Refer to the gbtools manual for detailed instructions.
Read the paper published in Frontiers in Microbiology
- Validate input files within R environment with
gbt_checkinput()(v2.6.0), validator no longer depends on non-core Perl module - You can now specify custom colors for taxonomic markers in plots with the
markCustomPalette=parameter in theplotfunction (v2.5.8) - Bug in Fastg-fishing script caused by inconsistent SPAdes header names has been fixed (v2.5.7)
Here are the bare basics that you can do in gbtools, using the Olavius example data (look in the example_data/Olavius_metagenome folder in this package).
The following commands are all in the R environment.
The tar.gz archives can be found in the R_source_package folder.
install.packages("sp") # Dependency
install.packages("plyr") # Dependency
install.packages("gbtools_2.6.0.tar.gz",repos=NULL,type="source")The devtools package allows you to install R packages directly from GitHub, similar to installing packages from the CRAN repository.
library(devtools)
install_github("kbseah/genome-bin-tools/gbtools") # Install latest version of the R packageFirst check that the input data are correctly formatted
gbt_checkinput (covstats=c("SampleG1.covstats","SampleA2.covstats"), # Coverage data
ssu="olavius_metagenome.ssu.tab", # SSU gene annotations
mark=c("amphora2_results.tab","blobology_results.tab")) # Marker genes
# Should give a message that no errors are foundNow import the data into the R environment
d <- gbt (covstats=c("SampleG1.covstats","SampleA2.covstats"), # Coverage data
ssu="olavius_metagenome.ssu.tab", # SSU gene annotations
mark=c("amphora2_results.tab","blobology_results.tab"), # Marker genes
marksource=c("amphora2","blob")) # Names for the marker gene setsSee summary stats by typing name of the gbt object
d
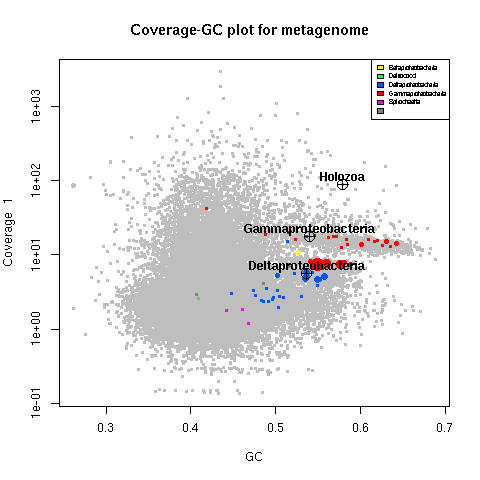
summary (d) # same thingplot (d, # Plots the first set of coverage data by default
ssu=TRUE, # Annotate SSU genes with crosshairs
textlabels=TRUE, # Add labels for SSU genes
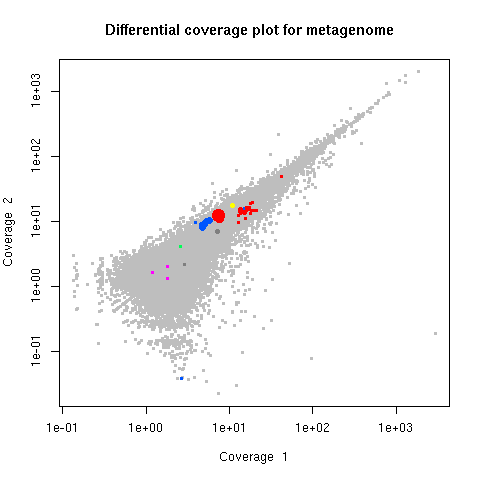
legend=TRUE) # Add legend for marker genesplot (d, slice=c(1,2)) # Plot one set of coverage data vs. anotherplot (d,slice=1,marker=FALSE) # Turn off color overlays
d.bin1 <- choosebin (d, slice=1) # Click on the plot to define the region you want
summary(d.bin1) # Summarize the newly-created bin
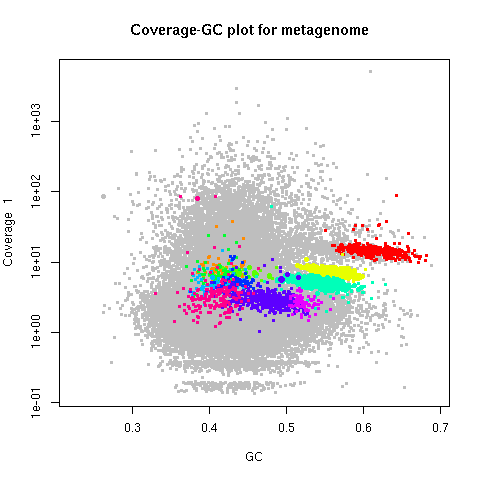
points(d.bin1, slice=1) # Overlay the new bin on your plotd.metabat_bins <- importBins (d, file="metabat_bins")
multiBinPlot (d, bins=d.metabat_bins)Each bin gets plotted in a different color
Documentation for each function can be accessed in R by typing ? followed by function name at the command line (the gbtools plot function is filed under plot.gbt to distinguish it from the generic plot function).
Problems with using gbtools? Create a new issue using the GitHub issue-tracker on the right. Or send me an email, with "gbtools help" in the subject line.
Problems with input file formats? Read the wiki and use the input_validator.pl script to check your input files.
Petersen et al. 2016. Nature Microbiology 2: 16195.
Rubin-Blum et al. 2017. Nature Microbiology 2: 17093.
Drop me a message if I've overlooked your publication(s)!
Citation: Seah BK and Gruber-Vodicka HR (2015). gbtools: Interactive visualization of metagenome bins in R. Front. Microbiol. 6:1451. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01451
Cite dependencies if you use them:
- R - R Core Team. 2014. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. (http://www.R-project.org/)
- BBMap - Bushnell B. 2015. BBMap (http://sourceforge.net/projects/bbmap/)
- AMPHORA2 - Wu M, Scott AJ. 2012. Bioinformatics 28 (7) : 1033-1034.
- barrnap - Seemann T. 2014. barrnap (http://www.vicbioinformatics.com/software.barrnap.shtml)
- Usearch - Edgar RC 2010. Bioinformatics 26 (19) : 2460-2461.
- Vsearch - https://github.com/torognes/vsearch
- ARB-SILVA - Quast C et al. 2013. Nucleic Acids Research 41 (D1) : D590-D596.
- tRNAscan-SE - Lowe T, Eddy S. 1997. Nucleic Acids Research 25 : 955-964.
- Blobology - Kumar S et al. 2013. Frontiers in Genetics 4 : 237
Contact: Brandon Seah (kbseah@mpi-bremen.de)
Department of Symbiosis, Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology