We also thank the DFINITY Foundation for their support and guidance throughout the project. We extend our heartfelt gratitude to Zesen Zhuang, whose invaluable contributions during the exploratory phases of this project, particularly in data querying and visualizations.
-
- SQLite
- Description
- Use Cases
- Local Management Tools
- Cloud Hosting Options
- MySQL
- Description
- Use Cases
- Local Management Tools
- Cloud Hosting Options
- PostgreSQL
- Description
- Use Cases
- Local Management Tools
- Cloud Hosting Options
- Advanced Options
- SQLite
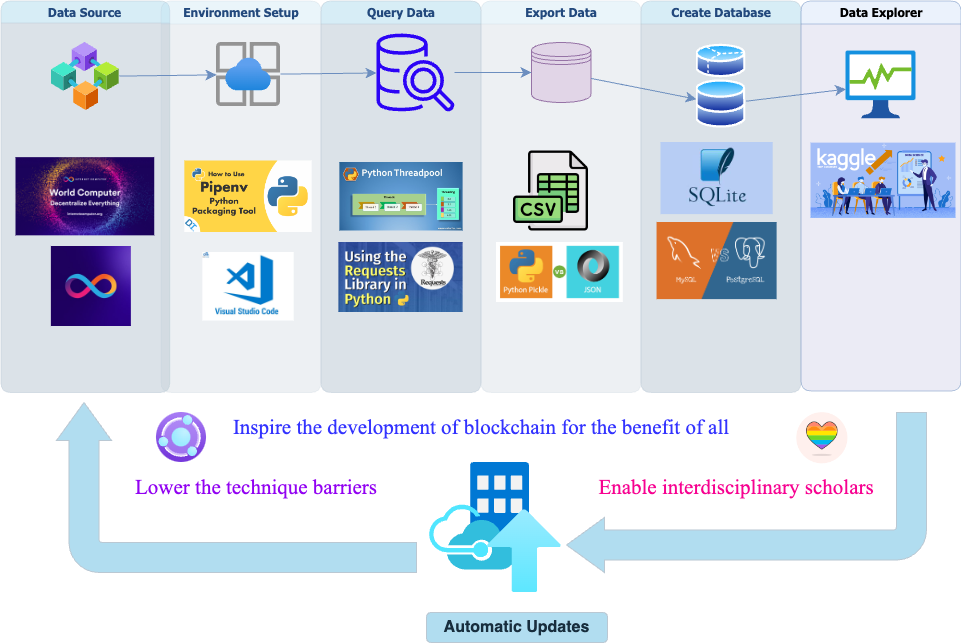
This project utilizes pipenv for package management. Ensure you have it installed and set up correctly by following the steps below.
Tip: We recommend using the ChatGPT code interpreter for debugging purposes.
-
Install Pipenv:
Install the package and confirm its version with:
pip install pipenv pipenv --version
-
Add Pipenv to the System Path:
To make
pipenvaccessible from any terminal window, you might need to add it to your system's PATH. First, find the installation location:pip show pipenv | grep LocationThen, add it to the PATH. Replace
path_to_site-packageswith the actual path you got from the above command:export PATH="$PATH:/path_to_site-packages/pipenv"
-
Create the Virtual Environment:
Activate the virtual environment using:
pipenv shell
The project can be configured to use various database management systems. For each option, we've detailed the primary local management tools and notable cloud hosting services available:
-
SQLite:
- Description: SQLite is a C-language library that provides a lightweight, serverless, self-contained SQL database engine.
- Use Cases: Ideal for small to medium-sized applications, prototypes, or when a minimal setup with no configuration is preferred.
- Local Management Tools:
- Cloud Hosting Options: Given SQLite's serverless and embedded nature, it is less common to see dedicated cloud-hosting solutions. Instead, SQLite databases are typically embedded within applications hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
-
MySQL:
- Description: MySQL is an open-source relational database system known for its speed and reliability.
- Use Cases: Suitable for a wide range of applications, especially web applications.
- Local Management Tools:
- Cloud Hosting Options:
-
PostgreSQL:
- Description: PostgreSQL is an open-source relational database that focuses on extensibility and compliance with SQL standards.
- Use Cases: Ideal for complex applications requiring advanced data types or geospatial support.
- Local Management Tools:
- Cloud Hosting Options:
- Amazon RDS (PostgreSQL): AWS's managed service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale PostgreSQL deployments. Website
- Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL: Managed PostgreSQL service offered by Google Cloud. Website
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL: Fully managed, enterprise-ready PostgreSQL database service provided by Azure. Website
- Advanced Options:
- GraphQL Integration:
- Description: Transform your PostgreSQL database into a GraphQL API without manually defining all resolvers.
