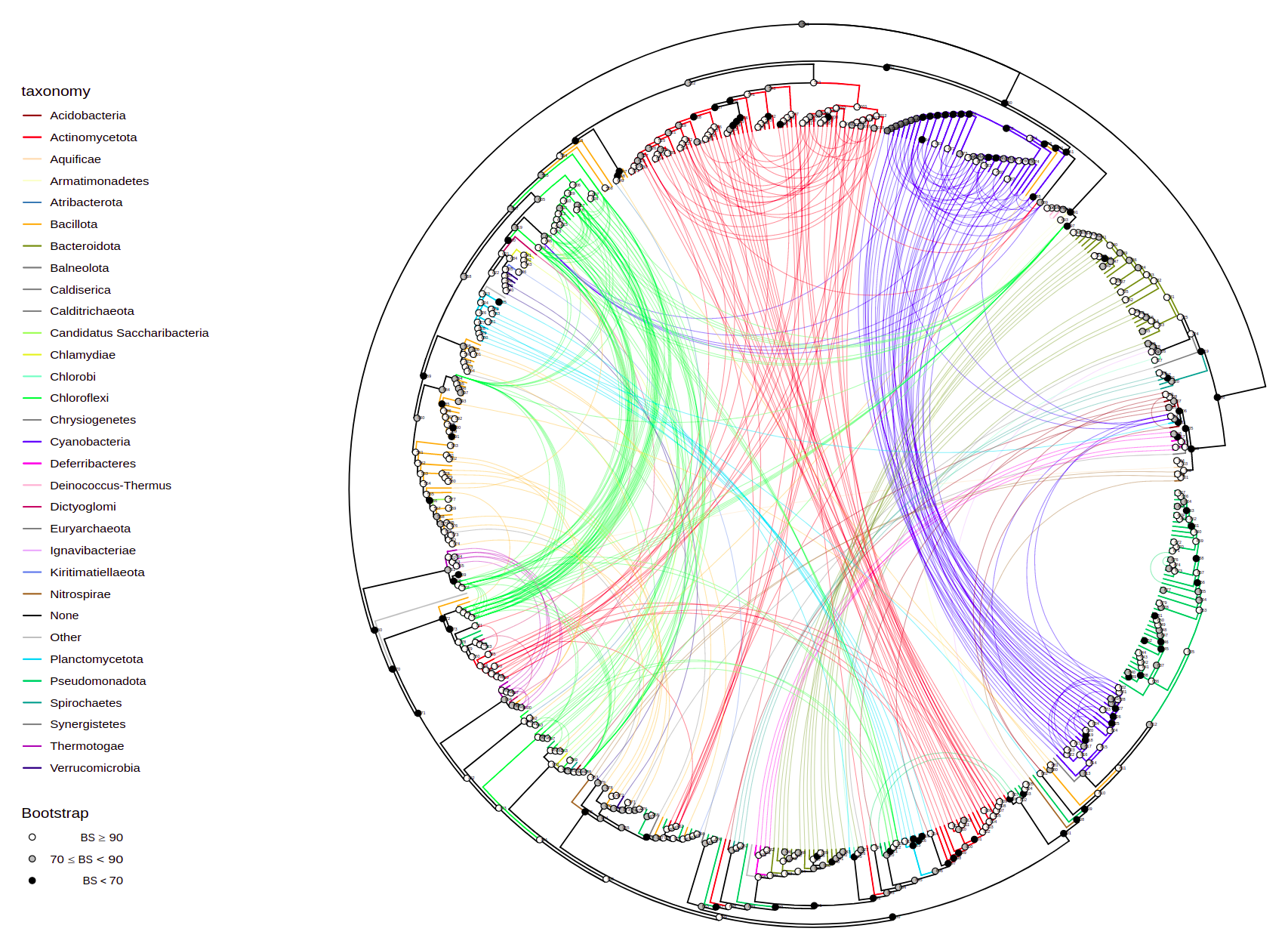
plot_tree(tree, layout="inward_circular", taxalink=T, branch_length='none', tips="gene",
tax_start="Actinomycetota", tax_expand=c("Actinomycetota", "Actinomycetes"),
width=100, height=100, filename="tree-taxalink-Act.svg")You can plot quantitative information from columns by bars parameter
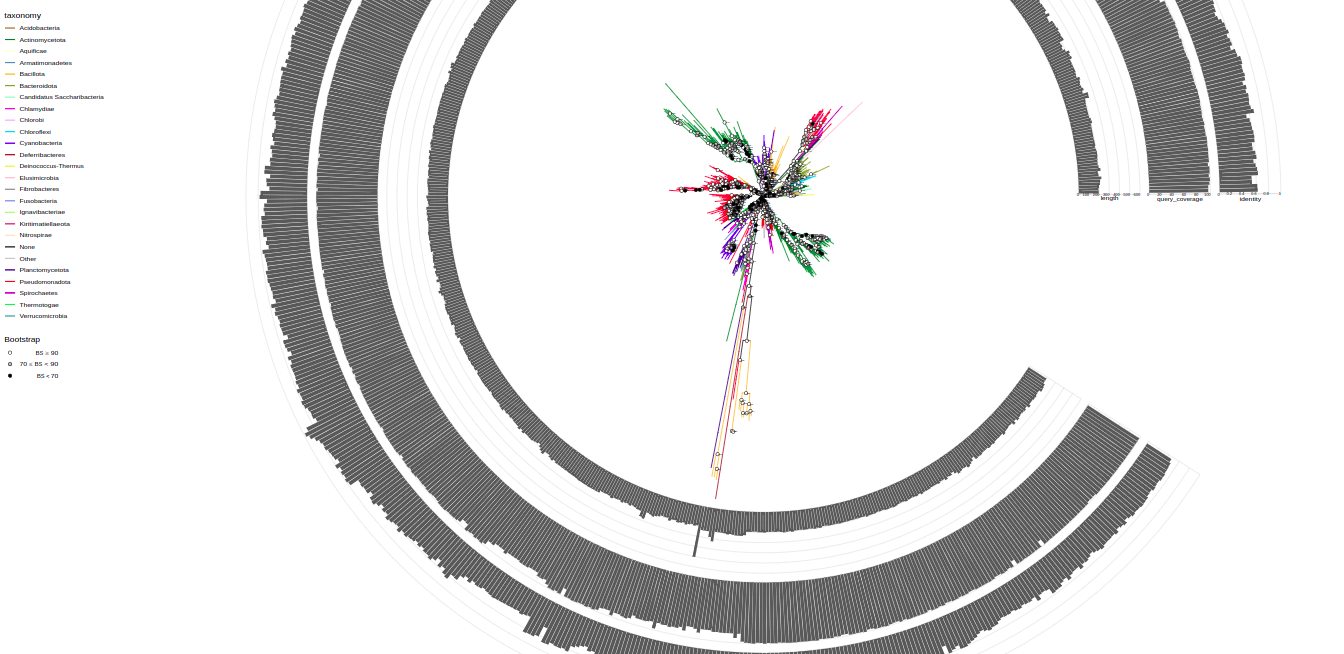
plot_tree(tree, filename="tree-bars.svg", bars=c("length", "query_coverage", "identity"), width=75, height=75)Use