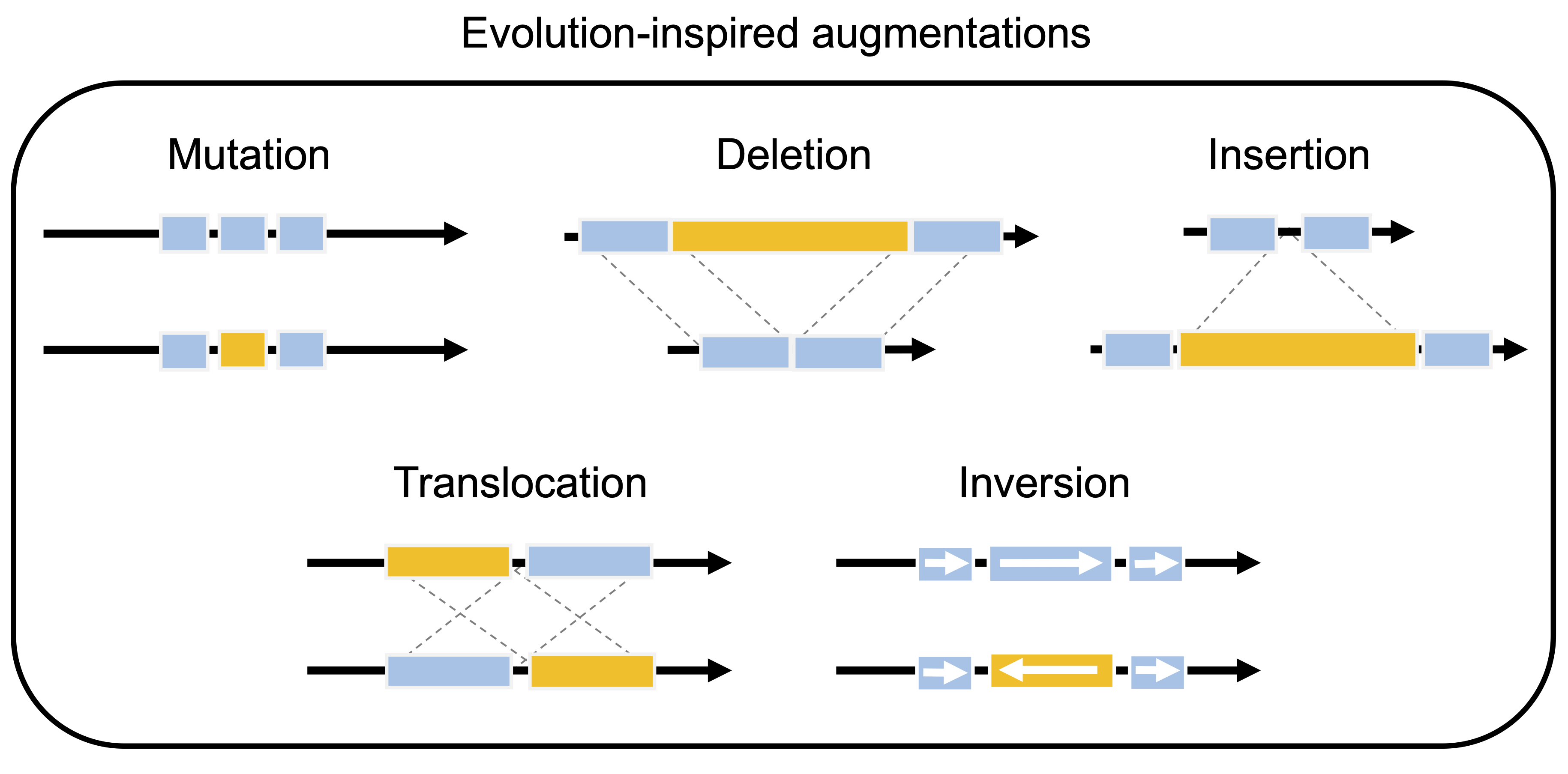
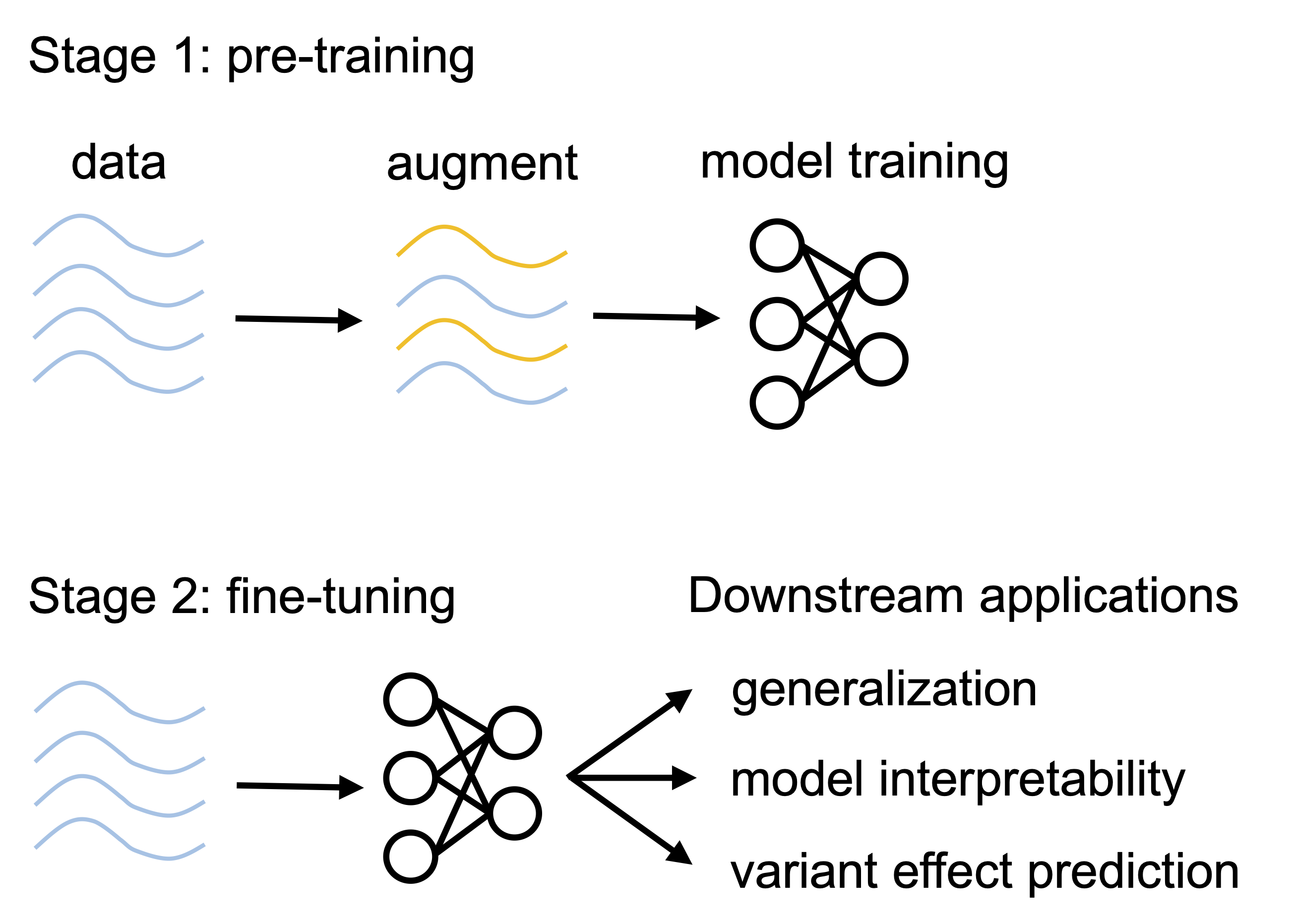
EvoAug is a PyTorch package to pretrain sequence-based deep learning models for regulatory genomics data with evolution-inspired data augmentations followed by a finetuning on the original, unperturbed sequence data. This work uses PyTorch Lightning -- LightningModule -- to define a model wrapper that is used for training. This is work that directly follows from "EvoAug: improving generalization and interpretability of genomic deep neural networks with evolution-inspired data augmentations" by Nicholas Keone Lee, Ziqi (Amber) Tang, Shushan Toneyan, and Peter K Koo. Code in this repository is shared under the MIT License. For additional information, see documentation on EvoAug.ReadTheDocs.io.