- Tools:
- GraphQL Integration:
-
Initialize Git LFS:
Before you can use Git LFS, you must initialize it for your repository. This only needs to be done once per repository.
git lfs install
-
Track Files:
You need to tell Git LFS which files to track. This is done using the
git lfs trackcommand. For example, to track all.pklfiles, you'd do:git lfs track "*.pkl"This command updates the
.gitattributesfile, indicating which file patterns should be managed by LFS. -
Add the Files:
Now, add the files to your repository like you would with standard Git.
git add .Note: This will add all changes. If you want to add specific files, replace the
.with the specific file paths. -
Commit and Push:
Commit your changes:
git commit -m "Add large files with Git LFS"Then push to your remote repository:
git push origin main
Remember, each time you add a new type of file that you want to be managed by Git LFS, you need to use the git lfs track command with the appropriate file pattern. The git lfs install command, however, only needs to be run once per repository.
Kaggle is a renowned platform for data science competitions, public datasets, and knowledge sharing. One such invaluable dataset hosted on Kaggle is related to the Internet Computer Protocol NNS Proposals. The dataset can be accessed via the following link: ICP NNS Proposals Dataset.
The ICP NNS Proposals data is available in three primary file formats, catering to various analysis and computational needs:
-
Pickle:
- Description: Pickle is a Python-specific binary serialization format. It's efficient for storing Python objects, especially data frames in pandas, but can't be easily read with other programming languages.
- How to Use: In Python, you can load a pickle file using the pandas library.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_pickle("path_to_file.pkl")
-
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation):
- Description: JSON is a lightweight data-interchange format that is easy for humans to read and write. It's commonly used for configuration files and data exchange between languages with different data structures.
- How to Use: In Python, the
jsonmodule can be used to load JSON files.import json with open('path_to_file.json', 'r') as file: data = json.load(file)
-
CSV (Comma Separated Values):
- Description: CSV is a plain-text format used for structured data. It's straightforward and supported by many data processing tools, databases, and spreadsheet applications.
- How to Use: In Python, the CSV can be loaded using the pandas library.
import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("path_to_file.csv")
To dive deep into the dataset and explore its potential, visit the provided Kaggle link. Kaggle offers an interactive environment, called Kaggle Kernels, which allows for in-browser data analysis. This feature is especially handy for those who want to explore the data without downloading it or setting up a local environment. We also provide a demo notebook that can be used as a starting point for your analysis using kaggle kernels Notebook URL.
The Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) operates under a decentralized governance system known as the Network Nervous System (NNS). This dataset provides a comprehensive account of proposals within the NNS, capturing the democratic governance process of the Internet Computer.
| Variable | Definition | Description | Frequency | Range | Unit | Type | Sample Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
action |
Type of action | Indicates the intent of the proposal (propose, reject, execute) | Per proposal | - | - | String | "ExecuteNnsFunction" |
action_nns_function |
Specific NNS function | Identifies the exact NNS function addressed by the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "NnsCanisterUpgrade" |
deadline_timestamp_seconds |
Voting deadline | Timestamp for the end of the voting period | Per proposal | - | Seconds | Integer | 1620340878 |
decided_timestamp_seconds |
Decision time | Timestamp when the decision on the proposal was made | Per proposal | - | Seconds | Float | 1620340878.0 |
executed_timestamp_seconds |
Execution time | Timestamp when the proposal was executed | Per proposal | - | Seconds | Integer | 0 |
failed_timestamp_seconds |
Failure time | Timestamp when the proposal was deemed unsuccessful | Per proposal | - | Seconds | Integer | 1 |
id |
Proposal identifier | Unique ID for each proposal | Per proposal | 0-104331 | - | Integer | 3 |
known_neurons_ballots |
Voting neurons | Record of neurons that voted | Per proposal | - | - | JSON | [] |
latest_tally |
Vote tally | Most recent vote count | Per proposal | - | - | JSON | {'no': 0, 'yes': 31539577669890139} |
payload |
Proposal details | Detailed JSON object of the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | JSON | {...} |
proposal_id |
Designated proposal ID | ID for the proposal | Per proposal | 0-104331 | - | Integer | 3 |
proposal_timestamp_seconds |
Proposal creation time | Timestamp for the inception of the proposal | Per proposal | - | Seconds | Integer | 1620339017 |
proposer |
Proposer address | Canister address that presented the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "35.0" |
reject_cost_e8s |
Rejection cost | Expense linked to a proposal's rejection | Per proposal | - | e8 ICP units | Integer | 100000000 |
reward_status |
Reward status | Current state of the proposal's reward | Per proposal | - | - | String | "SETTLED" |
settled_at |
Conclusion time | Timestamp marking the proposal's conclusion | Per proposal | - | Date & Time | String | "2021-05-06 16:00:00" |
status |
Proposal status | Current standing of the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "EXECUTED" |
summary |
Proposal overview | Concise overview of the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "Upgrade ledger canister..." |
title |
Proposal title | Headline of the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "Upgrade ledger canister to git commit 8a560f9..." |
topic |
Proposal topic | Primary theme or subject | Per proposal | - | - | String | "TOPIC_NETWORK_CANISTER_MANAGEMENT" |
updated_at |
Last update time | Last moment the proposal received modifications | Per proposal | - | Date & Time | String | "2021-08-05 15:50:43.155180" |
url |
Proposal link | Direct web link to the proposal | Per proposal | - | - | String | "GitHub Link" |
For detailed information on data generation and updates, visit our GitHub repository which also includes auto-update scheduling provisions for this dataset.