highlight parameter to highlight branches by values in a column
Use label_out parameter to make outer labels branches by values in a column
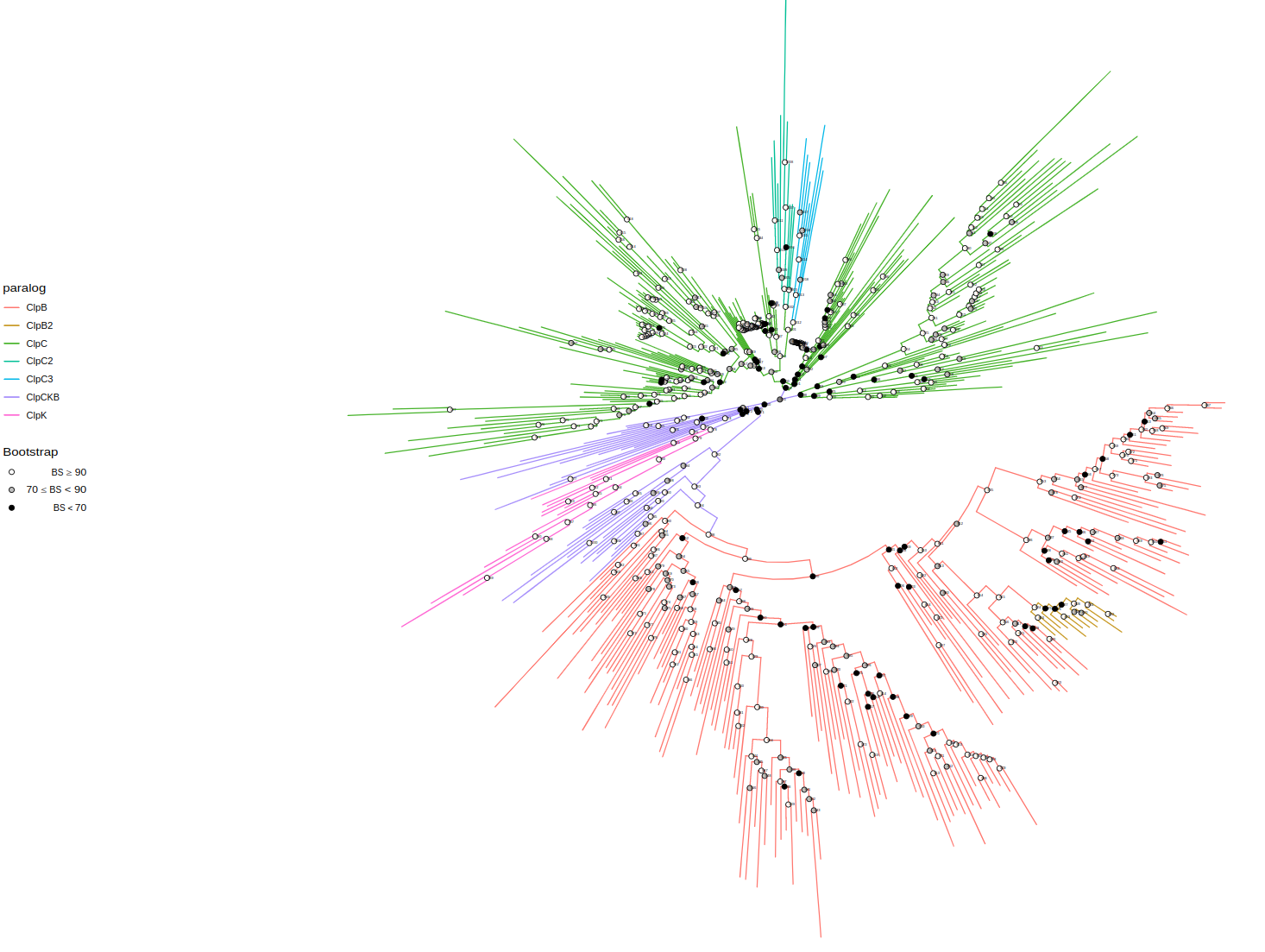
plot_tree(tree, highlight="paralog_anc", label_out="paralog_anc", bootstrap=F,
width=150, height=150, filename="tree-paralogs-HL.svg")Use label to label nodes by value in a column
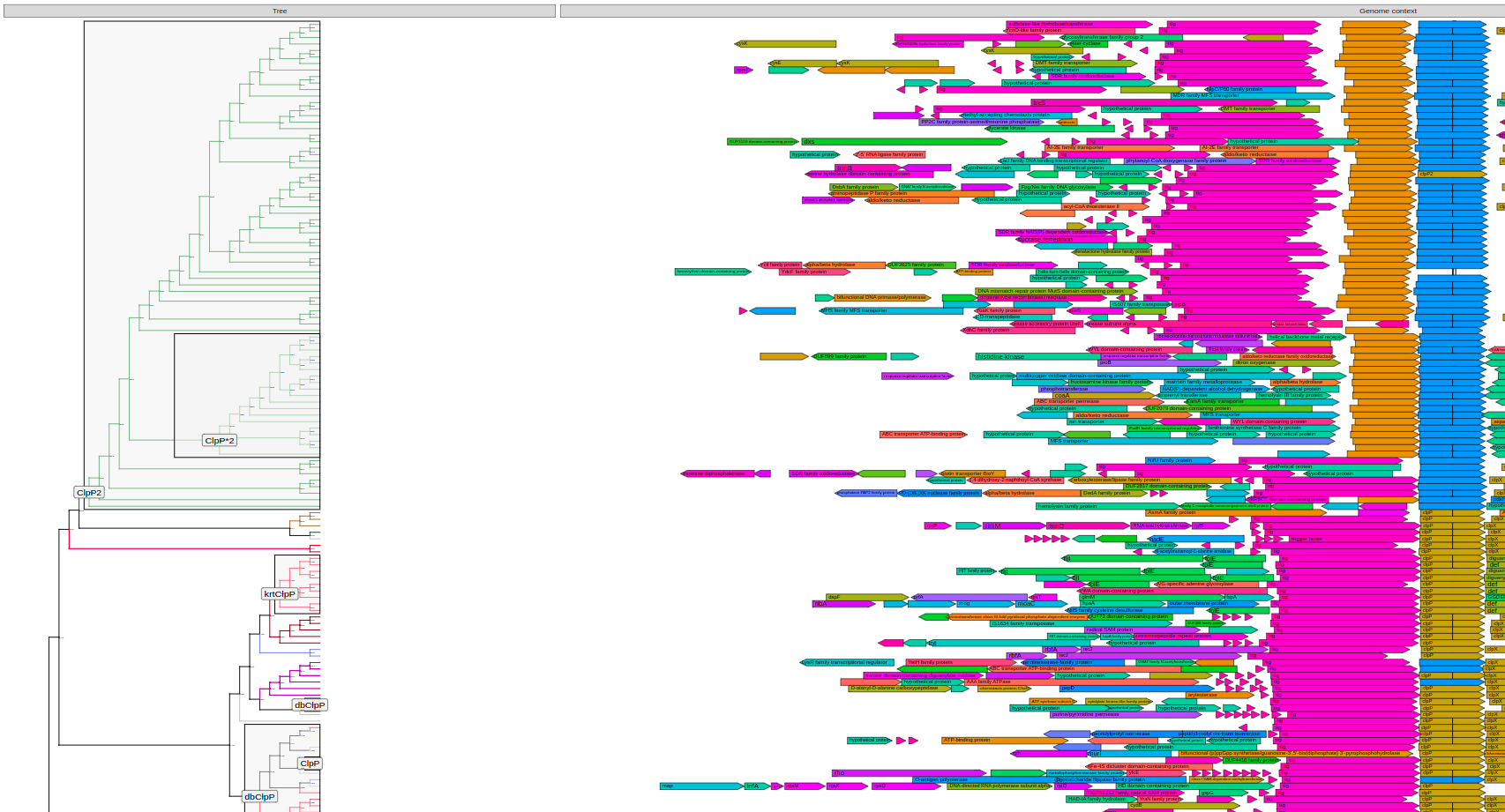
plot_tree(tree, label="paralog_anc", highlight="paralog_anc",context=context_data,