For questions, email: koo@cshl.edu
pip install evoaug
torch 1.12.1+cu113
pytorch_lightning 1.7.7
numpy 1.21.6
Note: For newer versions of pytorch_lightning, the pl.Trainer call will need to be modified accordingly as the arguments for gpus has changed from version 1.7.
from evoaug import evoaug, augment
import pytorch_lightning as pl
model = "DEFINE PYTORCH MODEL"
loss = "DEFINE PYTORCH LOSS"
optimizer_dict = "DEFINE OPTIMIZER OR OPTIMIZER DICT"
augment_list = [
augment.RandomDeletion(delete_min=0, delete_max=20),
augment.RandomRC(rc_prob=0.5),
augment.RandomInsertion(insert_min=0, insert_max=20),
augment.RandomTranslocation(shift_min=0, shift_max=20),
augment.RandomMutation(mut_frac=0.05),
augment.RandomNoise(noise_mean=0, noise_std=0.2),
]
robust_model = evoaug.RobustModel(
model,
criterion=loss,
optimizer=optimizer_dict,
augment_list=augment_list,
max_augs_per_seq=2, # maximum number of augmentations per sequence
hard_aug=True, # use max_augs_per_seq, otherwise sample randomly up to max
inference_aug=False # if true, keep augmentations on during inference time
)
# set up callback
callback_topmodel = pl.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
monitor='val_loss',
save_top_k=1,
dirpath=output_dir,
filename=ckpt_aug_path
)
# train model
trainer = pl.Trainer(
gpus=1,
max_epochs=100,
auto_select_gpus=True,
logger=None,
callbacks=["ADD CALLBACKS", callback_topmodel]
)
# pre-train model with augmentations
trainer.fit(robust_model, datamodule=data_module)
# load best model
robust_model = evoaug.load_model_from_checkpoint(robust_model, ckpt_aug_path)
# set up fine-tuning
robust_model.finetune = True
robust_model.optimizer = # set up optimizer for fine-tuning
# set up callback
callback_topmodel = pl.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
monitor='val_loss',
save_top_k=1,
dirpath=output_dir,
filename=ckpt_finetune_path
)
# set up pytorch lightning trainer
trainer = pl.Trainer(
accelerator="gpu",
device=1,
max_epochs=100,
auto_select_gpus=True,
logger=None,
callbacks=["ADD CALLBACKS", callback_topmodel]
)
# fine-tune model
trainer.fit(robust_model, datamodule=data_module)
# load best fine-tuned model
robust_model = evoaug.load_model_from_checkpoint(robust_model, ckpt_finetune_path)DeepSTARR analysis:
- Example analysis: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1a2fiRPBd1xvoJf0WNiMUgTYiLTs1XETf?usp=sharing
- Example load model and perform attribution analysis: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/11DVkhyX2VhhCSbCGkW3XjviMxTufBvZh?usp=sharing
ChIP-seq analysis:
- Example analysis: https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1GZ8v4Tq3LQMZI30qvdhF7ZW6Kf5GDyKX?usp=sharing
If you find out work useful, please cite our paper.
@article{lee2023evoaug,
title={EvoAug: improving generalization and interpretability of genomic deep neural networks with evolution-inspired data augmentations},
author={Lee, Nicholas Keone and Tang, Ziqi and Toneyan, Shushan and Koo, Peter K},
journal={Genome Biology},
volume={24},
number={1},
pages={105},
year={2023},
publisher={Springer}
}