AdaLAM: Revisiting Handcrafted Outlier Detection
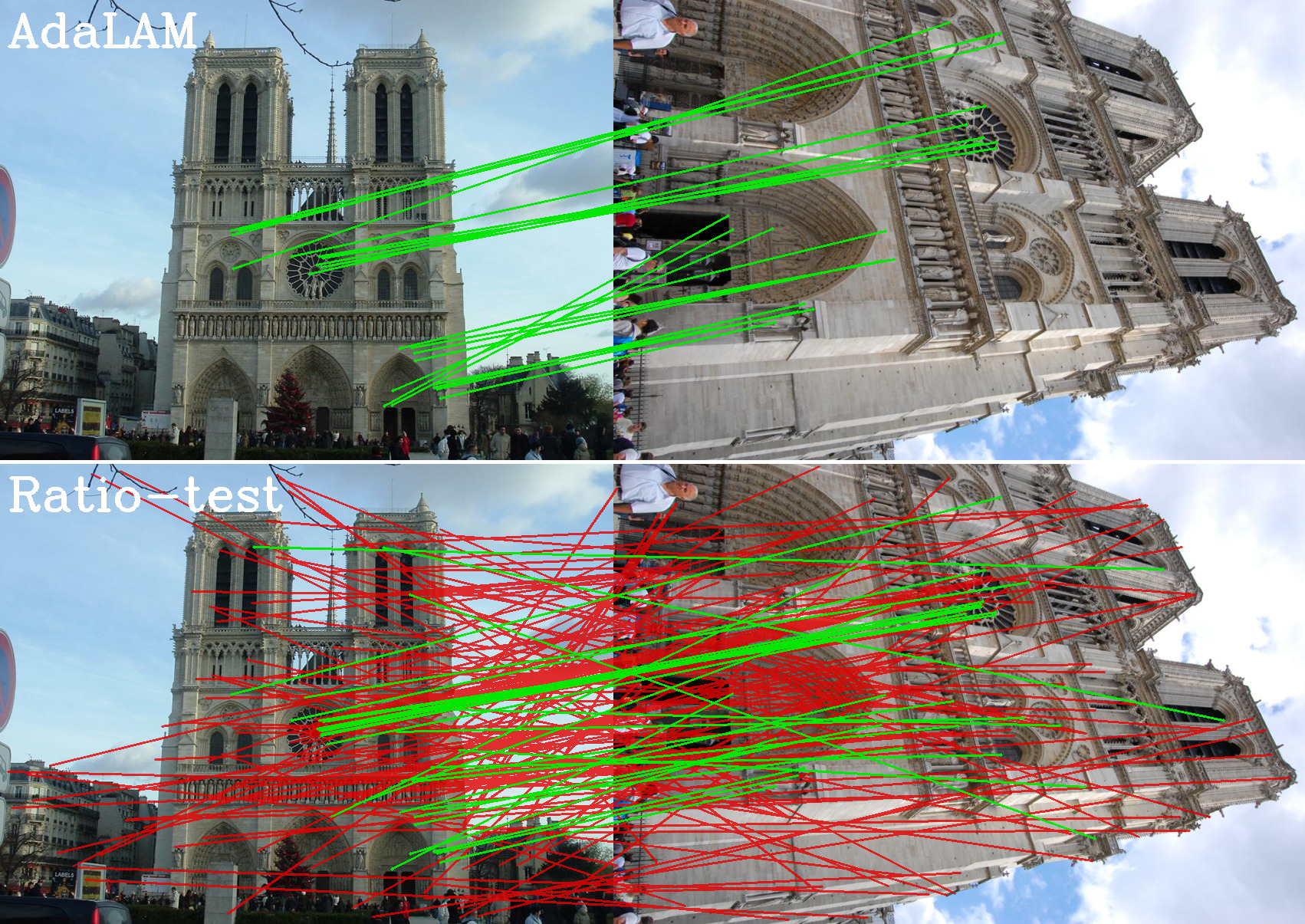
Local feature matching is a critical component of many computer vision pipelines, including among others Structure-from-Motion, SLAM, and Visual Localization. However, due to limitations in the descriptors, raw matches are often contaminated by a majority of outliers. Filtering outliers is a vital step in any sparse vision pipeline which is based on local feature matching.