layout="rectangular", branch_length="none", bootstrap=F, legend='none', # <-- params to make it not brake
filename="tree-context-para.svg", height=200)Depending on your observations you might want to reroot the tree using root() function provided by ggtree
tree = root(tree, node=697)Link tips that have the same "assembly" value (what genome they are encoded in). To be custom in the future
plot_tree(tree, layout="inward_circular", taxalink=T, branch_length='none',
width=50, height=33, filename="tree-taxalink.svg")plot_tree(tree, domains=domain_data, tips="product",
layout="rectangular", branch_length="none", bootstrap=F, # <-- params to make it not brake
filename="tree-domains.svg", height=200)plot_tree(tree, context=context_data, tips="product",
layout="rectangular", branch_length="none", bootstrap=F, legend='none', # <-- params to make it not brake
filename="tree-context.svg", height=200)paralog_df = data.frame(
node = c(798, 690, 698, 760, 798, 778, 1002, 1012, 824),
paralog = c("ClpB", "ClpC", "ClpC", "ClpCKB", "ClpB", "ClpK", "ClpC2", "ClpC3", "ClpB2")
)
tree <- assign_paralogs(tree, "ClpCKB", paralog_df)
plot_tree(tree, color="paralog",
width=50, height=50, filename="tree-paralogs.svg")
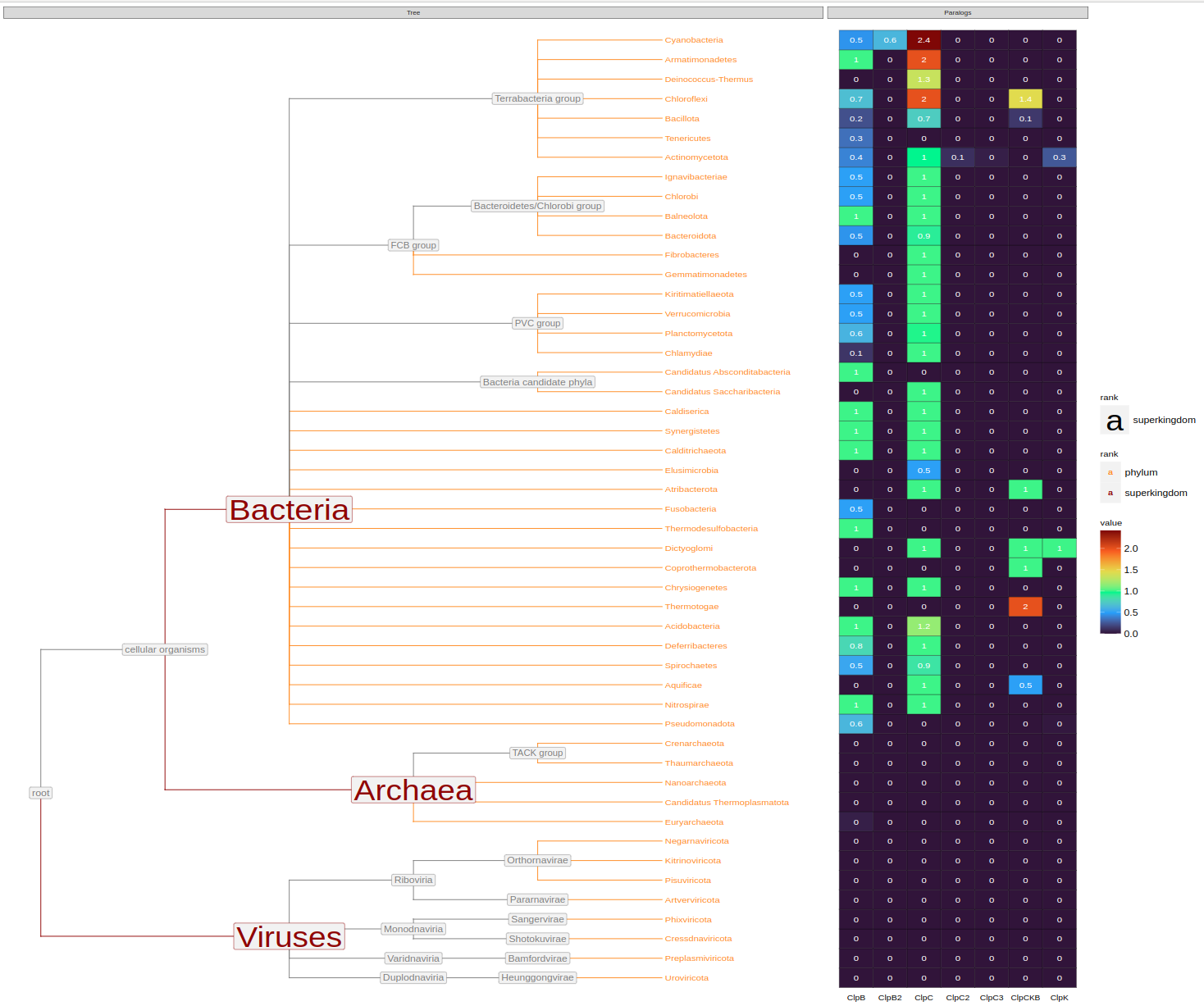
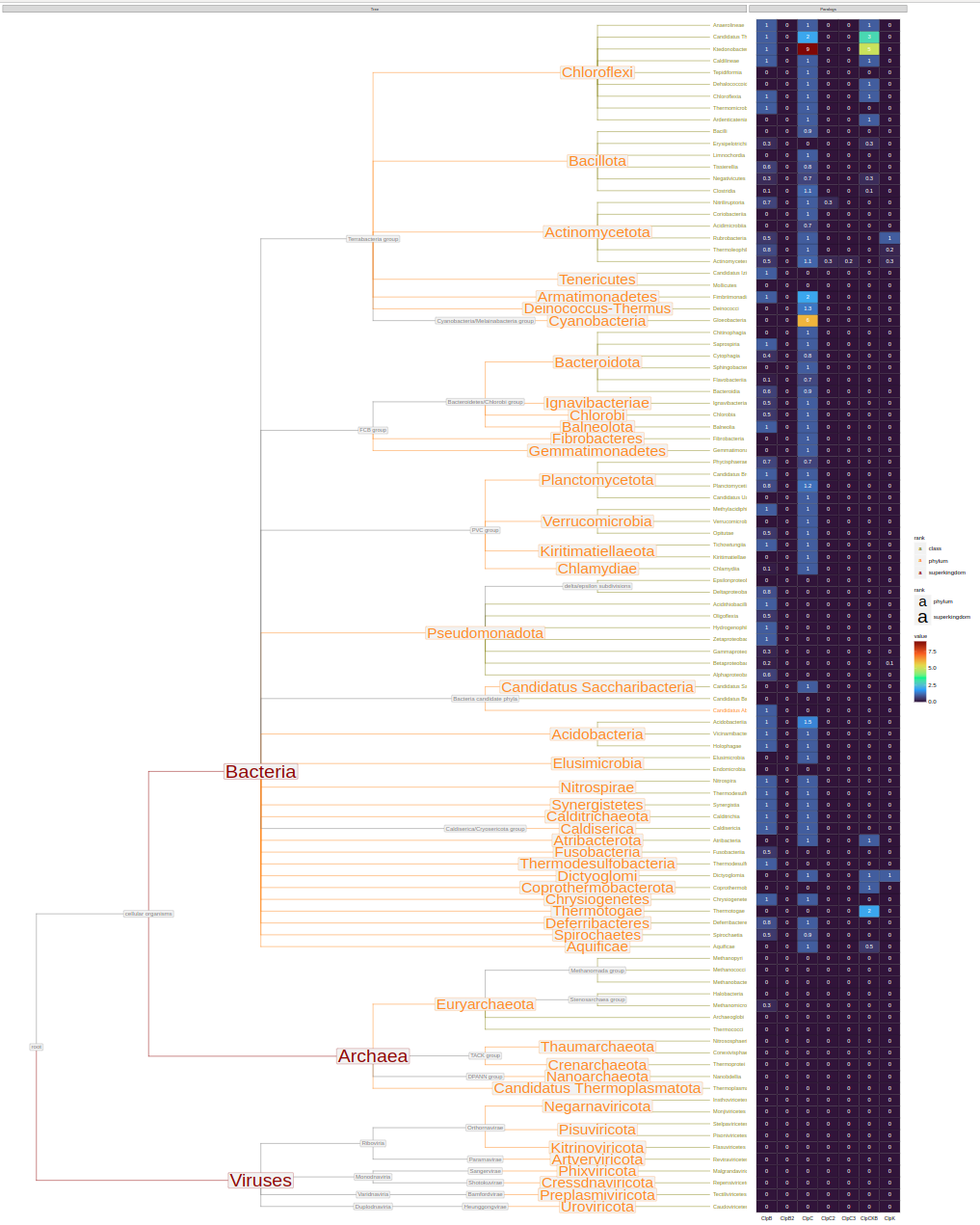
Once paralogs are assigned, you can annotate organism trees
species = annotate_org_tree(org_tree_full, org_data_full, tree)
phylum = copy_annotation(org_tree_family, org_tree_full_a)
class = copy_annotation(org_tree_class, org_tree_full_a)
order = copy_annotation(org_tree_class, org_tree_full_a)
family = copy_annotation(org_tree_class, org_tree_full_a)
genus = copy_annotation(org_tree_class, org_tree_full_a)And plot them at different taxonomic ranks
plot_org_tree(phylum, filename='org_tree_phylum.svg')plot_org_tree(class, filename='org_tree_class.svg')