AdaLAM is a fully handcrafted realtime outlier filter integrating several best practices into a single efficient and effective framework. It detects inliers by searching for significant local affine patterns in image correspondences.
AdaLAM proved to be very competitive with recent deep learning methods, taking the second place for the Image Matching Challenge at CVPR 2020 for the 8000 keypoints category. Here is our invited talk about AdaLAM and the challenge submission.
Check our paper for details about AdaLAM.
In this repository we provide a full pytorch implementation of AdaLAM. We suggest running AdaLAM on a CUDA device for best performance, but CPU execution is possible as well. We also provide an example script to run a COLMAP reconstruction using AdaLAM for matching.
The main aim of this repository is to provide a strong classical baseline that can be used easily for comparison purposes.
If you find our code or paper useful, please consider citing
@article{cavalli2020adalam,
title={AdaLAM: Revisiting Handcrafted Outlier Detection},
author={Cavalli, Luca and Larsson, Viktor and Oswald, Martin Ralf and Sattler, Torsten and Pollefeys, Marc},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.04250},
year={2020}}
For running AdaLAM you need a Python3.7 environment with pytorch and tqdm available.
If you already have one, let's call it yourenv, then installing AdaLAM is as simple as:
conda activate yourenv
pip install git+https://github.com/cavalli1234/AdaLAM
Here are detailed steps for setting up a sample environment:
Download and install anaconda3.
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2019.07-Linux-x86_64.sh
sh Anaconda3-2019.07-Linux-x86_64.sh
Clone this repository and move inside:
git clone 'https://github.com/cavalli1234/AdaLAM'
cd AdaLAM
Create and setup the virtual environment. We provide a yml file with the minimal environment configuration for running AdaLAM on GPU:
conda env create -f adalam.yml
This will create a conda environment named adalam with pytorch-gpu and tqdm.
Activate the environment and install AdaLAM:
conda activate adalam
pip install ./
Now you can freely use this AdaLAM implementation within the adalam environment.
If you want to run examples, you will need to setup a few extra dependencies. We assume you are in the examples folder and within a suitable conda environment, otherwise run:
cd examples
conda activate adalam
To run the demo on image couples we need to install opencv for extracting SIFT keypoints.
pip install opencv-python-nonfree
Now you can use our demo:
python example.py --im1 im1.jpg --im2 im2.jpg
To run the colmap reconstruction demo you will need to have colmap installed.
sudo apt install colmap
We now assume that you already have a folder /path/to/colmap/project where you want to make the reconstruction. /path/to/colmap/project only needs to have a subfolder images/ containing all the source images. Optionally you can include a text file named image_pairs.txt to specify a subset of image couples to match, exhaustive matching between all image couples is perfomed otherwise. You can perform the reconstruction with AdaLAM matching by running:
./colmap_reconstruction.sh /path/to/colmap/project
We suggest tuning the script the for best reconstruction results. For example, if you know that all your images were taken from the same camera, you may uncomment the option --ImageReader.single_camera 1 in the feature extraction stage.
Once adalam is installed in your environment, usage is very simple. Here is a minimal example for performing filtered matching:
from adalam import AdalamFilter
matcher = AdalamFilter()
matches = matcher.match_and_filter(k1=keypoints_of_source_image, k2=keypoints_of_destination_image,
o1=orientations_of_source_image, o2=orientations_of_destination_image,
d1=descriptors_of_source_image, d2=descriptors_of_destination_image,
s1=scales_of_source_image, s2=scales_of_destination_image,
im1shape=shape_of_source_image, im2shape=shape_of_destination_image).cpu().numpy()The AdalamFilter class provides wrapping functions around the core functionality of AdaLAM, which is essentially outlier filtering. You can find detailed documentation of the available methods within adalam.py.
Complete usage examples can be found in the examples folder.